Abstract
Objective
Gorham-Stout syndrome (GSS) is a rare disorder of uncertain etiology and unpredictable prognosis. This study aims to present a comprehensive understanding of this rare entity.
Methods
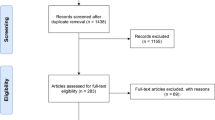
A literature search in PubMed and three Chinese databases was performed to screen histologically proven GSS cases among Chinese residents in the mainland. We analyzed the patients’ clinical characteristics, the value of different treatment modalities and their influence on the clinical outcome.
Results
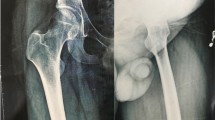
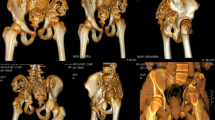
Sixty-seven cases were finally enrolled. There were 43 men (64.2%) and 24 women (35.8%). The mean age at diagnosis was 28 years (1.5–71 years). The most common clinical symptoms included pain (n=40, 59.7%), functional impairment (n=13, 19.4%), and swelling (n=12, 17.9%). The radiographic presentation of 37 cases (55.2%) was disappearance of a portion of the bone. The others presented as radiolucent foci in the intramedullary or subcortical regions. A total of 42 cases provided data on therapy, these included surgery (n=27, 40.3%), radiation therapy (n=6, 9.0%), surgery combined with radiation therapy (n=2, 3.0%), and medicine therapy (n=7, 10.4%). For 30 of these 42 cases, follow-up data were available: 21 cases had the disorder locally controlled and 9 had a symptom progression. Fortunately, the disease is not fatal in the majority of cases.
Conclusions
GSS has no specific symptoms and it should be taken into consideration when an unclear massive osteolysis occurs. The efficacies of different treatment modalities are still unpredictable and further research is required to assess the values of different treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aviv, R., McHugh, K., Hunt, J., 2001. Angiomatosis of bone and soft tissue: a spectrum of disease from diffuse lymphangiomatosis to vanishing bone disease in young patients. Clin. Radiol., 56(3):184–190. [doi:10.1053/crad. 2000.0606]
Barleon, B., Sozzani, S., Zhou, D., Weich, H.A., Mantovani, A., Marme, D., 1996. Migration of human monocytes in response to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is mediated via the VEGF receptor flt-1. Blood, 87(8): 3336–3343.
Boyer, P., Bourgeois, P., Boyer, O., Catonné, Y., Saillant, G., 2005. Massive Gorham-Stout syndrome of the pelvis. Clin. Rheumatol., 24(5):551–555. [doi:10.1007/s10067-005-1088-7]
Browne, J.A., Shives, T.C., Trousdale, R.T., 2011. Thirty-year follow-up of patient with Gorham disease (massive osteolysis) treated with hip arthroplasty. J. Arthropl., 26(2):339.e7–339.e10. [doi:10.1016/j.arth.2010.03.003]
Bruch-Gerharz, D., Gerharz, C.D., Stege, H., Krutmann, J., Pohl, M., Koester, R., Ruzicka, T., 2007. Cutaneous lymphatic malformations in disappearing bone (Gorham-Stout) disease: A novel clue to the pathogenesis of a rare syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 56(2): S21–S25. [doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.01.063]
Choma, N.D., Biscotti, C.V., Bauer, T.W., Mehta, A.C., Licata, A.A., 1987. Benign diseases syndrome: a case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Med., 83(6):1151–1156.
