Abstract
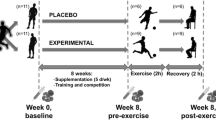
We determined the effects of dietary vitamin C supplementation on erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes and on plasma antioxidants during athletic competition and short-term recovery. Blood samples were taken from 16 volunteer endurance athletes, participating in a duathlon competition, under basal conditions and both immediately and 1 h after the competition. The results were analysed taking into account the individual vitamin C intake and the plasma levels. Athletes were assigned to either the vitamin C-supplemented or control groups (n=8 each). The control group had normal plasma ascorbate levels, the supplemented group high levels as a result of the higher vitamin C intake. Uric acid and lactate dehydrogenase increased after the competition only in the control group. Plasma ascorbate decreased after short-term recovery in the supplemented group. Erythrocyte catalase activity increased after the competition in the supplemented group. Glutathione peroxidase activity (determined with cumene hydroperoxide as substrate) increased only in the control group after short-term recovery. This pattern may suggest an important role for plasma ascorbate, and dietary vitamin C supplementation, in the defence against oxidative stress induced by exercise and in avoiding negative effects on erythrocyte integrity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi HE (1984) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods in enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Basel, pp 273–286
Aguiló A, Tauler P, Guix MP, Villa G, Córdova A, Tur JA, Pons A (2003) Effect of exercise intensity and training on antioxidants and cholesterol profile in cyclists. J Nutr Biochem (In press)
Alessio H (1993) Exercise-induced oxidative stress. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:218–224
Baker JK, Kapeghian J, Verlangieri A (1983) Determination of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid in blood plasma samples. J Liquid Chromatogr 6:1319–1332
Bendich A (1989) Interaction between antioxidant vitamins C and E and their effect on immune responses. In: Miquel J, Quintanilla AT, Weber H (eds) Handbook of free radicals and antioxidants in biomedicine II. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 153–160
Clarkson PM, Thompson HS (2000) Antioxidants: what role do they play in physical activity and health?. Am J Clin Nutr 72:637S–646S
Clemens MR, Waller HD (1987) Lipid peroxidation in erythrocytes. Chem Phys Lipids 45:251–268
Committee on Enzymes, The Scandinavian Society for Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Physiology (1974) Recommended methods for the determination of four enzymes in blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 33:291–306
Davies K, Quintanilha A, Brooks A, Packer L (1982) Free radicals and tissue damage produced by exercise. Biochem Soc Trans 21:346–353
Dhariwal KR, Washko PW Levine M (1990) Determination of dehydroascorbic acid using high performance liquid chomatography with coulometric electrochemical detection. Anal Biochem 189:18–23
Feinberg M, Favie C, Ireland-Ripert J (1991) Répertoire géneral des aliments. Tec et Doc Lavoisier, Paris
Flohé L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays for glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Fossati P, Prencipe L, Berti G (1980) Use of 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid/4-aminophenazone chromogenic system in direct enzymic assay of uric acid in serum and urine. Clin Chem 26:227–231
Garcia-de-la-Asunción J, Millan A, Pla R, Bruseghini L, Esteras A, Pallardo FV, Sastre J, Viña J (1996) Mitochondrial glutathione oxidation correlates with age-associated oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA. FASEB J 10:333–338
Hellsten Y (2000) The role of xanthine oxidase in exercise. In Sen CK, Parker L, Hänninen O (eds) Handbook of oxidants and antioxidants in exercise. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 153–176
Jones DP, Eklow L, Thor H, Orrenius S (1981) Metabolism of hydrogen peroxide in isolated hepatocytes: relative contributions of catalase and glutathione peroxidase in decomposition of endogenously generated H2O2. Arch Biochem Biophys 210:505–516
Kanter M (1994) Free radicals, exercise and antioxidant supplementation. Int J Sport Nutr 4:205–220
