Abstract
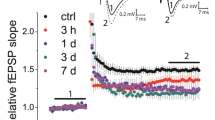
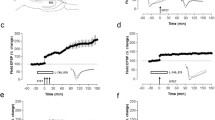
Cognitive deficits and memory loss are frequent in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Persistent changes in synaptic efficacy are considered as a cellular substrate underlying memory processes. Electrophysiological studies have shown that the properties of short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity in the cortex and hippocampus may undergo substantial changes after seizures. However, the neural mechanisms responsible for these changes are not clear. In this study, we investigated the properties of short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampal slices 24 h after pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced status epilepticus. We found that the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) in CA1 pyramidal cells is reduced compared to the control, while short-term facilitation is increased. The experimental results do not support the hypothesis that status epilepticus leads to background potentiation of hippocampal synapses and further LTP induction becomes weaker due to occlusion, as the dependence of synaptic responses on the strength of input stimulation was not different in the control and experimental animals. The decrease in LTP can be caused by impairment of molecular mechanisms of neuronal plasticity, including those associated with NMDA receptors and/or changes in their subunit composition. Realtime PCR demonstrated significant increases in the expression of GluN1 and GluN2A subunits 3 h after PTZ-induced status epilepticus. The overexpression of obligate GluN1 subunit suggests an increase in the total number of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus. A 3-fold increase in the expression of the GluN2B subunit observed 24 h after PTZ-induced status epilepticus might be indicative of an increase in the proportion of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors. Increased expression of the GluN2B subunit may be a cause for reducing the magnitude of LTP at hippocampal synapses after status epilepticus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACSF:
-
artificial cerebrospinal fluid
- CycA:
-
cyclophilin A
- fEPSP:
-
field excitatory postsynaptic potentials
- LTP:
-
long-term synaptic potentiation
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-Daspartate
- PTZ:
-
pentylenetetrazole
References
Giovagnoli, A. R., and Avanzini, G. (1999) Learning and memory impairment in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: relation to the presence, type, and location of brain lesion, Epilepsia, 40, 904–911.
Aniol, V. A., Ivanova-Dyatlova, A. Y., Keren, O., Guekht, A. B., Sarne, Y., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2013) A single pentylenetetrazole-induced clonic-tonic seizure episode is accompanied by a slowly developing cognitive decline in rats, Epilepsy Behav., 26, 196–202.
Kalemenev, S. V., Zubareva, O. E., Frolova, E. V., Sizov, V. V., Lavrentyeva, V. V., Lukomskaya, N. Y., Kim, K., Zaitsev, A. V., and Magazanik, L. G. (2015) Impairment of exploratory behavior and spatial memory in adolescent rats in lithium–pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 463, 175–177.
Kandel, E. R. (2004) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialog between genes and synapses, Biosci. Rep., 24, 475–522.
Abegg, M. H., Savic, N., Ehrengruber, M. U., McKinney, R. A., and Gahwiler, B. H. (2004) Epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus strengthens excitatory synapses, J. Physiol., 554, 439–448.
Muller, L., Tokay, T., Porath, K., Kohling, R., and Kirschstein, T. (2013) Enhanced NMDA receptor-dependent LTP in the epileptic CA1 area via upregulation of NR2B, Neurobiol. Dis., 54, 183–193.
Zhou, J. L., Shatskikh, T. N., Liu, X., and Holmes, G. L. (2007) Impaired single cell firing and long-term potentiation parallels memory impairment following recurrent seizures, Eur. J. Neurosci., 25, 3667–3677.
Meador, K. J. (2007) The basic science of memory as it applies to epilepsy, Epilepsia, 48, 23–25.
Debanne, D., Thompson, S. M., and Gahwiler, B. H. (2006) A brief period of epileptiform activity strengthens excitatory synapses in the rat hippocampus in vitro, Epilepsia, 47, 247–256.
Kryukov, K. A., Kim, K. K., Magazanik, L. G., and Zaitsev, A. V. (2016) Status epilepticus alters hippocampal long-term synaptic potentiation in a rat lithium-pilocarpine model, Neuroreport, 27, 1191–1195.
Suarez, L. M., Cid, E., Gal, B., Inostroza, M., BrotonsMas, J. R., Gomez-Dominguez, D., de la Prida, L. M., and Solis, J. M. (2012) Systemic injection of kainic acid differently affects LTP magnitude depending on its epileptogenic efficiency, PLoS One, 7, e48128.
Guli, X., Tokay, T., Kirschstein, T., and Kohling, R. (2016) Status epilepticus enhances depotentiation after fully established LTP in an NMDAR-dependent but GluN2B-independent manner, Neural Plast., 6592038.
O’Leary, H., Bernard, P. B., Castano, A. M., and Benke, T. A. (2016) Enhanced long term potentiation and decreased AMPA receptor desensitization in the acute period following a single kainate induced early life seizure, Neurobiol. Dis., 87, 134–144.
Monyer, H., Burnashev, N., Laurie, D. J., Sakmann, B., and Seeburg, P. H. (1994) Developmental and regional expression in the rat brain and functional properties of four NMDA receptors, Neuron, 12, 529–540.
Cull-Candy, S., Brickley, S., and Farrant, M. (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 11, 327–335.
Naylor, D. E., Liu, H., Niquet, J., and Wasterlain, C. G. (2013) Rapid surface accumulation of NMDA receptors increases glutamatergic excitation during status epilepticus, Neurobiol. Dis., 54, 225–238.
