Abstract
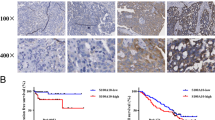
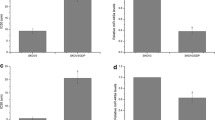
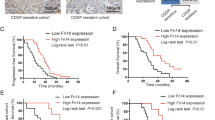
Ether á go-go 1 (Eag1) is frequently highly expressed in various malignant cancers and its excessive expression is correlated with poor prognosis in various cancers. However, the relationship of Eag1 expression with the clinical outcome of patients having ovarian cancer treated with cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy is still unknown. In this study, we measured the expression of Eag1 in ovarian cancer and investigated the association between cisplatin chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer cells and Eag1 expression level. We demonstrate that decreased expression of Eag1 correlates with favorable prognosis in patients treated with cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy and predicts higher cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. In vitro, knockdown of Eag1 by small interfering RNA facilitated the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells (SKOV3 and TYK) to cisplatin-induced apoptosis via nuclear factor κ-light chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway. Furthermore, knockdown of Eag1 expression was associated with decreased expression of the P-glycoprotein without affecting multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 expression. Taken together, Eag1 may serve as a potential indicator to predict Eag1 chemosensitivity, and silencing Eag1 may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for ovarian cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Permuth-Wey J, Sellers TA. Epidemiology of ovarian cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;472:413–437.
Poveda A, Ray-Coquard I, Romero I, Lopez-Guerrero JA, Colombo N. Emerging treatment strategies in recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: focus on trabectedin. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40(3):366–375.
Harter P, Hilpert F, Mahner S, Heitz F, Pfisterer J, du Bois A. Systemic therapy in recurrent ovarian cancer: current treatment options and new drugs. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010; 10(1):81–88.
Cannistra SA, Bast RC Jr, Berek JS, et al. Progress in the management of gynecologic cancer: consensus summary statement. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(10 suppl):129s–132s.
Cho KR, Shih IeM. Ovarian cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4: 287–313.
Colombo N, Van Gorp T, Parma G, et al. Ovarian cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006;60(2):159–179.
Pardo LA, Contreras-Jurado C, Zientkowska M, Alves F, Stühmer W. Role of voltage-gated potassium channels in cancer. J Membr Biol. 2005;205(3):115–124.
Wu J, Wu X, Zhong D, Zhai W, Ding Z, Zhou Y. Short Hairpin RNA (shRNA) Ether a go-go 1 (Eag1) inhibition of human osteosarcoma angiogenesis via VEGF/PI3K/AKT signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(10):12573–12583.
Camacho J. Ether a go-go potassium channels and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2006;233(1):1–9.
Stühmer W, Alves F, Hartung F, Zientkowska M, Pardo LA. Potassium channels as tumour markers. FEBS Lett. 2006; 580(12):2850–2852.
Ortiz CS, Montante-Montes D, Saqui-Salces M, et al. Eag1 potassium channels as markers of cervical dysplasia. Oncol Rep. 2011; 26(6):1377–1383.
Carlson AE, Brelidze TI, Zagotta WN. Flavonoid regulation of EAG1 channels. J Gen Physiol. 2013;141(3):347–358.
Ludwig J, Terlau H, Wunder F, et al. Functional expression of a rat homologue of the voltage gated either a go-go potassium channel reveals differences in selectivity and activation kinetics between the Drosophila channel and its mammalian counterpart. EMBO J. 1994;13(19):4451–4458.
Rodriguez-Rasgado JA, Acuna-Macias I, Camacho J. Eag1 channels as potential cancer biomarkers. Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(5): 5986–5995.
Hemmerlein B, Weseloh RM, Mello de Queiroz F, et al. Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:41.
Meyer R, Schönherr R, Gavrilova-Ruch O, Wohlrab W, Heinemann SH. Identification of ether a go-go and calcium-activated potassium channels in human melanoma cells. J Membr Biol. 1999;171(2):107–115.
Mello de Queiroz F, Suarez-Kurtz G, Stühmer W, Pardo LA. Ether a go-go potassium channel expression in soft tissue sarcoma patients. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:42.
Asher V, Khan R, Warren A, et al. The Eag potassium channel as a new prognostic marker in ovarian cancer. Diagn Pathol. 2010;5:78.
Wu J, Zhong D, Fu X, Liu Q, Kang L, Ding Z. Silencing of Ether a go-go 1 by shRNA inhibits osteosarcoma growth and cell cycle progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5570–5581.
Marks DC, Belov L, Davey MW, Davey RA, Kidman AD. The MTT cell viability assay for cytotoxicity testing in multidrug-resistant human leukemic cells. Leuk Res, 1992; 16(12):1165–1173.
García-Becerra R, Díaz L, Camacho J, et al. Calcitriol inhibits Ether-a go-go potassium channel expression and cell proliferation in human breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(3): 433–442.
Segovia J, Sabbah A, Mgbemena V, et al. TLR2/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway, reactive oxygen species, potassium efflux activates NLRP3/ASC inflammasome during respiratory syncytial virus infection. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29695.
Yang G, Xiao X, Rosen DG, et al. The biphasic role of NF-kappaB in progression and chemoresistance of ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2181–2194.
Li F, Sethi G. Targeting transcription factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1805(2):167–180.
Jones PM, George AM. The ABC transporter structure and mechanism: perspectives on recent research. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61(6):682–699.
Farias LM, Ocaña DB, Díaz L, et al. Ether a go-go potassium channels as human cervical cancer markers. Cancer Res. 2004; 64(19):6996–7001.
Patt S, Preussat K, Beetz C, et al. Expression of ether a go-go potassium channels in human gliomas. Neurosci Lett. 2004; 368(3):249–253.
Ousingsawat J, Spitzner M, Puntheeranurak S, et al. Expression of voltage-gated potassium channels in human and mouse colonic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(3):824–831.
Baud V, Karin M. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(1):33–40.
Cusack JC, Liu R, Baldwin AS. NF- kappa B and chemoresistance: potentiation of cancer drugs via inhibition of NF- kappa B. Drug Resist Update.1999;2(4):271–273.
Gedeon C, Behravan J, Koren G, Piquette-Miller M. Transport of glyburide by placental ABC transporters: implications in fetal drug exposure. Placenta. 2006;27(11–12):1096–1102.
Chang G. Multidrug resistance ABC transporters. FEBS Lett. 2003;555(1):102–105.
Falasca M, Linton KJ. Investigational ABC transporter inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012;21(5):657–666.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, C., Lan, Z., Yue-li, L. et al. Knockdown of Eag1 Expression by RNA Interference Increases Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Reprod. Sci. 22, 1618–1626 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115590665
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719115590665