Abstract
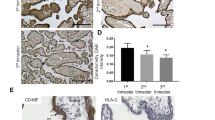
Metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) and its short form (MTA1s) regulate the function of estrogen receptors (ERs). Estrogens, via ERs, affect placental growth and fetal development, a process that may involve MTA1 signaling. Expression of MTA1, MTA1s, ERα, and ERβ genes and proteins in rat placentas was studied on 16, 19, and 21 days of gestation (dg). The ERβ messenger RNA decreased significantly toward the end of gestation, whereas its protein level increased in the nuclear fraction on 21 dg. Both MTA1 and MTA1s increased with gestation. Decidual, trophoblast giant, glycogen, and villous trophoblast cells expressed MTA1, ERα, and ERβ proteins on all dg with colocalization of MTA1 with ERα and ERβ in the nucleus and cytoplasm. Expression of MTA1 suggests a possible role in regulating placental functions; considering the repressive function of MTA1 on ERs, the expression of MTA1 suggests that placental cells may be less sensitive to estrogens during late pregnancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furukawa S, Hayashi S, Usuda K, Abe M, Hagio S, Ogawa I. Toxicological pathology in the rat placenta. J Toxicol Pathol. 2011;24(2):95–111.
Fonseca BM, Correia-da-Silva G, Teixeira NA. The rat as an animal model for fetoplacental development: a reappraisal of the post-implantation period. Reprod Biol. 2012;12(2):97–118.
Bartholomeusz RK, Bruce NW, Lynch AM. Embryo survival, and fetal and placental growth following elevation of maternal estradiol blood concentrations in the rat. Biol Reprod. 1999;61(1):46–50.
Manavathi B, Kumar R. Steering estrogen signals from the plasma membrane to the nucleus: two sides of the coin. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207(3):594–604.
Al-Bader M. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta in rat placenta: detection by RT-PCR, real time PCR and Western blotting. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2006;4:13.
Gambino YP, Maymo JL, Perez Perez A, et al. Elsevier trophoblast research award lecture: molecular mechanisms underlying estrogen functions in trophoblastic cells–focus on leptin expression. Placenta. 2012;(33 suppl): S63–S70.
Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA. Estrogen receptor action. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2002;12(4):237–257.
Manavathi B, Kumar R. Metastasis tumor antigens, an emerging family of multifaceted master coregulators. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(3):1529–1533.
Kumar R, Wang RA, Bagheri-Yarmand R. Emerging roles of MTA family members in human cancers. Semin Oncol. 2003;30(5 suppl 16):30–37.
Li W, Bao W, Ma J, et al. Metastasis tumor antigen 1 is involved in the resistance to heat stress-induced testicular apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(6):869–873.
Mao XY, Chen H, Wang H, et al. MTA1 expression correlates significantly with ER-alpha methylation in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(5):1565–1572.
Bruning A, Makovitzky J, Gingelmaier A, Friese K, Mylonas I. The metastasis-associated genes MTA1 and MTA3 are abundantly expressed in human placenta and chorionic carcinoma cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;132(1):33–38.
Li DQ, Pakala SB, Nair SS, Eswaran J, Kumar R. Metastasisassociated protein 1/nucleosome remodeling and histone deacetylase complex in cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72(2):387–394.
Mishra SK, Yang Z, Mazumdar A, Talukder AH, Larose L, Kumar R. Metastatic tumor antigen 1 short form (MTA1 s) associates with casein kinase I-gamma2, an estrogen-responsive kinase. Oncogene. 2004;23(25):4422–4429.
Cheng G, Imamov O, Omoto Y, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. What is the value of measuring MTA-1 s in breast cancer? Mol Interv. 2002;2(6):360–362, 338.
Al-Bader M, Al-Saji S, Ford CH, et al. Real-time PCR: detection of oestrogen receptor-alpha and -beta isoforms and variants in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(10):4147–4156.
Young K, Huang C, Lin S, et al. Two-phased alteration and clinical relevance of MTA1 and MTA1 s gene expression: a quantitative PCR analysis in breast cancer patients. J Cancer Mol. 2006;(2):79–84.
Al-Bader MD, El-Abdallah AA, Redzic ZB. Ontogenic profile of estrogen receptor alpha and beta mRNA and protein expression in fetal rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 2008;440(3):222–226.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408.
Wilson ME, Ford SP. Comparative aspects of placental efficiency. Reprod Suppl. 2001;58:223–232.
Bukovsky A, Caudle MR, Cekanova M, et al. Placental expression of estrogen receptor beta and its hormone binding variant–comparison with estrogen receptor alpha and a role for estrogen receptors in asymmetric division and differentiation of estrogendependent cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003;1:36.
Forster C, Makela S, Warri A, et al. Involvement of estrogen receptor beta in terminal differentiation of mammary gland epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(24):15578–15583.
Bukovsky A, Cekanova M, Caudle MR, et al. Expression and localization of estrogen receptor-alpha protein in normal and abnormal term placentae and stimulation of Trophoblast differentiation by estradiol. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2003;1:13.
Hodges-Gallagher L, Valentine CD, El Bader S, et al. Estrogen receptor beta increases the efficacy of antiestrogens by effects on apoptosis and cell cycling in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;109(2):241–250.
Treeck O, Lattrich C, Springwald A, Ortmann O. Estrogen receptor beta exerts growth-inhibitory effects on human mammary epithelial cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;120(3):557–565.
Malassine A, Frendo JL, Evain-Brion D. A comparison of placental development and endocrine functions between the human and mouse model. Hum Reprod Update. 2003;9(6):531–539.
Marotti JD, Collins LC, Hu R, Tamimi RM. Estrogen receptorbeta expression in invasive breast cancer in relation to molecular phenotype: results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Mod Pathol. 2010;23(2):197–204.
Matthews J, Gustafsson JA. Estrogen signaling: a subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta. Mol Interv. 2003;3(5):281–292.
Hsiao WC, Cho WC, Lin PW, Lin SL, Lee WY, Young KC. Quantitative profile of estrogen receptor variants/isoforms in Taiwanese women with breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2006;32(5):492–497.
Moon WS, Chang K, Tarnawski AS. Overexpression of metastatic tumor antigen 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship to vascular invasion and estrogen receptor-alpha. Hum Pathol. 2004;35(4):424–429.
Moon HE, Cheon H, Lee MS. Metastasis-associated protein 1 inhibits p53-induced apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2007;18(5):1311–1314.
Couse JF, Korach KS. Contrasting phenotypes in reproductive tissues of female estrogen receptor null mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;948:1–8.
Li DQ, Ohshiro K, Khan MN, Kumar R. Requirement of MTA1 in ATR-mediated DNA damage checkpoint function. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(25):19802–19812.
Cui Y, Niu A, Pestell R, et al. Metastasis-associated protein 2 is a repressor of estrogen receptor alpha whose overexpression leads to estrogen-independent growth of human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20(9):2020–2035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Bader, M.D., Kilarkaje, N., El-Farra, A. et al. Expression and Subcellular Localization of Metastasis-Associated Protein 1, Its Short Form, and Estrogen Receptors in Rat Placenta. Reprod. Sci. 22, 484–494 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719114549851
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719114549851