Abstract
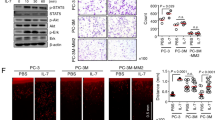
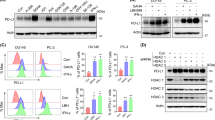
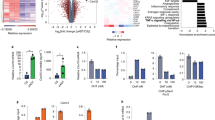
Levels of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) are increased in therapy-resistant prostate cancer. IL-6 has been considered a positive growth factor in late-stage prostate cancer cells and a potential target for therapeutic interference. Effects of inhibition of IL-6 on cell survival were studied in LNCaP-IL6+ cells, a model system for advanced prostate cancer, which produce IL-6. We show that the autocrine IL-6 loop is responsible for resistance to apoptosis and increased cellular levels of myeloid cell leukemia-1 (Mcl-1) protein, an antiapoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. Treatment of cells with a chimeric anti-IL-6 antibody (CNTO 328) led to the induction of apoptosis and downregulation of Mcl-1 protein levels. Specific knockdown of Mcl-1 gene expression by small interfering RNA also yielded an increase in apoptosis of LNCaP-IL-6+ cells. Vice versa, inactivation of IL-6 autocrine loop had no influence on apoptosis levels in the absence of Mcl-1, thus suggesting this molecule as a mediator of the survival action of IL-6. Mcl-1 protein regulation by the endogenous cytokine directly involved the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Our data support the concept of anti-IL-6 targeted therapy in therapy-resistant prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler HL, McCurdy MA, Kattan MW, Timme TL, Scardino PT, Thompson TC . (1999). Elevated levels of circulating interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor-beta1 in patients with metastatic prostatic carcinoma. J Urol 161: 182–187.
Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T . (1993). Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol 54: 1–78.
Borsellino N, Belldegrun A, Bonavida B . (1995). Endogenous interleukin 6 is a resistance factor for cis-diamminedichloroplatinum and etoposide-mediated cytotoxicity of human prostate carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 55: 4633–4639.
Borsellino N, Bonavida B, Ciliberto G, Toniatti C, Travali S, D'Alessandro N . (1999). Blocking signaling through the Gp130 receptor chain by interleukin-6 and oncostatin M inhibits PC-3 cell growth and sensitizes the tumor cells to etoposide and cisplatin-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer 85: 134–144.
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed JC, Laine J, Rivard N . (2000). MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 79: 355–369.
Bradford M . (1978). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Ann Biochem 72: 248–254.
Chung TD, Yu JJ, Kong TA, Spiotto MT, Lin JM . (2000). Interleukin-6 activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, which inhibits apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 42: 1–7.
Chung TD, Yu JJ, Spiotto MT, Bartkowski M, Simons JW . (1999). Characterization of the role of IL-6 in the progression of prostate cancer. Prostate 38: 199–207.
Craig RW . (2002). MCL1 provides a window on the role of the BCL2 family in cell proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 16: 444–454.
Debes JD, Comuzzi B, Schmidt LJ, Dehm SM, Culig Z, Tindall DJ . (2005). p300 regulates androgen receptor-independent expression of prostate-specific antigen in prostate cancer cells treated chronically with interleukin-6. Cancer Res 65: 5965–5973.
Derenne S, Monia B, Dean NM, Taylor JK, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL et al. (2002). Antisense strategy shows that Mcl-1 rather than Bcl-2 or Bcl-x(L) is an essential survival protein of human myeloma cells. Blood 100: 194–199.
Derouet M, Thomas L, Cross A, Moots RJ, Edwards SW . (2004). Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling and proteasome inhibition delay neutrophil apoptosis by increasing the stability of Mcl-1. J Biol Chem 279: 26915–26921.
Domina AM, Smith JH, Craig RW . (2000). Myeloid cell leukemia 1 is phosphorylated through two distinct pathways, one associated with extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and the other with G2/M accumulation or protein phosphatase 1/2A inhibition. J Biol Chem 275: 21688–21694.
