Abstract
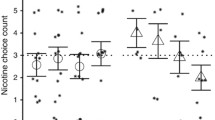
Results of this study indicate that nicotine from cigarette smoking increases circulating levels of cortisol, growth hormone, and prolactin in male chronic smokers. Previous studies have not addressed the question of whether the stimulus for smoking-related hormone release is the ‘stress’ of smoking or a pharmacologic action of nicotine and other tobacco substrates. Nicotine exposure is controlled in this study by allowing each subject to smoke only two 2.0 mg nicotine cigarettes during one experimental session and two 0.2 mg nicotine cigarettes in another session. Plasma levels of cortisol, growth hormone, and prolactin for the higher nicotine session were found to be significantly elevated over those for the low-nicotine session, indicating that nicotine itself plays a predominate role in smoking-induced hormone increases. All hormone levels for the 2.0 mg nicotine session had not returned to baseline 60 min after smoking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann G, Marynick SP, Winters SJ, Loriaux DL, (1977) The effect of osmotic stimuli on prolactin secretion and renal water excretion in normal man and in chronic hyperprolactinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 44:199–202
Blake CA (1974) Stimulation of pituitary prolactin and TSH release in lactating and proestrous rats. Endocrinology 94:503–508
Burn JA (1960) Action of nicotine on the heart. Ann NY Acad Sci 90:70–73
Cryer PE, Haymond MW, Santiago JV, Shah SD (1976) Norepinephrine and epinephrine release and adrenergic medication of smokingassociated hemodynamic and metabolic events New Engl J Med 295 (11):573–577
Dixon WJ, Brown MB (1979) BMPD Biomedical computer programs. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 540–601
Goodman FR (1974) Effects of nicotine on distribution and release of 14C-norepinephrine and 14C-dopamine in rat brain striatum and hypothalamus slices. Neuropharmacol 13:1025–1032
Guillemin P, Bargo T, Rossier J, Minick S, Ling N, Rivier C, Vale W, Bloom F (1977) β-Endorphin and adrenocorticotropin are secreted concomitantly by the pituitary gland. Science 197:1367–1369
Hokfelt B (1961) The effect of smoking on the production of adrenocorticoid hormones. Acta Med Scand Suppl 369:123–124
Kalin NH, Risch SC, Cohen RM, Insel T, Murphy DL (1980) Dexamethasone fails to suppress β-endorphin plasma concentrations in humans and rhesus monkeys. Science 209:827–828
Karras A, Kane JM (1980) Natoxone reduces cigarette smoking. Life Sci 27:1541–1545
Kershbaum A, Pappajohn D, Bellet S (1968) Effect of tobacco smoking on excretion of adrenal corticosteroids. J Amer Med Ass 203:275–278
Kozlowski LT, Jarvik ME, Gritz ER (1975) Nicotine regulation and cigarette smoking. Clin Pharmacol and Ther 17(1):93–97
Kimura S, Lewis R, Gerber L, Brink L, Rubinstein M, Stein S, Udenfriend S (1979) Pufification to homogeneity of camel pituitary preopiocortin, the common precursor of opioid peptides and corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1756–1759
Langone JJ, Gjika H, Van Vunakis H (1973) Nicotine and its metabolite. Radioimmunoassay for nicotine and cotinine. Biochem 12:5025–5030
Mains R, Eipper B, Ling N (1977) Common precursor to corticotropin and endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3014–3018
Orsetti A, Amara F, Collard F, Miraze J (1975) Influence due tabac sur les hormones essentielles de la glycoregulation (The influence of tobacco on hormones essential to glycoregulation). Nouvelle Press Medicale 4 (21):1571–1572
Pelletier G, Leclere R, Labrie F, Cote J, Chretien M, Lis M (1977) Immunohistochemical localization of β-lipotropic hormone in the pituitary gland. Endocrinology 100:770–776
Rossier J, French ED, Rivier C, Ling N, Gullemin R, Bloom FE (1977) Footshock induced stress increases β-endorphin levels in blood but not brain. Nature 270:618–620
Ruder HJ, Guy RL, Lipsett MD (1972) A radioimmunoassay for cortisol in plasma and urine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 35:219–222
Sandberg H, Roman L, Zavodnick J (1973) The effect of smoking on serum somatotropin, immunoreactive insulin and blood glucose levels of young adult males. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 184:787–791
Schalach DS, Parker ML (1964) A sensitive double antibody immunoassay for human growth hormone in plasma. Nature 203:1141–1142
Sinha YN, Selby FW, Lewis UJ, Vander Laan WP (1973) A homologous radioimmunoassaaay for human prolactin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 36:509–516
Soutairac A, Schaub C, Franchimont P, Aymard N, Van Cauwenberge H (1968) Étude de l'activation pharmacologique du pole central de l'axe hypothalamo-hypophysaire. Ann Endocrinol 28:45–54
Stollerman IP, Goldfarb T, Fink R, Jarvik ME (1973) Influencing cigarette smoking with nicotine antagonists. Psychopharmacology 28:247–259
Tucci JR, Sode J (1972) Chronic cigarette smoking: Effect on adrenocortical and sympathoadrenomedullary activity in man. J Amer Med Ass 221:282–288
Weber E, Voigt K, Martin R (1978) Concomitant storage of ACTH and endorphin-like immunoreactivity in the secretory granules of anterior pituitary corticotrophs. Brain Res 157:385–390
Westfall TC, Brase DA (1971) Studies on the mechanism of tolerance to nicotine-induced elevations of urinary catecholamines. Biochem Pharm 20:1627–1635
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 540–601
Winternitz WW, Quillen D (1977) Acute hormonal response to cigarette smoking. J Clin Pharmacol 17:389–397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkins, J.N., Carlson, H.E., Van Vunakis, H. et al. Nicotine from cigarette smoking increases circulating levels of cortisol, growth hormone, and prolactin in male chronic smokers. Psychopharmacology 78, 305–308 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433730
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433730