Abstract
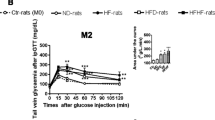
A diet high in fructose (HFr) induces insulin resistance in animals. Free radicals are involved in the pathogenesis of HFr-induced insulin resistance. Carnosine (CAR) is a dipeptide with antioxidant properties. We investigated the effect of CAR alone or in combination with α-tocopherol (CAR + TOC) on HFr-induced insulin-resistant rats. Rats fed with HFr containing 60 % fructose received CAR (2 g/L in drinking water) with/without TOC (200 mg/kg, i.m. twice a week) for 8 weeks. Insulin resistance, serum lipids, inflammation markers, hepatic lipids, lipid peroxides, and glutathione (GSH) levels together with glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase 1 (CuZnSOD; SOD1) activities and their protein expressions were measured. Hepatic histopathological examinations were performed. HFr was observed to cause insulin resistance, inflammation and hypertriglyceridemia, and increased triglyceride and lipid peroxide levels in the liver. GSH-Px activity and expression decreased, but GSH levels and SOD1 activity and expression did not alter in HFr rats. Hepatic marker enzyme activities in serum increased and marked macro- and microvesicular steatosis were seen in the liver. CAR treatment did not alter insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia, but it decreased steatosis and lipid peroxidation without any change in the antioxidant system of the liver. However, CAR + TOC treatment decreased insulin resistance, inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and lipid peroxidation and increased GSH-Px activity and expression in the liver. Our results may indicate that CAR + TOC treatment is more effective to decrease HFr-induced insulin resistance, inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and dysfunction and pro-oxidant status in rats than CAR alone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldini G, Facino RF, Beretta G, Carini M (2005) Carnosine and related dipeptides as quenchers of reactive carbonyl species: from structural studies to therapeutic perspectives. Biofactors 24:77–87
Artun BC, Küskü-Kiraz Z, Güllüoğlu M, Çevikbaş U, Koçak-Toker N, Uysal M (2010) The effect of carnosine pretreatment on oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in binge ethanol administered rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 329:659–665
Aydın AF, Küçükgergin C, Özdemirler-Erata G, Koçak-Toker N, Uysal M (2010) The effect of carnosine treatment on prooxidant–antioxidant balance in liver, heart and brain tissues of male aged rats. Biogerontology 11:103–109
Aydın AF, Küskü-Kiraz Z, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Güllüoğlu M, Uysal M, Koçak-Toker N (2010) Effect of carnosine against thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis in rat. Peptides 31:67–71
Aydın AF, Küskü-Kiraz Z, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Uysal M (2010) Effect of carnosine treatment on oxidative stress in serum, apo-B containing lipoproteins fraction and erythrocytes of aged rats. Pharmacol Rep 62:733–739
Baan M, Sherding RG, Johnson SE (2011) Effects of zinc-l-carnosine and vitamin E on aspirin-induced gastroduodenal injury in dogs. J Vet Intern Med 25:39–46
Bagul PK, Middela H, Matapally S, Padiya R, Bastia T, Madhusudana K, Reddy BR, Chakravarty S, Banerjee SK (2012) Attenuation of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and hepatic oxidative stress by resveratrol in fructose-fed rats. Pharmacol Res 66:260–268
Baykara B, Tekmen I, Pekcetin C, Ulukus C, Tuncel P, Sagol O, Ormen M, Ozogul C (2009) The protective effects of carnosine and melatonin in ischemia–reperfusion injury in the rat liver. Acta Histochem 111:42–51
Bellia F, Vecchio G, Cuzzocrea S, Calabrese V, Rizzarelli E (2011) Neuroprotective features of carnosine in oxidative driven diseases. Mol Aspects Med 32:258–266
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Boldyrev AA (2005) Protection of proteins from oxidative stress. Ann NY Acad Sci 1057:1–13
Buege JA, Aust JD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Castro MC, Massa ML, Schinella G, Gagliardino JJ, Francini F (2013) Lipoic acid prevents liver metabolic changes induced by administration of a fructose-rich diet. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830:2226–2232
Chan WKM, Decker EA, Chow CK, Boissonneault GA (1994) Effect of dietary carnosine on plasma and tissue antioxidant concentrations and on lipid oxidation in rat skeletal muscle. Lipids 29:461–466
Çoban J, Bingül I, Yeşil-Mızrak D-AS, Öztezcan S, Uysal M (2013) Effects of carnosine plus vitamin E and betaine treatments on oxidative stress in some tissues of aged rats. Curr Aging Sci 6:199–205
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Fouad AA, El-Rehany MAA, Maghraby HK (2007) The hepatoprotective effect of carnosine against ischemia/reperfusion liver injury in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 572:61–68
Francini F, Castro MC, Schinella G, García ME, Maiztegui B, Raschia MA, Gagliardino JJ, Massa ML (2010) Changes induced by a fructose-rich diet on hepatic metabolism and the antioxidant system. Life Sci 86:965–971
Girard A, Madani S, Boukortt F, Malki-Cherkaoui M, Belleville J, Prost J (2006) Fructose-enriched diet modifies antioxidant status and lipid metabolism in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nutrition 22:758–766
Grattagliano I, Palmieri VO, Portincasa P, Moschetta A, Palasciano G (2008) Oxidative stress-induced risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome: a unifying hypothesis. J Nutr Biochem 19:491–504
