Abstract
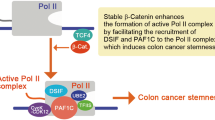
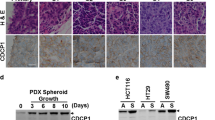
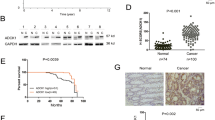
Programmed cell death 4 (Pdcd4) is a tumor suppressor that inhibits neoplastic transformation and tumor invasion. Tissue microarray analysis showed that Pdcd4 expression is downregulated in colon adenocarcinoma and carcinoma relative to adjacent normal tissues. To address the issue of whether reduced Pdcd4 expression is sufficient to promote tumor progression, we knocked down Pdcd4 expression in colon tumor HT29 cells using pdcd4 short hairpin RNA (shRNA). Pdcd4 knockdown results in a fibroblast-like transition, while the control cells (expressing LacZ shRNA) remain as clumped similar to the parental cells. In addition, expression of pdcd4 shRNA in HT29 cells promotes invasion. In an effort to characterize the molecular mechanism underlying these observations, we discovered that knockdown of Pdcd4 results in reduction of E-cadherin expression, and accumulation of active β-catenin in the nucleus. The active β-catenin binds with T-cell factor 4 (Tcf4) and activates β-catenin/Tcf-dependent transcription. Furthermore, Pdcd4 knockdown dramatically increases AP-1-dependent transcription. Thus, the mechanism by which reduced Pdcd4 expression promotes invasion appears to involve the activation of β-catenin/Tcf and AP-1-dependent transcription.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitomsky N, Bohm M, Klempnauer KH . (2004). Transformation suppressor protein Pdcd4 interferes with JNK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Jun and recruitment of the coactivator p300 by c-Jun. Oncogene 23: 7484–7493.
Bonome T, Lee JY, Park DC, Radonovich M, Pise-Masison C, Brady J et al. (2005). Expression profiling of serous low malignant potential, low-grade, and high-grade tumors of the ovary. Cancer Res 65: 10602–10612.
Cavallaro U, Christofori G . (2004). Cell adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 118–132.
Chen Y, Knosel T, Kristiansen G, Pietas A, Garber ME, Matsuhashi S et al. (2003). Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis. J Pathol 200: 640–646.
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder RG . (1983). Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 1475–1489.
Gao F, Zhang P, Zhou C, Li J, Wang Q, Zhu F et al. (2007). Frequent loss of PDCD4 expression in human glioma: possible role in the tumorigenesis of glioma. Oncol Rep 17: 123–128.
Gregorieff A, Clevers H . (2005). Wnt signaling in the intestinal epithelium: from endoderm to cancer. Genes Dev 19: 877–890.
Hennigan RF, Hawker KL, Ozanne BW . (1994). Fos-transformation activates genes associated with invasion. Oncogene 9: 3591–3600.
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Colburn NH . (2005). Epidermal expression of the translation inhibitor programmed cell death 4 suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 65: 6034–6041.
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Stark C, Colburn NH . (2004). Characterization of programmed cell death 4 in multiple human cancers reveals a novel enhancer of drug sensitivity. Mol Cancer Ther 3: 103–110.
Kemler R . (1992). Classical cadherins. Semin Cell Biol 3: 149–155.
Kinsella AR, Lepts GC, Hill CL, Jones M . (1994). Reduced E-cadherin expression correlates with increased invasiveness in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis 12: 335–342.
Lamb RF, Hennigan RF, Turnbull K, Katsanakis KD, MacKenzie ED, Birnie GD et al. (1997). AP-1-mediated invasion requires increased expression of the hyaluronan receptor CD44. Mol Cell Biol 17: 963–976.
Laufs S, Schumacher J, Allgayer H . (2006). Urokinase-receptor (u-PAR): an essential player in multiple games of cancer: a review on its role in tumor progression, invasion, metastasis, proliferation/dormancy, clinical outcome and minimal residual disease. Cell Cycle 5: 1760–1771.
Lee S, Bang S, Song K, Lee I . (2006). Differential expression in normal-adenoma-carcinoma sequence suggests complex molecular carcinogenesis in colon. Oncol Rep 16: 747–754.
Leupold JH, Yang HS, Colburn NH, Asangani I, Post S, Allgayer H . (2007). Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 inhibits invasion/intravasation and regulates urokinase receptor (u-PAR) gene expression via Sp-transcription factors. Oncogene 26: 4550–4562.
