Abstract
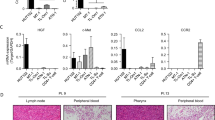
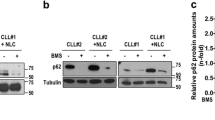
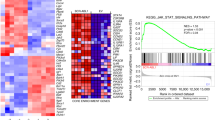
B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cell is characterized by the accumulation of long-lived CD5+ B lymphocytes, whose survival in vivo is in part dependent on exogenous factors such as cytokines and/or extracellular matrix proteins. Homeostatic chemokines are critical mediators of lymphoid cell trafficking. However, how they function in cell signaling and survival remains ill-defined. In this study, we have investigated the role of the homeostatic chemokines, CXCL12, CCL21, CCL19 and CXCL13, in B-CLL cell survival. Using primary leukemic cells isolated from 26 patients, we observed that each chemokine enhances cell survival. Chemokines induced the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p90RSK, and of Akt and its effectors GSK3 and FOXO3a. Consistently, inhibitors against mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibited chemokine-induced survival. Moreover, using a constitutively active mutated form of FOXO3a or siRNAs against FOXO3a in transfection experiments performed in primary B-CLL cells, we directly demonstrated the critical role of FOXO3a in both spontaneous and chemokine-induced B-CLL cell survival. Overall, our data support the notion that homeostatic chemokines contribute to B-CLL resistance to cell death through inactivation of the transcription factor FOXO3a, which may represent a novel therapeutic target in this hematopoietic malignancy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubin J, Davi F, Nguyen-Salomon F, Leboeuf D, Debert C, Taher M et al. (1995). Description of a novel FR1 IgH PCR strategy and its comparison with three other strategies for the detection of clonality in B cell malignancies. Leukemia 9: 471–479.
Baccarini M . (2002). An old kinase on a new path: Raf and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9: 783–785.
Birkenkamp KU, Coffer PJ . (2003). FOXO transcription factors as regulators of immune homeostasis: molecules to die for? J Immunol 171: 1623–1629.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. (1999). Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Burger JA, Tsukada N, Burger M, Zvaifler NJ, Dell'Aquila M, Kipps TJ . (2000). Blood-derived nurse-like cells protect chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from spontaneous apoptosis through stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 96: 2655–2663.
Burger M, Hartmann T, Krome M, Rawluk J, Tamamura H, Fujii N et al. (2005). Small peptide inhibitors of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor (CD184) antagonize the activation, migration, and antiapoptotic responses of CXCL12 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood 106: 1824–1830.
Burgering BM, Medema RH . (2003). Decisions on life and death: FOXO Forkhead transcription factors are in command when PKB/Akt is off duty. J Leukoc Biol 73: 689–701.
Caligaris-Cappio F, Hamblin TJ . (1999). B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a bird of a different feather. J Clin Oncol 17: 399–408.
Charvet C, Alberti I, Luciano F, Jacquel A, Bernard A, Auberger P et al. (2003). Proteolytic regulation of Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a by caspase-3-like proteases. Oncogene 22: 4557–4568.
Colamussi ML, Secchiero P, Gonelli A, Marchisio M, Zauli G, Capitani S . (2001). Stromal derived factor-1 alpha (SDF-1 alpha) induces CD4+ T cell apoptosis via the functional up-regulation of the Fas (CD95)/Fas ligand (CD95L) pathway. J Leukoc Biol 69: 263–270.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. (2003). ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 348: 1764–1775.
Durig J, Naschar M, Schmucker U, Renzing-Kohler K, Holter T, Huttmann A et al. (2002). CD38 expression is an important prognostic marker in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 16: 30–35.
Eldar-Finkelman H . (2002). Glycogen synthase kinase 3: an emerging therapeutic target. Trends Mol Med 8: 126–132.
Glimm H, Tang P, Clark-Lewis I, von Kalle C, Eaves C . (2002). Ex vivo treatment of proliferating human cord blood stem cells with stroma-derived factor-1 enhances their ability to engraft NOD/SCID mice. Blood 99: 3454–3457.
Hodohara K, Fujii N, Yamamoto N, Kaushansky K . (2000). Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) acts together with thrombopoietin to enhance the development of megakaryocytic progenitor cells (CFU-MK). Blood 95: 769–775.
Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, Yang JY et al. (2004). IkappaB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117: 225–237.
Kamiguti AS, Harris RJ, Slupsky JR, Baker PK, Cawley JC, Zuzel M . (2003). Regulation of hairy-cell survival through constitutive activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Oncogene 22: 2272–2284.
Kipps TJ . (2003). Immunobiology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol 10: 312–318.
