Abstract
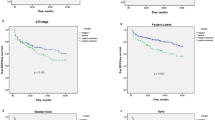
The objective of this work was to evaluate the oncological outcomes and complications of prostate cancer patients with prostate specific antigen (PSA) <10 ng/ml after radical prostatectomy by retropubic, perineal and laparoscopic approach. From 1988 to 2001, 306 patients with PSA <10 ng/ml underwent radical prostatectomy by the retropubic, perineal or laparoscopic approach. Mean operative time, complication rates, length of hospital stay, catheterization time and pathological results were reviewed. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to evaluate the likelihood of biochemical PSA recurrence. There were no statistical differences between the three groups in terms of preoperative characteristics except for PSA levels (5.5, 6.5 and 6.6 ng/ml for the retropubic, perineal, and laparoscopic approach, respectively, P<0.05) and for the T1c stage prevalence (50%, 43.1% and 68.4%, P<0.05). Operating time was significatively longer in the laparoscopic approach (266 min), whereas transfusion rate (22.1%), bladder catetherization (12.1 days), and length of hospital stay (12.1 days) were higher in the retropubic group (P<0.05). The percentage of medical and surgical complications were 6.9%, 3.1% and 3.4% (P<0.05) and 18.6%, 16.9% and 11.6% (P<0.05) for the retropubic, perineal, and laparoscopic approach, respectively. Pathological staging revealed pT2 in 76.7%, 78.4% and 81.3% for retropubic, perineal and laparoscopic approach, respectively (P<0.05). Positive surgical positive margins were noted in 20.9%, 18.4% and 20.6% (P>0.05). The actuarial 3-year recurrence-free survival rate was 89.3%, 89.2% and 86.2% (P>0.05) for retropubic, perineal and laparoscopic approach, respectively. It can be concluded that in patients with preoperative PSA<10 ng/ml, clinical outcome and complication rates were similar, regardless of the choice of surgical approach.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
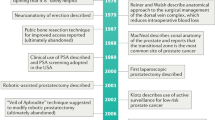
Young HH . The early diagnosis and radical cure of carcinoma of the prostate: being a study of 40 cases and presentation of a radical operation which was carried out in four cases Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 1905 175: 315–321
Millin T . Retropubic prostatectomy: a new extra vesical technique Lancet 1945 2: 693–696
Walsh PC, Lepor H, Eggleston JD . Radical prostatectomy with preservation of sexual function: anatomical and pathological considerations Prostate 1983 4: 473–485
Raboy A, Ferzli G, Albert P . Initial experience with extraperitoneal endoscopic radical retropubic prostatectomy Urology 1997 50: 849–853
Schuessler WW et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: initial short term experience Urology 1997 50: 854–857
Guillonneau B, Vallancien G . Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: initial experience and preliminary assessment after 65 operations Prostate 1999 39: 71–75
Walsh PC . The status of radical prostatectomy in the United States in 1993. Where do we go from here? J Urol 1994 152: 1816–1820
Abbou CC et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: preliminary results Urology 2000 55: 630–634
Partin AW et al. Contemporary update of prostate cancer staging nomograms (Partin tables) for the new millenium Urology 2001 58: 843–848
Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Redwine E . Morphometric and clinical studies on 68 consecutive radical prostatectomies J Urol 1988 139: 1235–1241
TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors: International Union Against Cancer. In: Sobin LH, Wittekind C (eds). Edition 5 Wiley-Liss: New York 1997 pp. 170–173
Pound CR, Partin AW, Epstein JI, Walsh PC . Prostate-specific antigen after anatomic radical retropubic prostatectomy Urol Clin North Am 1997 24: 395–406
Boccon-Gibod L et al. Radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: perineal approach increases risk of surgically induced positive margins and capsular incisions J Urol 1998 160: 1383–1385
Parra RO, Boullier JA, Rauscher JA, Cummings JM . The value of laparoscopic lymphadenectomy in conjunction with radical perineal or retropubic prostatectomy J Urol 1994 151: 1599–1602
Teichman JM, Reddy PK, Hulbert JC . Laparoscopic pelvic lymph node dissection, laparoscopically assisted seminal vesicle mobilization and total perineal prostatectomy vs radical retropubic prostatectomy for prostate cancer Urology 1995 5: 823–830
Frazier HA, Robertson JE, Paulson DF . Radical prostatectomy: the pros and cons of the perineal vs retropubic approach J Urol 1992 147: 888–890
Haab F et al. Perineal vs retropubic radical prostatectomy for T1, T2 prostate cancer Br J Urol 1994 74: 626–629
Salomon L et al. Voies rétropubiennes et périnéales: plaidoyer pour la prostatectomie radicale par voie périnéale Prog Urol 1997 7: 976–983
Kahn SA, Tiwari A, Narayan P . Radical perineal prostatectomy versus radical retropubic prostatectomy: a clinical comparison J Urol 1998 159: (abstract) 61
Lance RS et al. Comparison of radical perineal prostatectomy to radical retropubic prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer: Uniformed Services Urology Research Group (USURG) experience Br J Urol 1998 159: 61–65
Walther PJ . Radical perineal vs retropubic prostatectomy: a review of optimal application and technical consideration in the utilization of these procedures Eur Urol 1998 24: 34–38
Sulser T et al. Complications and initial 1228 laparoscopic radical prostatectomies at 6 European Centers J Urol 2001 165: (Suppl) 150 abstract 615
Guillonneau B, Vallancien G . Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: The Montsouris experience J Urol 2000 163: 418–422
Wieder JA, Soloway MS . Incidence, etiology, location, prevention and treatment of positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer J Urol 1998 160: 299–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salomon, L., Levrel, O., Anastasiadis, A. et al. Outcome and complications of radical prostatectomy in patients with PSA <10 ng/ml: comparison between the retropubic, perineal and laparoscopic approach. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 5, 285–290 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500605
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500605
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevention and management of ureteral injuries occurring during laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the Heilbronn experience and a review of the literature
World Journal of Urology (2009)
-
Rectal tube or no rectal tube? A viewpoint from Duke University Medical Center
Journal of Robotic Surgery (2008)
-
Sexual dysfunction after pelvic surgery
International Journal of Impotence Research (2006)
-
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy a review of the literature and comparison with open techniques
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2004)