Abstract
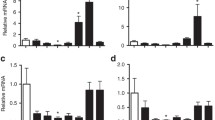
Our aim was to determine whether fetal exposure to intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) persistently alters the lungs following moderate preterm birth. Fetal sheep were exposed to LPS (1 mg/d) or saline from 0.75 to preterm birth at 0.90 of gestation. Eleven weeks after preterm birth, lung structure was unaltered. Interleukin (IL)-1β messenger RNA (mRNA) levels were elevated in lungs of LPS-exposed lambs (P < .05) but IL-1β protein levels were unaltered. Lung mRNA levels of IL-6, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor α, and percentage of inflammatory cells were not different between groups. Surfactant protein (SP)-A and SP-C mRNA levels and SP-B tissue protein expression were higher in LPS-exposed lambs than controls (all P < .05); however, expression of SP-A and SP-C proteins was reduced. Prenatal LPS exposure causes a persistent increase in gene expression of proinflammatory mediators and surfactant proteins and a decrease in lung tissue SP-A and -C protein expression after preterm birth, which may affect lung immunity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lahra MM, Jeffery HE. A fetal response to chorioamnionitis is associated with early survival after preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004;190(1):147–151.
Goldenberg RL, Hauth JC, Andrews WW. Intrauterine infection and preterm delivery. N Engl J Med. 2000;342(20):1500–1507.
Gantert M, Been JV, Gavilanes AW, Garnier Y, Zimmermann LJ, Kramer BW. Chorioamnionitis: a multiorgan disease of the fetus? J Perinatol. 2010;30(suppl):S21–S30.
Been JV, Kramer BW, Zimmermann LJ. In utero and early-life conditions and adult health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359(14):1523–1524; author reply 1524.
Jobe AH, Newnham JP, Willet KE, et al. Endotoxin-induced lung maturation in preterm lambs is not mediated by cortisol. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162(5):1656–1661.
Vayrynen O, Glumoff V, Hallman M. Regulation of surfactant proteins by LPS and proinflammatory cytokines in fetal and newborn lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002; 282(4):L803–L810.
Watterberg KL, Demers LM, Scott SM, Murphy S. Chorioamnionitis and early lung inflammation in infants in whom bronchopulmonary dysplasia develops. Pediatrics. 1996;97(2):210–215.
Lahra MM, Beeby PJ, Jeffery HE. Maternal versus fetal inflammation and respiratory distress syndrome: a 10-year hospital cohort study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2009;94(1): F13–F16.
Jobe AH, Newnham JP, Willet KE, et al. Effects of antenatal endotoxin and glucocorticoids on the lungs of preterm lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182(2):401–408.
Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Kramer BW, Ikegami M, Newnham JP, Jobe AH. Intra-amniotic endotoxin induces lung maturation by direct effects on the developing respiratory tract in preterm sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;187(4):1059–1065.
Kallapur SG, Jobe AH. Contribution of inflammation to lung injury and development. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006; 91(2):F132–F135.
Lee HJ, Kim EK, Kim HS, Choi CW, Kim BI, Choi JH. Chorioamnionitis, respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely low birth weight infants. J Perinatol. 2011;31(3):166–170.
Kent A, Dahlstrom JE. Chorioamnionitis/funisitis and the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Paediatr Child Health. 2004;40(7):356–359.
Bry K, Hogmalm A, Backstrom E. Mechanisms of inflammatory lung injury in the neonate: lessons from a transgenic mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol. 2010;34(3): 211–221.
Prendergast M, May C, Broughton S, et al. Chorioamnionitis, lung function and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in prematurely born infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010;96(4): F270–F274.
Hartling L, Liang Y, Lacaze-Masmonteil T. Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011; 97(1):F8–F17.
Willet KE, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Newnham J, Brennan S, Sly PD. Antenatal endotoxin and glucocorticoid effects on lung morphometry in preterm lambs. Pediatr Res. 2000;48(6):782–788.
Kumar R, Yu Y, Story RE, et al. Prematurity, chorioamnionitis, and the development of recurrent wheezing: a prospective birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;121(4):878–884; e876.
Kallapur SG, Nitsos I, Moss TJ, et al. Chronic endotoxin exposure does not cause sustained structural abnormalities in the fetal sheep lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;288(5): L966–L974.