Lataillade JJ, Clay D, Bourin P, Herodin F, Dupuy C, Jasmin C et al. (2002). Stromal cell-derived factor 1 regulates primitive hematopoiesis by suppressing apoptosis and by promoting G(0)/G(1) transition in CD34(+) cells: evidence for an autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Blood 99: 1117–1129.
Lee Y, Gotoh A, Kwon HJ, You M, Kohli L, Mantel C et al. (2002). Enhancement of intracellular signaling associated with hematopoietic progenitor cell survival in response to SDF-1/CXCL12 in synergy with other cytokines. Blood 99: 4307–4317.
Leupin N, Cenni B, Novak U, Hugli B, Graber HU, Tobler A et al. (2003). Disparate expression of the PTEN gene: a novel finding in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (B-CLL). Br J Haematol 121: 97–100.
Luther SA, Cyster JG . (2001). Chemokines as regulators of T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol 2: 102–107.
Majka M, Janowska-Wieczorek A, Ratajczak J, Kowalska MA, Vilaire G, Pan ZK et al. (2000). Stromal-derived factor 1 and thrombopoietin regulate distinct aspects of human megakaryopoiesis. Blood 96: 4142–4151.
Mori M, Uchida M, Watanabe T, Kirito K, Hatake K, Ozawa K et al. (2003). Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1 and ERK2 induces Bcl-xL up-regulation via inhibition of caspase activities in erythropoietin signaling. J Cell Physiol 195: 290–297.
Moser B, Loetscher P . (2001). Lymphocyte traffic control by chemokines. Nat Immunol 2: 123–128.
Nagata Y, Todokoro K . (1999). Requirement of activation of JNK and p38 for environmental stress-induced erythroid differentiation and apoptosis and of inhibition of ERK for apoptosis. Blood 94: 853–863.
Nishio M, Endo T, Tsukada N, Ohata J, Kitada S, Reed JC et al. (2005). Nurselike cells express BAFF and APRIL, which can promote survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells via a paracrine pathway distinct from that of SDF-1alpha. Blood 106: 1012–1020.
Okada T, Ngo VN, Ekland EH, Forster R, Lipp M, Littman DR et al. (2002). Chemokine requirements for B cell entry to lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. J Exp Med 196: 65–75.
Pepper C, Thomas A, Hoy T, Milligan D, Bentley P, Fegan C . (2003). The vitamin D3 analog EB1089 induces apoptosis via a p53-independent mechanism involving p38 MAP kinase activation and suppression of ERK activity in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in vitro. Blood 101: 2454–2460.
Ringshausen I, Schneller F, Bogner C, Hipp S, Duyster J, Peschel C et al. (2002). Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: association with protein kinase Cdelta. Blood 100: 3741–3748.
Suzuki Y, Rahman M, Mitsuya H . (2001). Diverse transcriptional response of CD4(+) T cells to stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1: cell survival promotion and priming effects of SDF-1 on CD4(+) T cells. J Immunol 167: 3064–3073.
Ticchioni M, Charvet C, Noraz N, Lamy L, Steinberg M, Bernard A et al. (2002). Signaling through ZAP-70 is required for CXCL12-mediated T-cell transendothelial migration. Blood 99: 3111–3118.
van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL et al. (2003). Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98–3936. Leukemia 17: 2257–2317.
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL . (2002). The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 489–501.
von Andrian UH, Mackay CR . (2000). T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N Engl J Med 343: 1020–1034.
Acknowledgements
We thank Frederic Brau for its help on confocal microscopy, Eric W-F Lam and Anne Brunet for Bim promoter and FRE luciferase reporter constructs, respectively, and Sophie Raynaud for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer and the Groupe d'Etudes et de Recherche Clinique, Biologique et Thérapeutique. ME is a recipient of a research fellowship from the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ML/MLD/CM-A03.04) and PYJ is a recipient of a research fellowship from the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ticchioni, M., Essafi, M., Jeandel, P. et al. Homeostatic chemokines increase survival of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through inactivation of transcription factor FOXO3a. Oncogene 26, 7081–7091 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210519
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210519
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CXC chemokine ligand 13 and galectin-9 plasma levels collaboratively provide prediction of disease activity and progression-free survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Annals of Hematology (2024)
-
Effect of ibrutinib on CCR7 expression and functionality in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its implication for the activity of CAP-100, a novel therapeutic anti-CCR7 antibody
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2022)
-
CCR7 as a novel therapeutic target in t-cell PROLYMPHOCYTIC leukemia
Biomarker Research (2020)
-
Mitochondrial apoptosis is induced by Alkoxy phenyl-1-propanone derivatives through PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of Bad and Foxo3A in CLL
Leukemia (2019)
-
CCL4 enhances preosteoclast migration and its receptor CCR5 downregulation by RANKL promotes osteoclastogenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2018)