Abstract
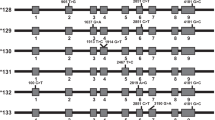
Cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) genotyping reliably predicts poor metabolizer phenotype in Caucasians, but is less accurate in African Americans. To evaluate discordance we have observed in phenotype to genotype correlation studies, select African American subjects were chosen for complete resequencing of the CYP2D6 gene including 4.2 kb of the CYP2D7-2D6 intergenic region. Comparisons were made to a CYP2D6*1 reference sequence revealing novel SNPs in the upstream, coding and intervening sequences. These sequence variations, defining four functional alleles (CYP2D6*41B, *45A and B and *46), were characterized for their ability to influence splice site strength, transcription level or catalytic protein activity. Furthermore, their frequency was determined in a population of 251 African Americans. A −692TGTG deletion (CYP2D6*45B) did not significantly decrease gene expression, nor could any other upstream SNP explain a genotype-discordant case. CYP2D6*45 and *46 have a combined frequency of 4% and can be identified by a common SNP. Carriers are predicted to exhibit an extensive or intermediate CYP2D6 phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scordo MG, Spina E . Cytochrome P450 polymorphisms and response to antipsychotic therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2002; 3: 201–218.
Yu AM, Idle JR, Herraiz T, Kupfer A, Gonzalez FJ . Screening for endogenous substrates reveals that CYP2D6 is a 5-methoxyindolethylamine O-demethylase. Pharmacogenetics 2003; 13: 307–319.
Yu AM, Idle JR, Krausz KW, Kupfer A, Gonzalez FJ . Contribution of individual cytochrome P450 isozymes to the O-demethylation of the psychotropic beta-carboline alkaloids harmaline and harmine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 305: 315–322.
Sachse C, Brockmöller J, Bauer S, Roots I . Cytochrome P450 2D6 variants in a Caucasian population: allele frequencies and phenotypic consequences. Am J Hum Genet 1997; 60: 284–295.
Griese E-U, Zanger UM, Brudermanns U, Gaedigk A, Mikus G, Mörike K et al. Assessment of the predictive power of genotypes for the in vivo catalytic function of CYP2D6 in a Caucasian population. Pharmacogenetics 1998; 8: 15–26.
Gaedigk A, Gotschall RR, Forbes NS, Simon SD, Leeder JS . Optimization of cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) phenotype assignment using a genotyping algorithm based on allele frequency data. Pharmacogenetics 1999; 9: 669–682.
Chou W-H, Yan F-X, Robbins-Weilert DK, Ryder TB, Liu WW, Perbost C et al. Comparison of two CYP2D6 genotyping methods and assessment of genotype–phenotype relationships. Clin Chem 2003; 49: 542–551.
Johansson I, Lundqvist E, Dahl M-L, Ingelman-Sundberg M . PCR-based genotyping for duplicated and deleted CYP2D6 genes. Pharmacogenetics 1996; 6: 351–355.
Kubota T, Yamaura Y, Ohkawa N, Hara H, Chiba K . Frequencies of CYP2D6 mutant alleles in a normal Japanese population and metabolic activity of dextromethorphan O-demethylation in diferent CYP2D6 genotypes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2000; 50: 31–34.
Yokoi T, Kosaka Y, Chida M, Chiba K, Nakamura H, Ishizaki T et al. A new CYP2D6 allele with a nine base insertion in exon 9 in a Japanese population associated with poor metabolizer phenotype. Pharmacogenetics 1996; 6: 395–401.
Wang S-L, Lai M-D, Huang J-D . G169R mutation diminishes the metabolic activity of CYP2D6 in Chinese. Drug Metab Dipos 1999; 27: 385–388.
Chida M, Yokoi T, Nemoto N, Inaba M, Kinoshita M, Kamataki T . A new variant CYP2D6 allele (CYP2D6*21) with a single base insertion in exon 5 in a Japanese population associated with a poor metabolizer phenotype. Pharmacogenetics 1999; 9: 287–293.