Collins, J., 2006. Case 92: Gorham syndrome1. Radiology, 238(3):1066. [doi:10.1148/radiol.2383032126]
Deveci, M., İnan, N., Çorapçıoğlu, F., Ekingen, G., 2011. Gorham-Stout syndrome with chylothorax in a six-year-old boy. Ind. J. Pediatr., 78(6):737–739. [doi:10.1007/s12098-010-0328-2]
Devlin, R.D., Bone, H.G.3rd, Roodman, G.D., 1996. Interleukin-6: a potential mediator of the massive osteolysis in patients with Gorham-Stout disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabol., 81(5):1893–1897. [doi:10.1210/jc.81.5.1893]
Dunbar, S.F., Rosenberg, A., Mankin, H., Rosenthal, D., Suit, H.D., 1993. Gorham’s massive osteolysis: the role of radiation therapy and a review of the literature. Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 26(3):491–497. [doi:10.1016/0360-3016(93)90968-2]
Dupond, J.L., Bermont, L., Runge, M., de Billy, M., 2010. Plasma VEGF determination in disseminated lymphangiomatosis-Gorham-Stout syndrome: a marker of activity? A case report with a 5-year follow-up. Bone, 46(3): 873–876. [doi:10.1016/j.bone.2009.11.015]
Escande, C., Schouman, T., Fran Oise, G., Haroche, J., Ménard, P., Piette, J.C., Bertrand, J.C., Ruhin-Poncet, B., 2008. Histological features and management of a mandibular Gorham disease: a case report and review of maxillofacial cases in the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol., 106(3):e30–e37. [doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.02.028]
Foult, H., Goupille, P., Aesch, B., Valat, J.P., Burdin, P., Jan, M., 1995. Massive osteolysis of the cervical spine: a case report. Spine, 20(14):1636.
Fujiu, K., Kanno, R., Suzuki, H., Nakamura, N., Gotoh, M., 2002. Chyothorax associated with massive osteolysis (Gorham’s syndrome). Ann. Thoracic Surg., 73(6): 1956–1957. [doi:10.1016/S0003-4975(02)03413-6]
Gorham, L.W., Stout, A.P., 1955. Massive osteolysis (acute spontaneous absorption of bone, phantom bone, disappearing bone). Its relation to hemangiomatosis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am., 37(5):985–1004.
Hagberg, H., Lamberg, K., Astrom, G., 1997. Alpha-2b interferon and oral clodronate for Gorham’s disease. Lancet, 350(9094):1822–1823. [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05) 63639-2]
Hammer, F., Kenn, W., Wesselmann, U., Hofbauer, L.C., Delling, G., Allolio, B., Arlt, W., 2005. Gorham-Stout disease stabilization during bisphosphonate treatment. J. Bone Mineral Res., 20(2):350–353. [doi:10.1359/JBMR. 041113]
Heffez, L., Doku, H.C., Carter, B.L., Feeney, J.E., 1983. Perspectives on massive osteolysis: report of a case and review of the literature. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol., 55(4):331–343.
Heyd, R., Micke, O., Surholt, C., Berger, B., Martini, C., Füller, J., Schimpke, T., Seegenschmiedt, M.H., 2011a. Radiation therapy for Gorham-Stout syndrome: results of a national patterns-of-care study and literature review. Int. J. Rad. Oncol. Biol. Phys., 81(3):e179–185. [doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.01.006]
Heyd, R., Rabeneck, D., Rnenburg, O., Tselis, N., Zamboglou, N., 2011b. Gorham-Stout syndrome of the pelvic girdle treated by radiation therapy. Strahlenther. Onkol., 187(2):140–143. [doi:10.1007/s00066-010-2174-6]
Hirayama, T., Sabokbar, A., Itonaga, I., Watt-Smith, S., Athanasou, N.A., 2001. Cellular and humoral mechanisms of osteoclast formation and bone resorption in Gorham-Stout disease. J. Pathol., 195(5):624–630. [doi:10.1002/path.989]
Jackson, J., 1838. A boneless arm. Boston Med. Surg. J. 18:368–369.
Johnstun, J., Brady, L., Simstein, R., Duker, N., 2010. Chronic recurrent Gorham-Stout syndrome with cutaneous involvement. Rare Tumors, 2(3):e40. [doi:10.4081/rt. 2010.e40]
Kulenkampff, H.A., Richter, G.M., Hasse, W.E., Adler, C.P., 1990. Massive pelvic osteolysis in the Gorham-Stout syndrome. Int. Orthop., 14(4):361–366.
