Abstract
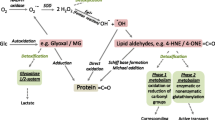
Oxidative stress, defined as an increase in reactive oxygen species, leads to peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and generates a vast number of biologically active molecules, many of which might contribute in some way to health and disease. This chapter will focus on one specific class of peroxidation products, the levuglandins and isoketals (also called isolevuglandins). These γ-ketoaldehydes are some of the most reactive products derived from the peroxidation of lipids and exert their biological effects by rapidly adducting to primary amines such as the lysyl residues of proteins. The mechanism of their formation and remarkable reactivity will be described, along with evidence for their increased formation in disease conditions linked with oxidative stress and inflammation. Finally, the currently known effects of these γ-ketoaldehydes on cellular function will then be discussed and when appropriate compared to the effects of α,β-unsaturated fatty aldehydes, in order to illustrate the significant differences between these two classes of peroxidation products that modify proteins.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarnath, V., Valentine, W.M., Amarnath, K., Eng, M.A., and Graham, D.G. The mechanism of nucleophilic substitution of alkylpyrroles in the presence of oxygen. Chem Res Toxicol 7 (1994) 56–61.
Amarnath, V., Amarnath, K., Amarnath, K., Davies, S., and Roberts, L.J., Pyridoxamine: an extremely potent scavenger of 1,4-dicarbonyls. Chem Res Toxicol 17 (2004) 410–415.
Bernoud-Hubac, N., Davies, S.S., Boutaud, O., Montine, T.J., and Roberts, L.J., Formation of highly reactive gamma-ketoaldehydes (neuroketals) as products of the neuroprostane pathway. J Biol Chem 276 (2001) 30964–30970.
Bernoud-Hubac, N., Fay, L.B., Armarnath, V., Guichardant, M., Bacot, S., Davies, S.S., Roberts, L.J., 2nd, and Lagarde, M. Covalent binding of isoketals to ethanolamine phospholipids. Free Radic Biol Med 37 (2004) 1604–1611.
Boutaud, O., Montine, T.J., Chang, L., Klein, W.L., and Oates, J.A. PGH2-derived levuglandin adducts increase the neurotoxicity of amyloid beta1-42. J Neurochem 96 (2006) 917–923.
Boutaud, O., Li, J., Zagol, I., Shipp, E.A., Davies, S.S., Roberts, L.J., 2nd, and Oates, J.A. Levuglandinyl adducts of proteins are formed via a prostaglandin H2 synthase-dependent pathway after platelet activation. J Biol Chem 278 (2003) 16926–16928.
Boutaud, O., Brame, C.J., Chaurand, P., Li, J., Rowlinson, S.W., Crews, B.C., Ji, C., Marnett, L.J., Caprioli, R.M., Roberts, L.J., 2nd, and Oates, J.A. Characterization of the lysyl adducts of prostaglandin H-synthases that are derived from oxygenation of arachidonic acid. Biochemistry 40 (2001) 6948–6955.
Brame, C.J., Salomon, R.G., Morrow, J.D., and Roberts, L.J. Identification of extremely reactive gamma-ketoaldehydes (isolevuglandins) as products of the isoprostane pathway and characterization of their lysyl protein adducts. J Biol Chem 274 (1999) 13139–13146.
Brame, C.J., Boutaud, O., Davies, S.S., Yang, T., Oates, J.A., Roden, D., and Roberts, L.J. Modification of proteins by isoketal-containing oxidized phospholipids. J Biol Chem 279 (2004) 13447–13451.
Cecarini, V., Ding, Q., and Keller, J.N. Oxidative inactivation of the proteasome in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Res 41 (2007) 673–680.
Davies, S.S., Amarnath, V., Brame, C.J., Boutaud, O., and Roberts, L.J. Measurement of chronic oxidative and inflammatory stress by quantification of isoketal/levuglandin gamma-ketoaldehyde protein adducts using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc 2 (2007) 2079–2091.
Davies, S.S., Amarnath, V., Montine, K.S., Bernoud-Hubac, N., Boutaud, O., Montine, T.J., and Roberts, L.J., Effects of reactive gamma-ketoaldehydes formed by the isoprostane pathway (isoketals) and cyclooxygenase pathway (levuglandins) on proteasome function. Faseb J 16 (2002) 715–717.
Davies, S.S., Talati, M., Wang, X., Mernaugh, R.L., Amarnath, V., Fessel, J., Meyrick, B.O., Sheller, J., and Roberts, L.J., Localization of isoketal adducts in vivo using a single-chain antibody. Free Radic Biol Med 36 (2004) 1163–1174.
Davies, S.S., Brantley, E.J., Voziyan, P.A., Amarnath, V., Zagol-Ikapitte, I., Boutaud, O., Hudson, B.G., Oates, J.A., and Ii, L.J. Pyridoxamine Analogues Scavenge Lipid-Derived gamma-Ketoaldehydes and Protect against H(2)O(2)-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Biochemistry 45 (2006) 15756–15767.
DiFranco, E., Subbanagounder, G., Kim, S., Murthi, K., Taneda, S., Monnier, V.M., and Salomon, R.G. Formation and stability of pyrrole adducts in the reaction of levuglandin E2 with proteins. Chem Res Toxicol 8 (1995) 61–67.
Fukuda, K., Davies, S.S., Nakajima, T., Ong, B.H., Kupershmidt, S., Fessel, J., Amarnath, V., Anderson, M.E., Boyden, P.A., Viswanathan, P.C., Roberts, L.J., 2nd, and Balser, J.R. Oxidative mediated lipid peroxidation recapitulates proarrhythmic effects on cardiac sodium channels. Circ Res 97 (2005) 1262–1269.