Kanter MM, Lesmes GR, Kaminsky LA, Laham-Saeger J, Nequin ND (1988) Serum creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase changes following an eighty kilometres race. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:60–63
Mataix J, Mañas M, Llopis J, Martínez de Victoria E, Juan J, Borregón A (1998) Tablas de composición de alimentos españoles. INTA, Universidad de Granada, Granada
Maxwell SR, Jakeman P, Thomason H, Leguen C, Thorpe GH (1993) Changes in plasma antioxidant status during eccentric exercise and the effect of vitamin supplementation. Free Radic Res Commun 19:191–202
McCord J, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase an enzymic for erythrocuprein (haemocuprein). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Mena P, Maynar M, Gutierrez JM, Maynar J, Timon J, Campillo JE (1991) Erythrocyte free radical scavenger enzymes in bicycle professional racers. Adaptation to training. Int J Sports Med 12:563–566
Moreiras O, Carbajal A, Cabrera L, Cuadrado C (1999) Tablas de composición de alimentos. Pirámide, Madrid
Niess AM, Dickhuth HH, Northoff H, Fehrenbach E (1999) Free radicals and oxidative stress in exercise-immunological aspects. Exerc Immunol Rev 5:22–56
Novros JS, Koch TR, Knoblock EC (1979) Improved method for accurate quantitation of total and conjugated bilirubin in serum. Clin Chem 25:1891–1899
Parera M, Guix P, Pérez G, Quetglas P, Fuentespina E, Llompart I (1996) Estudio del error aleatorio en distintos parámetros de rutina bioquímica en el autoanalizador DAX-78. Quim Clin 15:232–239
Pearlman FC, Lee RT (1974) Detection and measurement of total bilirubin in serum, with use of surfactants as solubilizing agents. Clin Chem 20:447–53
Radak Z, Asano K, Inoue M, Kizaki T, Oh-Ishi S, Suzuki K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H (1996) Superoxide dismutase derivative prevents oxidative damage in liver and kidney of rats induced by exhausting exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 72:189–194
Rifkind M, Stäubli M, Straub PW (1983) Impaired red cell filterability with elimination of old red blood cell during a 100Km race. J Appl Physiol 54:827–830
Ripoll L (1992) Cocina de las Baleares. Ripoll, Palma de Mallorca
Rivers JM (1987) Safety of high-level vitamin C ingestion. Ann N Y Acad Sci 498:445–454
Robertson JD, Maughan RJ, Duthie GG, Morrice PC (1991) Increased blood antioxidant systems of runners in response to training load. Clin Sci 80:611–618
Stagsted J, Young JF (2002) Large differences in erythrocyte stability between species reflect different antioxidative defense mechanisms. Free Radic Res 36:779–789
Tauler P, Aguiló A, Gimeno I, Guix MP, Pons A (1999) Regulation of erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in athletes during competition and short-term recovery. Pflugers Arch 438:782–787
Tauler P, Aguiló A, Fuentespina E, Tur JA, Pons A (2001) Diet supplementation with vitamin E, vitamin C and β-carotene cocktail enhances basal neutrophil antioxidant enzymes in athletes. Pflugers Arch 443:791–797
Tsao CS, Salimi, SL (1982) Differential determination of L-ascorbic acid andd-isoascorbic acid by reversed-phase high performance liquid chomatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr 245:355–358
Viña J, Servera E, Asensi J, Pallardo FV, Ferrero JA, Garcia-de-la-Asunción J, Anton V, Marin J (1996) Exercise causes blood glutathione oxidation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: prevention by O2 therapy. J Appl Physiol 81:2198–2202
Viña J, Gimeno A, Sastre J, Desco C, Asensi M, Pallardó FV, Cuesta A, Ferrero JA, Terada LS, Repine JE (2000) Mechanisms of free radical production in exhaustive exercise in humans and rats; role of xanthine oxidase and protection by allopurinol. Life Sci 49:539–544
Vuilleumier JP, Keller HE, Fidanza F (1986) Vitamin nutriture methodology. Vitamin E (α-tocoferol). In Fidanza F (ed) Nutritional status assessment. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 209–213
Zamocky M, Koller F (1999) Understanding the structure and function of catalases: clues from molecular evolution and in vitro mutagenesis. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72:19–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tauler, P., Aguiló, A., Gimeno, I. et al. Influence of vitamin C diet supplementation on endogenous antioxidant defences during exhaustive exercise. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 446, 658–664 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1112-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1112-1