Abstract
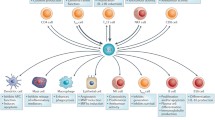
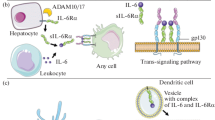
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is one of the most important proinflammatory cytokines that has a broad spectrum of immunoregulatory properties. The molecular mechanisms of signal transduction of IL-6 and its receptor, which have been previously established, were later supplemented with a concept of trans-signaling. The selective inhibition of this signaling cascade would allow the modulation of the pathological effects of IL-6. Reverse genetics methods helped to establish the physiological functions of IL-6 in normal state and in various diseases, including neoplasias. Therapeutic inhibitors of IL-6 or its receptor are already used to treat several autoimmune diseases; however, the systemic inhibition inevitably also neutralizes the protective functions of this cytokine. It is expected that, in the future, systemic therapy will be replaced by more specific and effective approaches that take into account the peculiarities of molecular signaling pathways in target cells and differences in the function of IL-6 depending on the cell source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. 1989. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 58, 573–581.
He G., Dhar D., Nakagawa H., Font-Burgada J., et al. 2013. Identification of liver cancer progenitors whose malignant progression depends on autocrine IL-6 signaling. Cell. 155, 384–396.
Grivennikov S., Karin E., Terzic J., et al. 2009. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell. 15, 103–113.
Eto D., Lao C., Di Toro D., Barnett B., Escobar T.C., Kageyama R., Yusuf I., Crotty S. 2011. IL-21 and IL-6 are critical for different aspects of B cell immunity and redundantly induce optimal follicular helper CD4 T cell (Tfh) differentiation. PLOS ONE. 6, e17739.
Mattoli S., Marini M., Fasoli A. 1992. Expression of the potent inflammatory cytokines, GM-CSF, IL-6, and IL-8, in bronchial epithelial cells of asthmatic patients. Chest. 101, 27S–29S.
Quintana A., Erta M., Ferrer B., Comes G., Giralt M., Hidalgo J. 2013. Astrocyte-specific deficiency of interleukin-6 and its receptor reveal specific roles in survival, body weight and behavior. Brain Behav. Immun. 27, 162–173.
Samoilova E.B., Horton J.L., Hilliard B., Liu T.-S.T., Chen Y. 1998. IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Roles of IL-6 in the activation and differentiation of autoreactive T cells. J. Immunol. 161, 6480–6486.
Leech M.D., Barr T.A., Turner D.G., Brown S., O’ Connor R.A., Gray D., Mellanby R.J., Anderton S.M. 2013. Cutting edge: IL-6-dependent autoimmune disease: Dendritic cells as a sufficient, but transient, source. J. Immunol. 190, 881–885.
Barr T.A., Shen P., Brown S., et al. 2012. B cell depletion therapy ameliorates autoimmune disease through ablation of IL-6-producing B cells. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1001–1010.
Molnarfi N., Schulze-Topphoff U., Weber M.S., et al. 2013. MHC class II-dependent B cell APC function is required for induction of CNS autoimmunity independent of myelin-specific antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 210, 2921–2937.
Tanaka K., Hashizume M., Mihara M., Yoshida H., Suzuki M., Matsumoto Y. 2014. Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody prevents systemic bone mass loss via reducing the number of osteoclast precursors in bone marrow in a collagen-induced arthritis model. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 175, 172–180.
De Hooge A.S., van De Loo F.A., Arntz O.J., van Den Berg W.B. 2000. Involvement of IL-6, apart from its role in immunity, in mediating a chronic response during experimental arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 2081–2091.
Thiolat A., Semerano L., Pers Y.M., et al. 2014. Interleukin-6 receptor blockade enhances CD39+ regulatory T cell development in rheumatoid arthritis and in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66, 273–283.
Rincon M., Irvin C.G. 2012. Role of IL-6 in asthma and other inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 8, 1281–1290.
Qiu Z., Fujimura M., Kurashima K., Nakao S., Mukaida N. 2004. Enhanced airway inflammation and decreased subepithelial fibrosis in interleukin 6-deficient mice following chronic exposure to aerosolized antigen. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 34, 1321–1328.
Doganci A., Eigenbrod T., Krug N., et al. 2005. The IL-6R a chain controls lung CD4+CD25+ Treg development and function during allergic airway inflammation in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 313–325.
Matsumoto S., Hara T., Mitsuyama K., et al. 2010. Essential roles of IL-6 trans-signaling in colonic epithelial cells, induced by the IL-6/soluble–IL-6 receptor derived from lamina propria macrophages, on the development of colitis-associated premalignant cancer in a murine model. J. Immunol. 184, 1543–1551.
Becker C., Fantini M.C., Schramm C., et al. 2004. TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 21, 491–501.
Bollrath J., Phesse T.J., von Burstin V.A., et al. 2009. Gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 15, 91–102.
Putoczki T.L., Thiem S., Loving A., et al. 2013. Interleukin-11 is the dominant IL-6 family cytokine during gastrointestinal tumorigenesis and can be targeted therapeutically. Cancer Cell. 24, 257–271.
Depner S., Lederle W., Gutschalk C., Linde N., Zajonz A., Mueller M.M. 2014. Cell type specific interleukin-6 induced responses in tumor keratinocytes and stromal fibroblasts are essential for invasive growth. Int. J. Cancer. 135, 551–562.
Tanaka T., Narazaki M., Ogata A., Kishimoto T. 2014. A new era for the treatment of inflammatory autoimmune diseases by interleukin-6 blockade strategy. Semin. Immunol. 26, 88–96.
Ueda O., Tateishi H., Higuchi Y., et al. 2013. Novel genetically-humanized mouse model established to evaluate efficacy of therapeutic agents to human interleukin-6 receptor. Sci. Rep. 3, 1196.
Astrakhantseva I.V., Efimov G.A., Drutskaya M.S., Kruglov A.A., Nedospasov S.A. 2014. Modern anticytokine therapy of autoimmune diseases. Biochemistry (Moscow). 79, 1308–1321.
Efimov G.A., Kruglov A.A., Shvarev D.S., Drutskaya M.S., Nedospasov S.A. 2014. New trends in anti-cytokine therapy. Russ. J. Immunol. 8, 706–710.
Scheller J., Garbers C., Rose-John S. 2014. Interleukin-6: From basic biology to selective blockade of proinflammatory activities. Semin. Immunol. 26, 2–12.
Campbell I.L., Erta M., Lim S.L., Frausto R., May U., Rose-John S., Scheller J., Hidalgo J. 2014. Trans-signaling is a dominant mechanism for the pathogenic actions of interleukin-6 in the brain. J. Neurosci. 34, 2503–2513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article was translated by the authors.
Original Russian Text © M.S. Drutskaya, M.A. Nosenko, K.-S.N. Atretkhany, G.A. Efimov, S.A. Nedospasov, 2015, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 6, pp. 937–943.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drutskaya, M.S., Nosenko, M.A., Atretkhany, KS.N. et al. Interleukin-6: From molecular mechanisms of signal transduction to physiological properties and therapeutic targeting. Mol Biol 49, 837–842 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893315060060
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893315060060