Shimada T, Tsumura F, Yamasaki H, Guengerich FP, Inoue K . Characterization of (±)-bufuralol hydroxylation activities in liver microsomes of Japanese and Caucasian subjects genotyped for CYP2D. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 143–156.
Ji L, Pan S, Wu J, Marti-Jaun J, Hersberger M . Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2D6 in Chinese mainland. Chin Med J 2002; 115: 1780–1784.
Chida M, Ariyoshi N, Yokoi T, Nemoto N, Inaba M, Kinoshita M et al. New allelic arrangement CYP2D6*36 × 2 found in a Japanese poor metabolizer of debrisoquine. Pharmacogenetics 2002; 12: 559–562.
Lennard MS, Iyun AO, Jackson PR, Tucker GT, Woods HF . Evidence for a dissociation in the control of sparteine, debrisoquine and metoprolol metabolism in Nigerians. Pharmacogenetics 1992; 2: 89–92.
Simooya OO, Njunju E, Hodjegan AR, Lennard MS, Tucker GT . Debrisoquine and metoprolol oxidation in Zambians: a population study. Pharmacogenetics 1993; 3: 205–208.
Masimirembwa C, Hasler J, Bertilsson L, Johansson I, Ekberg O, Ingelman-Sundberg M . Phenotype and genotype analysis of debrisoquine hydroxylase (CYP2D6) in a black Zimbabwean population. Reduced enzyme activity and evaluation of metabolic correlation of CYP2D6 probe drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1996b; 51: 117–122.
Droll K, Bruce-Mensah K, Otton SV, Gaedigk A, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF . Comparison of three CYP2D6 probe substrates and genotype in Ghanaians, Chinese, and Caucasians. Pharmacogenetics 1998; 8: 325–333.
Leathart JBS, London SJ, Steward A, Adams JD, Idle JR, Daly AK . CYP2D6 phenotype–genotype relationships in African-Americans and Caucasians in Los Angeles. Pharmacogenetics 1998; 8: 529–541.
Griese U-E, Asante-Poku S, Ofori-Adjei D, Mikus G, Eichelbaum M . Analysis of the CYP2D6 gene mutations and their consequences for enzyme function in a West African population. Pharmacogenetics 1999; 9: 715–723.
Wan Y-JY, Poland RE, Han G, Konishi T, Zheng Y-P, Berman N et al. Analysis of the CYP2D6 gene polymorphism and enzyme activity in African-Americans in Southern California. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 489–499.
Gaedigk A, Bradford LD, Marcucci KA, Leeder JS . Unique CYP2D6 activity distribution and genotype–phenotype discordance in African Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 72: 76–89.
Raimundo S, Fischer J, Eichelbaum M, Griese E-U, Schwab M, Zanger UM . Elucidation of the genetic basis of the common ‘intermediate metabolizer’ phenotype for drug oxidation by CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 2000; 10: 577–581.
Zanger UM, Fischer J, Raimundo S, Stüven T, Evert BO, Schwab M et al. Comprehensive analysis of the genetic factors determining expression and function of hepatic CYP2D6. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 573–585.
Gaedigk A, Ryder DL, Bradford LD, Leeder JS . CYP2D6 poor metabolizer status can be ruled out by a single genotyping assay testing for the −1584G promoter polymorphism. Clin Chem 2003; 49: 1008–1011.
Kimura S, Umeno M, Skoda RC, Meyer UA, Gonzalez FJ . The human debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase (CYP2D) locus: sequence and identification of the polymorphic CYP2D6 gene, a related gene, and a pseudogene. Am J Hum Genet 1989; 45: 889–904.
Abdel-Rahman SM, Leeder JS, Wilson JT, Gaedigk A, Gotschall RR, Medve R et al. Concordance between tramadol and dextromethorphan parent/metabolite ratios: the influence of CYP2D6 and non-CYP2D6 pathways on biotransformation. J Clin Pharmacol 2002; 42: 24–29.