Kramer BW, Kallapur SG, Moss TJ, et al. Modulation of fetal inflammatory response on exposure to lipopolysaccharide by chorioamnion, lung, or gut in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202(1):77; e71–77; e79.
Moss TJ, Davey MG, Harding R, Newnham JP. Effects of intraamniotic endotoxin on lung structure and function two months after term birth in sheep. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2002;9(4):220–225.
Ueda K, Cho K, Matsuda T, et al. A rat model for arrest of alveolarization induced by antenatal endotoxin administration. Pediatr Res. 2006;59(3):396–400.
Berard A, Le Tiec M, De Vera MA. Study of the costs and morbidities of late-preterm birth [published online ahead of print January 31, 2012]. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012.
Boyle JD, Boyle EM. Born just a few weeks early: does it matter? [published online ahead of print August 24, 2011]. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011.
Escobar GJ, Clark RH, Greene JD. Short-term outcomes of infants born at 35 and 36 weeks gestation: we need to ask more questions. Semin Perinatol. 2006;30(1):28–33.
Nitsos I, Rees SM, Duncan J, et al. Chronic exposure to intraamniotic lipopolysaccharide affects the ovine fetal brain. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2006;13(4):239–247.
De Matteo R, Blasch N, Stokes V, Davis P, Harding R. Induced preterm birth in sheep: a suitable model for studying the developmental effects of moderately preterm birth. Reprod Sci. 2010; 17(8):724–733.
Hooper SB, Han VK, Harding R. Changes in lung expansion alter pulmonary DNA synthesis and IGF-II gene expression in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(4 Pt 1):L403–L409.
Nardo L, Hooper SB, Harding R. Stimulation of lung growth by tracheal obstruction in fetal sheep: relation to luminal pressure and lung liquid volume. Pediatr Res. 1998;43(2):184–190.
Adkisson VT, Callas G. Morphometric changes in the lungs of rats following adrenalectomy supplemented by desiccated thyroid. Anat Rec. 1982;203(1):147–156.
Maritz G, Probyn M, De Matteo R, Snibson K, Harding R. Lung parenchyma at maturity is influenced by postnatal growth but not by moderate preterm birth in sheep. Neonatology. 2008;93(1):28–35.
O’Reilly M, Hooper SB, Allison BJ, et al. Persistent bronchiolar remodeling following brief ventilation of the very immature ovine lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009;297(5): L992–L1001.
Bai A, Eidelman DH, Hogg JC, et al. Proposed nomenclature for quantifying subdivisions of the bronchial wall. J Appl Physiol. 1994;77(2):1011–1014.
Sozo F, O’Day L, Maritz G, et al. Repeated ethanol exposure during late gestation alters the maturation and innate immune status of the ovine fetal lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009; 296(3):L510–L518.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254.
Orgeig S, Crittenden TA, Marchant C, McMillen IC, Morrison JL. Intrauterine growth restriction delays surfactant protein maturation in the sheep fetus. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(4):L575–L583.
Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Willett KE, Kramer BW, Jobe AH, Ikegami M. Early gestational intra-amniotic endotoxin: lung function, surfactant, and morphometry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(6):805–811.
Kallapur SG, Willet KE, Jobe AH, Ikegami M, Bachurski CJ. Intra-amniotic endotoxin: chorioamnionitis precedes lung maturation in preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2001; 280(3):L527–L536.
Harding R, Tester ML, Moss TJ, et al. Effects of intra-uterine growth restriction on the control of breathing and lung development after birth. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000;27(1–2):114–119.
Zhan CY, Yuan TM, Sun Y, Yu HM. Early gestational intrauterine infection induces postnatal lung inflammation and arrests lung development in a rat model. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011; 24(2):213–222.
Cao L, Wang J, Tseu I, Luo D, Post M. Maternal exposure to endotoxin delays alveolarization during postnatal rat lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009;296(5): L726–L737.
Lee AJ, Lambermont VA, Pillow JJ, et al. Fetal responses to lipopolysaccharide-induced chorioamnionitis alter immune and airway responses in 7-week-old sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2011;204(4):364; e317–e324.
Kramer BW, Joshi SN, Moss TJ, et al. Endotoxin-induced maturation of monocytes in preterm fetal sheep lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007;293(2):L345–L353.
Strunk T, Doherty D, Jacques A, et al. Histologic chorioamnionitis is associated with reduced risk of late-onset sepsis in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):e134–e141.