Hipkiss AR (2009) Carnosine and its possible roles in nutrition and health. Adv Food Nutr Res 57:87–154
Jang EM, Choi MS, Jung UJ, Kim MJ, Kim HJ, Jeon SM, Shin SK, Seong CN, Lee MK (2008) Beneficial effects of curcumin on hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed hamsters. Metab Clin Exp 57:1576–1583
Kalaz EB, Çoban J, Aydın AF, Doğan-Ekici I, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Öztezcan S, Uysal M (2013) Carnosine and taurine treatments decreased oxidative stress and tissue damage induced by d-galactose in rat liver. J Physiol Biochem. doi:10.1007/s13105-013-0275-2
Kannappan S, Palanisamy N, Anuradha CV (2010) Suppression of hepatic oxidative events and regulation of eNOS expression in the liver by naringenin in fructose-administered rats. Eur J Pharmacol 645:177–184
Kim MY, Kim EJ, Kim YN, Choi C, Lee BH (2011) Effects of α-lipoic acid and l-carnosine supplementation on antioxidant activities and lipid profiles in rats. Nutr Res Pract 5:421–428
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:1313–1321
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958
Lee Y, Hsu C, Lin M, Yin M (2005) Histidine and carnosine delay diabetic deterioration in mice and protect human low density lipoprotein against oxidation and glycation. Eur J Pharmacol 513:145–150
Lim JS, Mietus-Synder M, Valente A, Schwartz J-M, Lustig RH (2010) The role of fructose in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:251–264
Liu W, Liu T, Yin M (2008) Beneficial effects of histidine and carnosine on ethanol-induced chronic liver injury. Food Chem Toxicol 46:1503–1509
Maynard LM, Boissonneault GA, Chow CK, Bruckner GG (2001) High levels of dietary carnosine are associated with increased concentrations of carnosine and histidine in rat soleus muscle. J Nutr 131:287–290
Mehmetçik G, Özdemirler G, Koçak-Toker N, Çevikbaş U, Uysal M (2008) Role of carnosine in preventing in thioacetamide-induced liver injury in the rat. Peptides 29:425–429
Miller A, Adeli K (2008) Dietary fructose and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:204–209
Mong MC, Chao CY, Yin MC (2011) Histidine and carnosine alleviated hepatic steatosis in mice consumed high saturated fat diet. Eur J Pharmacol 653:82–88
Mylorie AA, Collins H, Umbles C, Kyle J (1986) Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase activity and other parameters of copper status in rats ingesting lead acetate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 82:512–520
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxidation in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ohnogi H, Hayami S, Kudo Y, Deguchi S, Mizutani S, Enoki T, Tanimura Y, Aoi W, Naito Y, Kato I, Yoshikawa T (2012) Angelica keiskei extract improves insulin resistance and hypertriglyceridemia in rats fed a high fructose drink. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:928–932
Oner-İyidoğan Y, Koçak H, Seyidhanoğlu M, Gürdöl F, Gülçubuk A, Yildirim F, Cevik A, Uysal M (2013) Curcumin prevents liver fat accumulation and serum fetuin-A increase in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Physiol Biochem 69:677–686
Panchal SK, Poudyal H, Brown L (2012) Quercetin ameliorates cardiovascular, hepatic and metabolic changes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J Nutr 142:1026–1032
Pfister F, Riedl E, Wang Q, vom Hagen F, Deinzer M, Harmsen MC, Molema G, Yard B, Feng Y, Hammes HP (2011) Oral carnosine supplementation prevents vascular damage in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:125–136
Rashid I, Van Reyk DM, Davies MJ (2007) Carnosine and its constituents inhibit glycation of low-density lipoproteins that promotes foam cell formation in vitro. FEBS Lett 581:1067–1070
Riedl E, Pfister F, Braunagel M, Brinkkötter P, Sternik P, Deinzer M, Bakker SJ, Henning RH, van den Born J, Krämer BK, Navis G, Hammes HP, Yard B, Koeppel H (2011) Carnosine prevents apoptosis of glomerular cells and podocyte loss in STZ diabetic rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:279–288
Roberts CK, Sindhu KK (2009) Oxidative stress and metabolic syndrome. Life Sci 84:705–712
Salih SM, Nallasamy P, Muniyandi P, Periyasami V, Venkatraman AC (2009) Genistein improves liver function and attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a rat model of insulin resistance. J Diabetes 11:278–287
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Stvolinsky SL, Bulygina ER, Fedorova TN, Meguro K, Sato T, Tyulina OV, Abe H, Boldyrev AA (2010) Biological activity of novel synthetic derivatives of carnosine. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:395–404
Tappy L, Lê KA, Tran C, Paquot N (2010) Fructose and metabolic diseases: new findings, new questions. Nutrition 26:1044–1049
Yan SL, Wu ST, Yin MC, Chen HT, Chen HC (2009) Protective effects from carnosine and histidine on acetaminophen-induced liver injury. J Food Sci 74:H259–265
Yokozawa T, Kim HJ, Cho EJ (2008) Gravinol ameliorates high-fructose-induced metabolic syndrome through regulation of lipid metabolism and proinflammatory state in rats. J Agric Food Chem 56:5026–5032
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University (project no. 6727).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giriş, M., Doğru-Abbasoğlu, S., Kumral, A. et al. Effect of carnosine alone or combined with α-tocopherol on hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress in fructose-induced insulin-resistant rats. J Physiol Biochem 70, 385–395 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0314-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0314-7