Lehmann, G., Pfeil, A., Böttcher, J., Kaiser, W.A., Füller, J., Hein, G., Wolf, G., 2009. Benefit of a 17-year long-term bisphosphonate therapy in a patient with Gorham-Stout syndrome. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg., 129(7):967–972. [doi:10.1007/s00402-008-0742-3]
Li, X., Liu, B., Xiao, J., Yuan, Y., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., 2011. Roles of VEGF-C and Smad4 in the lymphangiogenesis, lymphatic metastasis, and prognosis in colon cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg., 15(11):1–10. [doi:10.1007/s11605-011-1627-2]
McNeil, K.D., Fong, K., Walker, Q., Jessup, P., Zimmerman, P., 1996. Gorham’s syndrome: a usually fatal cause of pleural effusion treated successfully with radiotherapy. Thorax, 51(12):1275–1276.
Möller, G., Priemel, M., Amling, M., Werner, M., Kuhlmey, A., Delling, G., 1999. The Gorham-Stout syndrome (Gorham’s massive osteolysis). A report of six cases with histopathological findings. J. Bone Joint Surg., 81(3): 501–506.
Ng, C.L., Sell, P., 2003. Gorham disease of the cervical spine—a case report and review of the literature. Spine, 28(18):E355–E358. [doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000084557.38858.85]
Paley, M., Lloyd, C., Penfold, C., 2005. Total mandibular reconstruction for massive osteolysis of the mandible (Gorham-Stout syndrome). Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg., 43(2):166–168. [doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2004.09.008]
Patel, D.V., 2005. Gorham’s disease or massive osteolysis. Clin. Med. Res., 3(2):65–74.
Radhakrishnan, K., Rockson, S.G., 2008. Gorham’s disease: An osseous disease of lymphangiogenesis?. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1131:203–205. [doi:10.1196/annals.1413.022]
Rauh, G., Gross, M., 1997. Disappearing bone disease (Gorham-Stout disease): report of a case with a follow-up of 48 years. Eur. J. Med Res., 2(10):425–427.
Ricalde, P., Ord, R., Sun, C.C.J., 2003. Vanishing bone disease in a five year old: report of a case and review of the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg., 32(2):222–226. [doi:10.1054/ijom.2002.0306]
Spieth, M., Greenspan, A., Forrester, D.M., Ansari, A.N., Kimura, R.L., Gleason-Jordan, I., 1997. Gorham’s disease of the radius: radiographic, scintigraphic, and MRI findings with pathologic correlation. Skel. Radiol., 26(11): 659–663.
Stove, J., Reichelt, A., 1995. Massive osteolysis of the pelvis, femur and sacral bone with a Gorham-Stout syndrome. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg., 114(4):207–210.
Takahashi, A., Ogawa, C., Kanazawa, T., Watanabe, H., Suzuki, M., Suzuki, N., Tsuchida, Y., Morikawa, A., Kuwano, H., 2005. Remission induced by interferon α in a patient with massive osteolysis and extension of lymph-hemangiomatosis: a severe case of Gorham-Stout syndrome. J. Pediatr. Surg., 40(3):E47–E50. [doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2004.11.015]
Tie, M.L., Poland, G.A., Rosenow, E.C.3rd, 1994. Chylothorax in Gorham’s syndrome. A common complication of a rare disease. Chest, 105(1):208–213.
Tong, A.C.K., Leung, T.M., Cheung, P.T., 2010. Management of massive osteolysis of the mandible: a case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol., 109(2):238–241. [doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.08.044]
Vinée, P., Tanyü, M., Hauenstein, K., Sigmund, G., St Ver, B., Adler, C., 1994. CT and MRI of Gorham syndrome. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr., 18(3):985–989.
von Marschall, Z., Scholz, A., Cramer, T., Schäfer, G., Schirner, M., Öberg, K., Wiedenmann, B., Höcker, M., Rosewicz, S., 2003. Effects of interferon α on vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription and tumor angiogenesis. J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 95(6):437–438.
Wang, H.C., Lin, G.T., 2004. Close-wedge osteotomy for bony locking stiffness of the elbow in Gorham disease patients: a case report. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci., 20(5):250–255. [doi:10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70115-9]
Woodward, H.R., Chan, D.P.K., Lee, J., 1981. Massive osteolysis of the cervical spine a case report of bone graft failure. Spine, 6(6):545–549.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, P., Yuan, Xg., Hu, Xy. et al. Gorham-Stout syndrome in mainland China: a case series of 67 patients and review of the literature. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 14, 729–735 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200308
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200308