Drachenberg DE, Elgamal AA, Rowbotham R, Peterson M, Murphy GP . (1999). Circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate 41: 127–133.
Fadeel B, Orrenius S . (2005). Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human disease. J Intern Med 258: 479–517.
Gioeli D, Mandell JW, Petroni GR, Frierson Jr HF, Weber MJ . (1999). Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase associated with prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res 59: 279–284.
Giri D, Ozen M, Ittmann M . (2001). Interleukin-6 is an autocrine growth factor in human prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 159: 2159–2165.
Gong Y, Blok LJ, Perry JE, Lindzey JK, Tindall DJ . (1995). Calcium regulation of androgen receptor expression in the human prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Endocrinology 136: 2172–2178.
Hajnoczky G, Davies E, Madesh M . (2003). Calcium signaling and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304: 445–454.
Hideshima T, Podar K, Chauhan D, Anderson KC . (2005). Cytokines and signal transduction. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 18: 509–524.
Hobisch A, Ramoner R, Fuchs D, Godoy-Tundidor S, Bartsch G, Klocker H et al. (2001). Prostate cancer cells (LNCaP) generated after long-term interleukin 6 (IL-6) treatment express IL-6 and acquire an IL-6 partially resistant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 7: 2941–2948.
Hobisch A, Rogatsch H, Hittmair A, Fuchs D, Bartsch Jr G, Klocker H et al. (2000). Immunohistochemical localization of interleukin-6 and its receptor in benign, premalignant and malignant prostate tissue. J Pathol 191: 239–244.
Hodge DR, Hurt EM, Farrar WL . (2005). The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer 41: 2502–2512.
Jourdan M, Veyrune JL, Vos JD, Redal N, Couderc G, Klein B . (2003). A major role for Mcl-1 antiapoptotic protein in the IL-6-induced survival of human myeloma cells. Oncogene 22: 2950–2959.
Kaufmann SH, Karp JE, Svingen PA, Krajewski S, Burke PJ, Gore SD et al. (1998). Elevated expression of the apoptotic regulator Mcl-1 at the time of leukemic relapse. Blood 91: 991–1000.
Kawada M, Inoue H, Usami I, Takamoto K, Masuda T, Yamazaki Y et al. (2006). Establishment of a highly tumorigenic LNCaP cell line having inflammatory cytokine resistance. Cancer Lett 242: 46–52.
Keller ET, Wanagat J, Ershler WB . (1996). Molecular and cellular biology of interleukin-6 and its receptor. Front Biosci 1: 340–357.
Kitada S, Andersen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S et al. (1998). Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses. Blood 91: 3379–3389.
Kozopas KM, Yang T, Buchan HL, Zhou P, Craig RW . (1993). MCL1, a gene expressed in programmed myeloid cell differentiation, has sequence similarity to BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 3516–3520.
Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Epstein JI, Shabaik A, Sauvageot J, Song K et al. (1996). Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2, bax, bcl-X, and Mcl-1 expression in prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 148: 1567–1576.
Krajewski S, Bodrug S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Gascoyne R, Berean K et al. (1995). Immunohistochemical analysis of Mcl-1 protein in human tissues. Differential regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 protein production suggests a unique role for Mcl-1 in control of programmed cell death in vivo. Am J Pathol 146: 1309–1319.
Kramer G, Erdal H, Mertens HJ, Nap M, Mauermann J, Steiner G et al. (2004). Differentiation between cell death modes using measurements of different soluble forms of extracellular cytokeratin 18. Cancer Res 64: 1751–1756.
Kyprianou N, English HF, Isaacs JT . (1988). Activation of a Ca2+–Mg2+-dependent endonuclease as an early event in castration-induced prostatic cell death. Prostate 13: 103–117.
Le Gouill S, Podar K, Amiot M, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Ishitsuka K et al. (2004). VEGF induces Mcl-1 up-regulation and protects multiple myeloma cells against apoptosis. Blood 104: 2886–2892.