Di Maio, R., Mastroberardino, P. G., Hu, X., Montero, L., and Greenamyre, J. T. (2011) Pilocarpine alters NMDA receptor expression and function in hippocampal neurons: NADPH oxidase and ERK1/2 mechanisms, Neurobiol. Dis., 42, 482–495.
Bartlett, T. E., Bannister, N. J., Collett, V. J., Dargan, S. L., Massey, P. V., Bortolotto, Z. A., Fitzjohn, S. M., Bashir, Z. I., Collingridge, G. L., and Lodge, D. (2007) Differential roles of NR2Aand NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in LTP and LTD in the CA1 region of two-week-old rat hippocampus, Neuropharmacology, 52, 60–70.
Wang, D., Cui, Z., Zeng, Q., Kuang, H., Wang, L. P., Tsien, J. Z., and Cao, X. (2009) Genetic enhancement of memory and long-term potentiation but not CA1 longterm depression in NR2B transgenic rats, PLoS One, 4, e7486.
Swijsen, A., Nelissen, K., Janssen, D., Rigo, J. M., and Hoogland, G. (2012) Validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR studies in the dentate gyrus after experimental febrile seizures, BMC Res. Notes, 5, 685.
Livak, K. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method, Methods, 25, 402–408.
Zaitsev, A. V., and Anwyl, R. (2012) Inhibition of the slow afterhyperpolarization restores the classical spike timingdependent plasticity rule obeyed in layer 2/3 pyramidal cells of the prefrontal cortex, J. Neurophysiol., 107, 205–215.
Buonomano, D. V. (1999) Distinct functional types of associative long-term potentiation in neocortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons, J. Neurosci., 19, 6748–6754.
Ben-Ari, Y., and Gho, M. (1988) Long-lasting modification of the synaptic properties of rat CA3 hippocampal neurones induced by kainic acid, J. Physiol., 404, 365–384.
Amakhin, D. V., Ergina, J. L., Chizhov, A. V., and Zaitsev, A. V. (2016) Synaptic conductances during interictal discharges in pyramidal neurons of rat entorhinal cortex, Front. Cell. Neurosci., 10, 233.
Zaitsev, A. V., Kim, K. K., Vasilev, D. S., Lukomskaya, N. Y., Lavrentyeva, V. V., Tumanova, N. L., Zhuravin, I. A., and Magazanik, L. G. (2015) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blockers prevent pentylenetetrazoleinduced convulsions and morphological changes in rat brain neurons, J. Neurosci. Res., 93, 454–465.
Aniol, V. A., Stepanichev, M. Y., Lazareva, N. A., and Gulyaeva, N. V. (2011) An early decrease in cell proliferation after pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures, Epilepsy Behav., 22, 433–441.
Ahmed, M. M., Arif, M., Chikuma, T., and Kato, T. (2005) Pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures affect the levels of prolyl oligopeptidase, thimet oligopeptidase and glial proteins in rat brain regions, and attenuation by MK-801 pretreatment, Neurochem. Int., 47, 248–259.
Zhvania, M. G., Ksovreli, M., Japaridze, N. J., and Lordkipanidze, T. G. (2015) Ultrastructural changes to rat hippocampus in pentylenetetrazoland kainic acidinduced status epilepticus: a study using electron microscopy, Micron, 74, 22–29.
Ahmadirad, N., Shojaei, A., Javan, M., Pourgholami, M. H., and Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J. (2014) Effect of minocycline on pentylenetetrazol-induced chemical kindled seizures in mice, Neurol. Sci., 35, 571–576.
Davoudi, M., Shojaei, A., Palizvan, M. R., Javan, M., and Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J. (2013) Comparison between standard protocol and a novel window protocol for induction of pentylenetetrazol kindled seizures in the rat, Epilepsy Res., 106, 54–63.
Wasterlain, C. G., Naylor, D. E., Liu, H., Niquet, J., and Baldwin, R. (2013) Trafficking of NMDA receptors during status epilepticus: therapeutic implications, Epilepsia, 54, 78–80.
Paoletti, P., Bellone, C., and Zhou, Q. (2013) NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 14, 383–400.
Fox, C. J., Russell, K. I., Wang, Y. T., and Christie, B. R. (2006) Contribution of NR2A and NR2B NMDA subunits to bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus in vivo, Hippocampus, 16, 907–915.
Xu, Z., Chen, R. Q., Gu, Q. H., Yan, J. Z., Wang, S. H., Liu, S. Y., and Lu, W. (2009) Metaplastic regulation of long-term potentiation/long-term depression threshold by activity-dependent changes of NR2A/NR2B ratio, J. Neurosci., 29, 8764–8773.
Frasca, A., Aalbers, M., Frigerio, F., Fiordaliso, F., Salio, M., Gobbi, M., Cagnotto, A., Gardoni, F., Battaglia, G. S., Hoogland, G., Di Luca, M., and Vezzani, A. (2011) Misplaced NMDA receptors in epileptogenesis contribute to excitotoxicity, Neurobiol. Dis., 43, 507–515.
Parsons, M. P., and Raymond, L. A. (2014) Extrasynaptic NMDA receptor involvement in central nervous system disorders, Neuron, 82, 279–293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T. Y. Postnikova, O. E. Zubareva, A. A. Kovalenko, K. K. Kim, L. G. Magazanik, A. V. Zaitsev, 2017, published in Biokhimiya, 2017, Vol. 82, No. 3, pp. 418-428.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Postnikova, T.Y., Zubareva, O.E., Kovalenko, A.A. et al. Status epilepticus impairs synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampus and is followed by changes in expression of NMDA receptors. Biochemistry Moscow 82, 282–290 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917030063
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297917030063