Li JJ, Rhim JS, Schlegel R, Vousden KH, Colburn NH . (1998). Expression of dominant negative Jun inhibits elevated AP-1 and NF-κB transactivation and suppresses anchorage independent growth of HPV immortalized human keratinocytes. Oncogene 16: 2711–2721.
Mann B, Gelos M, Siedow A, Hanski ML, Gratchev A, Ilyas M et al. (1999). Target genes of beta-catenin-T cell-factor/lymphoid-enhancer-factor signaling in human colorectal carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 1603–1608.
Matsuhashi S, Narisawa Y, Ozaki I, Mizuta T . (2007). Expression patterns of programmed cell death 4 protein in normal human skin and some representative skin lesions. Exp Dermatol 16: 179–184.
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N, Clevers H, Vogelstein B et al. (1997). Activation of beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in beta-catenin or APC. Science 275: 1787–1790.
Ozanne BW, McGarry L, Spence HJ, Johnston I, Winnie J, Meagher L et al. (2000). Transcriptional regulation of cell invasion: AP-1 regulation of a multigenic invasion programme. Eur J Cancer 36: 1640–1648.
Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A . (2004). Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 48: 365–375.
Portereiko MF, Lloyd A, Steffen JG, Punwani JA, Otsuga D, Drews GN . (2006). AGL80 is required for central cell and endosperm development in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18: 1862–1872.
Takeichi M . (1991). Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science 251: 1451–1455.
Van Aken J, Cuvelier CA, De Wever N, Roels J, Gao Y, Mareel MM . (1993). Immunohistochemical analysis of E-cadherin expression in human colorectal tumours. Pathol Res Pract 189: 975–978.
Yang HS, Cho MH, Zakowicz H, Hegamyer G, Sonenberg N, Colburn NH . (2004). A novel function of the MA-3 domains in transformation and translation suppressor Pdcd4 is essential for its binding to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A. Mol Cell Biol 24: 3894–3906.
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Komar AA, Zheng X, Merrick WC, Costes S et al. (2003a). The transformation suppressor Pdcd4 is a novel eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A binding protein that inhibits translation. Mol Cell Biol 23: 26–37.
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R, Shibahara K, Verma AK, Cmarik JL et al. (2001). A novel transformation suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but not NF-kappaB or ODC transactivation. Oncogene 20: 669–676.
Yang HS, Knies JL, Stark C, Colburn NH . (2003b). Pdcd4 suppresses tumor phenotype in JB6 cells by inhibiting AP-1 transactivation. Oncogene 22: 3712–3720.
Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T, Wang Q, Baker AR, Li CC et al. (2006a). Tumorigenesis suppressor Pdcd4 downregulates MAP4K1 expression to suppress colon carcinoma cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol 26: 1297–1306.
Yang J, Zhang W, Evans PM, Chen X, He X, Liu C . (2006b). Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) differentially regulates beta-catenin phosphorylation and ubiquitination in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281: 17751–17757.
Yuspa SH . (1998). The pathogenesis of squamous cell cancer: lessons learned from studies of skin carcinogenesis. J Dermatol Sci 17: 1–7.
Zhang H, Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Hamajima H, Yasutake T, Eguchi Y et al. (2006). Involvement of programmed cell death 4 in transforming growth factor-beta1-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 25: 6101–6112.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Eun Lee (University of Kentucky) for examination of immunohistochemical staining of Pdcd4 in colon tissues, Mary Vore (University of Kentucky) and Chou-Chi Li (SAIC-Frederick) for reading the article and helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Sun, Z. & Yang, HS. Downregulation of tumor suppressor Pdcd4 promotes invasion and activates both β-catenin/Tcf and AP-1-dependent transcription in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 27, 1527–1535 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210793
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210793
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IGF-1R inhibition induces MEK phosphorylation to promote survival in colon carcinomas
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
SKP2 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and radiation tolerance through PDCD4 ubiquitination
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Genome-wide promoter DNA methylation profiling of hepatocellular carcinomas arising either spontaneously or due to chronic exposure to Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE) in B6C3F1/N mice
Archives of Toxicology (2019)
-
Reversine inhibits Colon Carcinoma Cell Migration by Targeting JNK1
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Tumor suppressor Pdcd4 attenuates Sin1 translation to inhibit invasion in colon carcinoma
Oncogene (2017)