Lee SO, Lou W, Johnson CS, Trump DL, Gao AC . (2004). Interleukin-6 protects LNCaP cells from apoptosis induced by androgen deprivation through the Stat3 pathway. Prostate 60: 178–186.
Li J, Hu XF, Xing PX . (2005). CNTO-328 (Centocor). Curr Opin Invest Drugs 6: 639–645.
Lin DL, Whitney MC, Yao Z, Keller ET . (2001). Interleukin-6 induces androgen responsiveness in prostate cancer cells through up-regulation of androgen receptor expression. Clin Cancer Res 7: 1773–1781.
Lotem J, Sachs L . (1992). Hematopoietic cytokines inhibit apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor beta 1 and cancer chemotherapy compounds in myeloid leukemic cells. Blood 80: 1750–1757.
Lou W, Ni Z, Dyer K, Tweardy DJ, Gao AC . (2000). Interleukin-6 induces prostate cancer cell growth accompanied by activation of stat3 signaling pathway. Prostate 42: 239–242.
Martikainen P, Isaacs J . (1990). Role of calcium in the programmed death of rat prostatic glandular cells. Prostate 17: 175–187.
Nakashima J, Tachibana M, Horiguchi Y, Oya M, Ohigashi T, Asakura H et al. (2000). Serum interleukin 6 as a prognostic factor in patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6: 2702–2706.
Nam S, Buettner R, Turkson J, Kim D, Cheng JQ, Muehlbeyer S et al. (2005). Indirubin derivatives inhibit Stat3 signaling and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 5998–6003.
Niu G, Bowman T, Huang M, Shivers S, Reintgen D, Daud A et al. (2002). Roles of activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth. Oncogene 21: 7001–7010.
Okamoto M, Lee C, Oyasu R . (1997). Interleukin-6 as a paracrine and autocrine growth factor in human prostatic carcinoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res 57: 141–146.
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P . (2003). Regulation of cell death: the calcium–apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 552–565.
Pu YS, Hour TC, Chuang SE, Cheng AL, Lai MK, Kuo ML . (2004). Interleukin-6 is responsible for drug resistance and anti-apoptotic effects in prostatic cancer cells. Prostate 60: 120–129.
Puthier D, Derenne S, Barille S, Moreau P, Harousseau JL, Bataille R et al. (1999). Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL are co-regulated by IL-6 in human myeloma cells. Br J Haematol 107: 392–395.
Raje N, Kumar S, Hideshima T, Roccaro A, Ishitsuka K, Yasui H et al. (2005). Seliciclib (CYC202 or R-roscovitine), a small-molecule cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, mediates activity via down-regulation of Mcl-1 in multiple myeloma. Blood 106: 1042–1047.
Royuela M, Arenas MI, Bethencourt FR, Sanchez-Chapado M, Fraile B, Paniagua R . (2001). Immunoexpressions of p21, Rb, mcl-1 and bad gene products in normal, hyperplastic and carcinomatous human prostates. Eur Cytokine Netw 12: 654–663.
Royuela M, Arenas MI, Bethencourt FR, Sanchez-Chapado M, Fraile B, Paniagua R . (2002). Regulation of proliferation/apoptosis equilibrium by mitogen-activated protein kinases in normal, hyperplastic, and carcinomatous human prostate. Hum Pathol 33: 299–306.
Rubinfeld H, Seger R . (2005). The ERK cascade: a prototype of MAPK signaling. Mol Biotechnol 31: 151–174.
Selzer E, Thallinger C, Hoeller C, Oberkleiner P, Wacheck V, Pehamberger H et al. (2002). Betulinic acid-induced Mcl-1 expression in human melanoma – mode of action and functional significance. Mol Med 8: 877–884.
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Kishi M, Yonehara S, Konishi N . (2002). Contributions of mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa B to N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Mol Carcinogen 35: 127–137.
Siegall CB, Schwab G, Nordan RP, FitzGerald DJ, Pastan I . (1990). Expression of the interleukin 6 receptor and interleukin 6 in prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 50: 7786–7788.
