Abstract
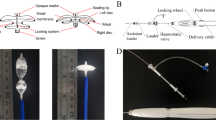
The purpose of this report was to develop novel biodegradable occlusion devices for closure of atrial septal defects (ASD). To manufacture the biodegradable occluders, polycaprolactone (PCL) components were first fabricated by a lab-scale micro-injection molding machine. They were then assembled and hot-spot welded into double umbrella-like devices of 50 mm in diameter. A special mechanism at the axis of the occluder was designed to self-lock the occluder after the two umbrellas were expanded. Furthermore, a nanofibrous matrix of poly-d-l-lactide-glycolide (PLGA)/type I collagen blend was produced via electrospinning to develop biodegradable and biomimetic anti-shunt membranes for the occluders. Characterization of the biodegradable PCL occluders was carried out. PCL occluders exhibited mechanical properties comparable to that of commercially available Amplatzer occluders. The sealing capability of biodegradable occluders was found superior to that of Amplatzer occluders. In addition, the cell attachment and spreading of endothelial cells seeded on the PLGA/collagen nanofibrous matrix and the interaction between cells and PLGA/collagen nanofibers were studied. The nanofibrous membranes made of PLGA/collagen were very effective in promoting cell proliferation during culture.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, Z., Z. M. Hijazi, J. L. Bass, J. P. Cheatham, W. E. Hellenbrand, and C. S. Kleinman. Erosion of Amplatzer septal occluder device3 after closure of secundum atrial septal defects: review of registry of complications and recommendations to minimize future risk. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 63:496–502, 2004.
Bridges, N. D., W. Hellenbrand, L. Latson, J. Filiano, J. W. Newburger, and J. E. Lock. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale after presumed paradoxical embolism. Circulation 86:1902–1908, 1992.
Buecker, A., E. Spuentrup, R. Grabitz, F. Freudenthal, E. G. Muehler, T. Schaeffer, J. J. van Vaals, and R. W. Guenther. Magnetic resonance-guided placement of atrial septal closure device in animal model of patent foramen ovale. Circulation 106:511–515, 2002.
Djer, M. M., H. A. Latiff, M. Alwi, H. Samion, and G. Kandavello. Transcatheter closure of muscular ventricular septal defect using the Amplatzer devices. Heart Lung Circul. 15:12–17, 2006.
Fraisse, A., P. Chetaille, Z. Amin, F. Rouault, and M. Humbert. Use of Amplatzer fenestrated atrial septal defect device in a child with familial pulmonary hypertension. Pediatr. Cardiol. 27:759–762, 2006.
Han, Y.-M., X. Gu, J. L. Titus, C. Rickers, J. L. Bass, M. Urness, and K. Amplatz. New self-expanding patent foramen ovale occlusion device. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 47:370–376, 1999.
Kamal, M., A. I. Isayev, and S. J. Liu. Injection Molding: Technology and Fundamentals. Munich: Hanser, 2009.
Kiblawi, F. M., R. J. Sommer, and S. G. Levchuck. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale in older adults. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 68:136–142, 2006.
Kuhn, M. A., L. A. Latson, J. P. Cheatham, B. McManus, J. M. Anderson, K. L. Kilzer, and J. Furst. Biological response to Bard Clamshell Septal Occluders in the canine heart. Circulation 93:1459–1463, 1996.
Lee, E. M., D. H. Robers, and K. P. Walsh. Transcatheter closure of a residual postmyocardial infarction ventricular septal defect with the Amplatzer septal occluder. Heart 80:522–524, 1998.
Liu, S. J., F. J. Chiang, C. Y. Hsiao, Y. C. Kau, and K. S. Liu. Fabrication of balloon-expandable self-lock drug-eluting polycaprolactone stents using micro-injection molding and spray coating techniques. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:3185–3194, 2010.
Liu, S. J., Y. C. Kau, C. Y. Chou, J. K. Chen, R. C. Wu, and W. L. Yeh. Electrospun PLGA/collagen nanofibrous membrane as early-stage wound dressing. J. Membrane. Sci. 355:53–59, 2010.
Malm, T., S. Bowald, S. Karacagil, A. Bylock, and C. Busch. A new biodegradable patch for closure of atrial septal defect: an experimental study. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 26:9–14, 1992.
Meier, J. M., A. Berger, A. Delabays, G. Girod, D. Gras, X. Lyon, C. Rohuelov, P. Bogt, J. C. Stauffer, and E. Eeckhout. Percuraneous closure of patent foramen ovale: head-to-head comparison of two different devices. EuroIntervention 1:22–26, 2005.
Mellen, M. J., D. Hildick-Smith, J. V. De Giovanni, C. Duke, W. S. Hills, W. L. Morrison, and C. Jux. BioSTAR Evaluation Study (BEST): a prospective multicenter, phase I clinical trial to evaluate the feasibility, efficacy, and safety of the BioSTAR bioabsorbable septal repair implant for the closure of atrial-level shunts. Circulation 114:1962–1967, 2006.
Predescu, D., R. R. Chaturvedi, M. K. Friedberg, L. N. Benson, A. Ozawa, and K. J. Lee. Complete heart block associated with device closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 136:1223–1228, 2008.
Sharafuddin, M. J. A., X. Gu, J. L. Titus, M. Urness, J. J. Cervera-Ceballos, and L. Amplatz. Transversoun closure of secundum atrial septal defects. Preliminary results with a new self-expanding nitonol prosthesis in a swine model. Circulation 95:2162–2168, 1997.
Sherman, J. M., D. J. Hagler, and F. Cetta. Thrombosis after septal closure device placement: a review of the current literature. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 63:486–489, 2004.
Wertman, B., B. Azarbal, M. Riedl, and J. Tobis. Adverse events associated with nickel allergy in patients undergoing percutaneous atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale closure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 47:1226–1227, 2006.
Wilson, N. J., J. Smith, B. Prommete, C. O’Donnell, T. L. Gentles, and P. N. Ruygrok. Transcatheter closure of secumdum atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder in adults and children-follow-up closure rates, degree of mitral regurgitation and evolution of arrhythmias. Heart Lung Circul. 17:318–324, 2008.
Woodruff, M. A., and D. W. Hutmacher. The return of a forgotten polymer—polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35:1217–1256, 2010.
Yang, S., K.-F. Leong, Z. Du, and C.-K. Chua. The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part I. Traditional factors. Tissue Eng. 7:679–689, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer West oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SJ., Peng, KM., Hsiao, CY. et al. Novel Biodegradable Polycaprolactone Occlusion Device Combining Nanofibrous PLGA/Collagen Membrane for Closure of Atrial Septal Defect (ASD). Ann Biomed Eng 39, 2759–2766 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0368-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0368-4