Cao L, Wang J, Zhu Y, Tseu I, Post M. Maternal endotoxin exposure attenuates allergic airway disease in infant rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;298(5):L670–L677.
Ito Y, Mason RJ. The effect of interleukin-13 (IL-13) and interferongamma (IFN-gamma) on expression of surfactant proteins in adult human alveolar type II cells in vitro. Respir Res. 2010;11:157.
Cheah FC, Jobe AH, Moss TJ, Newnham JP, Kallapur SG. Oxidative stress in fetal lambs exposed to intra-amniotic endotoxin in a chorioamnionitis model. Pediatr Res. 2008;63(3):274–279.
Kramer BW, Ladenburger A, Kunzmann S, et al. Intravenous lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary maturation and structural changes in fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;200(2):195; e1–10.
Chaiworapongsa T, Hong JS, Hull WM, Romero R, Whitsett JA. Amniotic fluid concentration of surfactant proteins in intraamniotic infection. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;21(9): 663–670.
Islam KN, Mendelson CR. Permissive effects of oxygen on cyclic AMP and interleukin-1 stimulation of surfactant protein A gene expression are mediated by epigenetic mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(8):2901–2912.
Glumoff V, Vayrynen O, Kangas T, Hallman M. Degree of lung maturity determines the direction of the interleukin-1-induced effect on the expression of surfactant proteins. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2000;22(3):280–288.
Perez-Gil J. Lipid-protein interactions of hydrophobic proteins SP-B and SP-C in lung surfactant assembly and dynamics. Pediatr Pathol Mol Med. 2001;20(6):445–469.
Haagsman HP, Hogenkamp A, van Eijk M, Veldhuizen EJ. Surfactant collectins and innate immunity. Neonatology. 2008;93(4): 288–294.
Orgeig S, Hiemstra PS, Veldhuizen EJ, et al. Recent advances in alveolar biology: evolution and function of alveolar proteins. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2010;173(suppl):S43–S54.
Haczku A. Role and regulation of lung collectins in allergic airway sensitization. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;110(1):14–34.
Haczku A. Protective role of the lung collectins surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D in airway inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122(5):861–879; quiz 880–881.
Galinsky R, Moss TJ, Gubhaju L, Hooper SB, Black MJ, Polglase GR. Effect of intra-amniotic lipopolysaccharide on nephron number in preterm fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011; 301(2):F280–F285.
Itabashi K, Ohno T, Nishida H. Indomethacin responsiveness of patent ductus arteriosus and renal abnormalities in preterm infants treated with indomethacin. J Pediatr. 2003;143(2):203–207.
Gimonet V, Bussieres L, Medjebeur AA, Gasser B, Lelongt B, Laborde K. Nephrogenesis and angiotensin II receptor subtypes gene expression in the fetal lamb. Am J Physiol. 1998;274(6 Pt 2):F1062–F1069.
Robillard JE, Weismann DN, Herin P. Ontogeny of single glomerular perfusion rate in fetal and newborn lambs. Pediatr Res. 1981;15(9):1248–1255.
Rodriguez MM, Gomez A, Abitbol C, Chandar J, Montane B, Zilleruelo G. Comparative renal histomorphometry: a case study of oligonephropathy of prematurity. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20(7): 945–949.
Abitbol CL, Ingelfinger JR. Nephron mass and cardiovascular and renal disease risks. Semin Nephrol. 2009;29(4):445–454.
Toti P, De Felice C, Occhini R, et al. Spleen depletion in neonatal sepsis and chorioamnionitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122(5): 765–771.
Kramer BW, Ikegami M, Moss TJ, Nitsos I, Newnham JP, Jobe AH. Antenatal betamethasone changes cord blood monocyte responses to endotoxin in preterm lambs. Pediatric Res. 2004; 55(5):764–768.
Kallapur SG, Kramer BW, Moss TJ, et al. Maternal glucocorticoids increase endotoxin-induced lung inflammation in preterm lambs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284(4): L633–L642.
Newnham JP, Moss TJ, Padbury JF, et al. The interactive effects of endotoxin with prenatal glucocorticoids on short-term lung function in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;185(1):190–197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atik, A., Sozo, F., Orgeig, S. et al. Long-Term Pulmonary Effects of Intrauterine Exposure to Endotoxin Following Preterm Birth in Sheep. Reprod. Sci. 19, 1352–1364 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719112450327
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719112450327