Siegsmund MJ, Yamazaki H, Pastan I . (1994). Interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in prostate carcinomas and benign prostate hyperplasia. J Urol 151: 1396–1399.
Smith PC, Hobisch A, Lin DL, Culig Z, Keller ET . (2001). Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12: 33–40.
Smith PC, Keller ET . (2001). Anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody induces regression of human prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice. Prostate 48: 47–53.
Sridhar SS, Hedley D, Siu LL . (2005). Raf kinase as a target for anticancer therapeutics. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 677–685.
Steiner H, Berger AP, Godoy-Tundidor S, Bjartell A, Lilja H, Bartsch G et al. (2004). An autocrine loop for vascular endothelial growth factor is established in prostate cancer cells generated after prolonged treatment with interleukin 6. Eur J Cancer 40: 1066–1072.
Steiner H, Caarretta IT, Moser PL, Berger AP, Bektic J, Dietrich H et al. (2006). Regulation of growth of prostate cancer cells selected in the presence of interleukin-6 by the anti-interleukin-6 antibody CNTO 328. (in press).
Steiner H, Godoy-Tundidor S, Rogatsch H, Berger AP, Fuchs D, Comuzzi B et al. (2003). Accelerated in vivo growth of prostate tumors that up-regulate interleukin-6 is associated with reduced retinoblastoma protein expression and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Am J Pathol 162: 655–663.
Trikha M, Corringham R, Klein B, Rossi JF . (2003). Targeted anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody therapy for cancer: a review of the rationale and clinical evidence. Clin Cancer Res 9: 4653–4665.
Twillie DA, Eisenberger MA, Carducci MA, Hseih WS, Kim WY, Simons JW . (1995). Interleukin-6: a candidate mediator of human prostate cancer morbidity. Urology 45: 542–549.
Wallner L, Dai J, Escara-Wilke J, Zhang J, Yao Z, Lu Y et al. (2006). Inhibition of interleukin-6 with CNTO 328, an anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal antibody, inhibits conversion of androgen-dependent prostate cancer to an androgen-independent phenotype in orchiectomized mice. Cancer Res 66: 3087–3095.
Yonish-Rouach E, Resnitzky D, Lotem J, Sachs L, Kimchi A, Oren M . (1991). Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature 352: 345–347.
Yoon S, Seger R . (2006). The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors 24: 21–44.
Zelivianski S, Spellman M, Kellerman M, Kakitelashvilli V, Zhou XW, Lugo E et al. (2003). ERK inhibitor PD98059 enhances docetaxel-induced apoptosis of androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 107: 478–485.
Zhang B, Gojo I, Fenton RG . (2002). Myeloid cell factor-1 is a critical survival factor for multiple myeloma. Blood 99: 1885–1893.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge G Sierek for expert technical assistance, M Puhr, K Malinowska and Drs G Bartsch and P Berger for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavarretta, I., Neuwirt, H., Untergasser, G. et al. The antiapoptotic effect of IL-6 autocrine loop in a cellular model of advanced prostate cancer is mediated by Mcl-1. Oncogene 26, 2822–2832 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210097
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210097
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Diacerein-mediated inhibition of IL-6/IL-6R signaling induces apoptotic effects on breast cancer
Oncogene (2016)
-
IL6 secreted by Ewing sarcoma tumor microenvironment confers anti-apoptotic and cell-disseminating paracrine responses in Ewing sarcoma cells
BMC Cancer (2015)
-
Bicarbonate transport inhibitor SITS modulates pH homeostasis triggering apoptosis of Dalton’s lymphoma: implication of novel molecular mechanisms
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2014)
-
Pseudolaric acid B inhibits inducible cyclooxygenase-2 expression via downregulation of the NF-κB pathway in HT-29 cells
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2012)
-
Mesothelin confers pancreatic cancer cell resistance to TNF-α-induced apoptosis through Akt/PI3K/NF-κB activation and IL-6/Mcl-1 overexpression
Molecular Cancer (2011)