Abstract
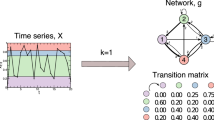
Recently, a map from time series to networks has been proposed [7, 8], allowing the use of network statistics to characterize time series. In this approach, time series quantiles are naturally mapped into nodes of a graph. Networks generated by this method, called Quantile Graphs (QGs), are able to capture and quantify features such as long-range correlations or randomness present in the underlying dynamics of the original signal. Here we apply the QG method to the problem of detecting the differences between electroencephalographic time series (EEG) of healthy and unhealthy subjects. Our main goal is to illustrate how the differences in dynamics are reflected in the topology of the corresponding QGs. Results show that the QG method cannot only differentiate epileptic from normal data, but also distinguish the different abnormal stages/patterns of a seizure, such as pre-ictal (EEG changes preceding a seizure) and ictal (EEG changes during a seizure).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seizures and epilepsy: hope through research (2004). http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/epilepsy/detail_epilepsy.htm
Albert, R., Barabási, A.L.: Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Modern Phys. 74, 47 (2002)
Alotaiby, T.N., Alshebeili, S.A., Alshawi, T., Ahmad, I., El-samie, F.E.A.: EEG seizure detection and prediction algorithms: a survey. EURASIP J. Adv. Sig. Process. 183, 1–21 (2014)
Andrzejak, R.G., Lehnertz, K., Mormann, F., Rieke, C., David, P., Elger, C.E.: Indications of nonlinear dynamics and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64, 061907 (2001)
Andrzejak, R.G., Schindler, K., Rummel, C.: Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E 86, 046206 (2012)
Campanharo, A., Ramos, F.M.: Quantile graphs for the characterization of chaotic dynamics in time series. In: WCCS 2015 – IEEE Third World Conference on Complex Systems. IEEE (2016)
Campanharo, A., Ramos, F.M.: Hurst exponent estimation of self-affine time series using quantile graphs. Physica A 444, 43–48 (2016)
Campanharo, A., Sirer, M.I., Malmgren, R.D., Ramos, F.M., Amaral, L.A.N.: Duality between time series and networks. PLoS ONE 6, e23378 (2011)
Costa, L.F., Rodrigues, F.A., Travieso, G., Villas, P.R.: Characterization of complex networks. Adv. Phys. 56, 167–242 (2007)
Doescher, E., Campanharo, A.S.L.O., Ramos, F.M.: Quantile graphs: exact results and applications (2017, in preparation)
Güler, I., Übeyli, E.D.: Expert systems for time-varying biomedical signals using eigenvector methods. Expert Syst. Appl. 32, 1045–1058 (2007)
Guo, L., Rivero, D., Pazos, A.: Epileptic seizure detection using multiwavelet transform based approximate entropy and artificial neural networks. J. Neurosci. Meth. 193, 156–163 (2010)
Khamis, H., Mohamed, A., Simpson, S.: Frequency-moment signatures: a method for automated seizure detection from scalp EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 124, 2317–2327 (2013)
Liu, Y., Zhou, W., Yuan, Q., Chen, S.: Automatic seizure detection using wavelet transform and svm in long-term intracranial EEG. EEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 20, 749–755 (2012)
Rana, P., Lipor, J., Lee, H., Van Drongelen, W., Kohrman, M.H., Van Veen, B.: Seizure detection using the phase-slope index and multichannel ECoG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 1125–1134 (2012)
Vlachos, I., Kugiumtzis, D.: Nonuniform state-space reconstruction and coupling detection. Phys. Rev. E 82, 016207 (2010)
Acknowledgments
A.S.L.O. Campanharo acknowledges the support of FAPESP: 2013/19905-3. The support of Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (Brazil) is acknowledged by F.M. R. All figures were generated with PyGrace (http://pygrace.github.io/) with color schemes from Colorbrewer (http://colorbrewer.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Campanharo, A.S.L.O., Doescher, E., Ramos, F.M. (2017). Automated EEG Signals Analysis Using Quantile Graphs. In: Rojas, I., Joya, G., Catala, A. (eds) Advances in Computational Intelligence. IWANN 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10306. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59147-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59147-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-59146-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-59147-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)