Rogan PK, Svojanovsky S, Leeder JS . Information theory-based analysis of CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 splicing mutations. Pharmacogenetics 2003; 13: 207–218.
Aklillu E, Herrlin K, Gustafsson LL, Bertilsson L, Ingelman-Sundberg M . Evidence for environmental influence on CYP2D6-catalysed debrisoquine hydroxylation as demonstrated by phenotyping and genotyping of Ethiopians living in Ethiopia or in Sweden. Pharmacogenetics 2002; 12: 375–383.
Gaedigk A, Ndjountsche L, Gaedigk R, Bradford LD, Leeder JS . Discovery of a novel non-functional cytochrome P4502D6 allele, CYP2D6*42, in AfricanAmericans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2003; 73: 575–576.
Grant DM . Pharmacogenetics and the regulation of gene transcription. Phamacogenetics 2004; 14: 391–393.
Cairns W, Smith CAD, McLaren AW, Wolf CR . Characterization of the human cytochrome P4502D6 promoter. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 25269–25276.
Kuehl P, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lamba J, Assem M, Schuetz J et al. Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet 2001; 27: 383–391.
Rogan PK, Faux BM, Schneider TD . Information analysis of human splice site mutations. Hum Mutat 1998; 12: 153–171.
Vockley J, Rogan PK, Anderson BD, Willard J, Seelan RS, Smith DI et al. Exon skipping in IVD RNA processing in isovaleric acidemia caused by point mutations in the coding region of the IVD gene. Am J Hum Genet 2000; 66: 356–367.
Howard LA, Miksys S, Hoffmann E, Mash D, Tyndale RF . Brain CYP2E1 is induced by nicotine and ethanol in rat and is higher in smokers and alcoholics. Br J Pharmacol 2003; 138: 1376–1386.
Raimundo S, Toscano C, Klein K, Fischer J, Griese E-U, Eichelbaum M et al. A novel intronic mutation, 2988G>A, with high predictivity for impaired function of cytochrome P450 2D6 in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther (CPT) 2004; 76: 128–138.
Abdel-Rahman SM, Gotschall RR, Kauffman RE, Leeder JS, Kearns GL . Investigation of terbinafine as a CYP2D6 inhibitor in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1999; 65: 465–472.
Marcucci KA, Pearce RE, Crespi C, Leeder JS, Gaedigk A . Characterization of cytochrome P450 2D6.1 (CYP2D6.1), CYP2D6.2 and CYP2D6.17 activities toward model CYP2D6 substrates dextromethorphan, bufuralol, and debrisoquine. Drug Metab Dispos 2002; 30: 1–7.
Acknowledgements
We thank Roger Gaedigk, PhD and Peter K Rogan, PhD for continuous support and advice and Darren W Baker, BS for technical support. We further express our gratitude to Rachel F Tyndale, PhD for her generous gift of IMR-32 cells and to John T Wilson, MD and Gregory L Kearns, PharmD, PhD who served as the Principal Investigators for the pediatric studies of tramadol. This project was supported in part by intramural grants from the Katherine B Richardson Associates Endowment Fund (AG and SWA) and the National Institute of Child Health Human Development (Pediatric Pharmacology Research Unit Network) and RO1ES10855-04 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DUALITY OF INTEREST
None declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaedigk, A., Bhathena, A., Ndjountché, L. et al. Identification and characterization of novel sequence variations in the cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) gene in African Americans. Pharmacogenomics J 5, 173–182 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500305
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Meta-analysis of probability estimates of worldwide variation of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Full-gene haplotypes refine CYP2D6 metabolizer phenotype inferences
International Journal of Legal Medicine (2018)
-
Constellation: a tool for rapid, automated phenotype assignment of a highly polymorphic pharmacogene, CYP2D6, from whole-genome sequences
npj Genomic Medicine (2016)
-
The CYP4502D6 *4 and *6 alleles are the molecular genetic markers for drug response: implications in colchicine non-responder FMF patients
European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (2016)
-
Polymorphic metabolism by functional alterations of human cytochrome P450 enzymes
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2011)