Govindarajan, B., Laird, J., Salomon, R.G., and Bhattacharya, S.K. 2008. Isolevuglandin-Modified Proteins, Including Elevated Levels of Inactive Calpain-1, Accumulate in Glaucomatous Trabecular Meshwork. Biochemistry in press.
Hoppe, G., Subbanagounder, G., O'Neil, J., Salomon, R.G., and Hoff, H.F. Macrophage recognition of LDL modified by levuglandin E2, an oxidation product of arachidonic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1344 (1997) 1–5.
Iyer, R.S., Ghosh, S., and Salomon, R.G. 1989. Levuglandin E2 crosslinks proteins. Prostaglandins 37 (1989) 471–480.
Metz, T.O., Alderson, N.L., Chachich, M.E., Thorpe, S.R., and Baynes, J.W. Pyridoxamine traps intermediates in lipid peroxidation reactions in vivo: evidence on the role of lipids in chemical modification of protein and development of diabetic complications. J Biol Chem 278 (2003) 42012–42019.
Morrow, J.D., Harris, T.M., and Roberts, L.J., Noncyclooxygenase oxidative formation of a series of novel prostaglandins: analytical ramifications for measurement of eicosanoids. Anal Biochem 184 (1990) 1–10.
Murthi, K.K., Salomon, R.G., and Sternlicht, H. Levuglandin E2 inhibits mitosis and microtubule assembly. Prostaglandins 39 (1990) 611–622.
Murthi, K.K., Friedman, L.R., Oleinick, N.L., and Salomon, R.G. Formation of DNA-protein cross-links in mammalian cells by levuglandin E2. Biochemistry 32 (1993) 4090–4097.
Poliakov, E., Meer, S.G., Roy, S.C., Mesaros, C., and Salomon, R.G. Iso[7]LGD2-protein adducts are abundant in vivo and free radical-induced oxidation of an arachidonyl phospholipid generates this D series isolevuglandin in vitro. Chem Res Toxicol 17 (2004) 613–622.
Poliakov, E., Brennan, M.L., Macpherson, J., Zhang, R., Sha, W., Narine, L., Salomon, R.G., and Hazen, S.L. Isolevuglandins, a novel class of isoprostenoid derivatives, function as integrated sensors of oxidant stress and are generated by myeloperoxidase in vivo. Faseb J 17 (2003) 2209–2220.
Salomon, R.G., Miller, D.B., Zagorski, M.G., and Coughlin, D.J. Solvent Induced Fragmentation of Prostaglandin Endoperoxides. New Aldehyde Products from PGH2 and Novel Intramolecular 1,2-Hydride Shift During Endoperoxide Fragmentation in Aqueous Solution. J Am Chem Soc 106 (1984) 6049–6060.
Salomon, R.G., Subbanagounder, G., Singh, U., O'Neil, J., and Hoff, H.F. Oxidation of low-density lipoproteins produces levuglandin-protein adducts. Chem Res Toxicol 10 (1997a) 750–759.
Salomon, R.G., Subbanagounder, G., O'Neil, J., Kaur, K., Smith, M.A., Hoff, H.F., Perry, G., and Monnier, V.M. Levuglandin E2-protein adducts in human plasma and vasculature. Chem Res Toxicol 10 (1997b) 536–545.
Salomon, R.G., Sha, W., Brame, C., Kaur, K., Subbanagounder, G., O'Neil, J., Hoff, H.F., and Roberts, L.J., Protein adducts of iso[4]levuglandin E2, a product of the isoprostane pathway, in oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem 274 (1999) 20271–20280.
Salomon, R.G., Batyreva, E., Kaur, K., Sprecher, D.L., Schreiber, M.J., Crabb, J.W., Penn, M.S., DiCorletoe, A.M., Hazen, S.L., and Podrez, E.A. Isolevuglandin-protein adducts in humans: products of free radical-induced lipid oxidation through the isoprostane pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1485 (2000) 225–235.
Schmidley, J.W., Dadson, J., Iyer, R.S., and Salomon, R.G. Brain tissue injury and blood-brain barrier opening induced by injection of LGE2 or PGE2. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 47 (1992) 105–110.
Talati, M., Meyrick, B., Peebles, R.S., Jr., Davies, S.S., Dworski, R., Mernaugh, R., Mitchell, D., Boothby, M., Roberts, L.J., and Sheller, J.R. Oxidant stress modulates murine allergic airway responses. Free Radic Biol Med 40 (2006) 1210–1219.
Voziyan, P.A., Metz, T.O., Baynes, J.W., and Hudson, B.G. A post-Amadori inhibitor pyridoxamine also inhibits chemical modification of proteins by scavenging carbonyl intermediates of carbohydrate and lipid degradation. J Biol Chem 277 (2002) 3397–3403.
Zagol-Ikapitte, I., Bernoud-Hubac, N., Amarnath, V., Roberts, L.J., 2nd, Boutaud, O., and Oates, J.A. Characterization of bis(levuglandinyl) urea derivatives as products of the reaction between prostaglandin H2 and arginine. Biochemistry 43 (2004) 5503–5510.
Zagol-Ikapitte, I., Masterson, T.S., Amarnath, V., Montine, T.J., Andreasson, K.I., Boutaud, O., and Oates, J.A. Prostaglandin H(2)-derived adducts of proteins correlate with Alzheimer's disease severity. J Neurochem 94 (2005) 4 :1140–1145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Davies, S.S. (2008). Modulation of Protein Function by Isoketals and Levuglandins. In: Quinn, P.J., Wang, X. (eds) Lipids in Health and Disease. Subcellular Biochemistry, vol 49. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8831-5_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8831-5_2
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-8830-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-8831-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)