Abstract
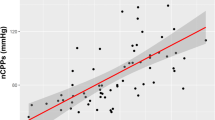
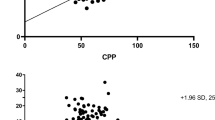
The method of direct calculation of cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) as the difference between mean arterial pressure and intracranial pressure (ICP) produces a number, which not always adequately expresses brain perfusion. We investigated an alternative non-invasive method, based on waveform analysis of Transcranial Doppler blood flow velocity in Middle Cerebral Arteries (MCA). 25 consecutive head injured patients, paralysed, sedated and ventilated were studied. Intracranial pressure (ICP) arterial blood pressure (ABP) were monitored continuously. The left and right MCAs were insonated daily (116 measurements) using a purpose-built transcranial Doppler monitor (Deltex Ltd, Chichester, U.K.) with software capable of the non-invasive estimation of CPP. Time averaged values of ABP, mean and diastolic flow velocities (FVm, FVd) were calculated and CPPe was computed as ABPFVd/FVm + 14.
An absolute difference between real CPP and CPPe was less than 10 mm Hg in 82% of measurements and less than 13 mm Hg in 90% of measurements. The method demonstrated a high potential to detect both short-term and long-term changes in CPP. The method is of potential benefit for the intermittent measurement and continuous monitoring of changes in brain perfusion pressure in situations where the direct measurement of CPP is not available or its reliability is in question.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Czosnyka M, Matta BF, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Pickard JD (1998) Cerebral perfusion pressure in head-injured patients: a noninvasive assessment using transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. J Neurosurg 88 [5]: 802–808
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Schmidt, E.A., Czosnyka, M., Matta, B.F., Gooskens, I., Piechnik, S., Pickard, J.D. (2000). Non-Invasive Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (nCPP): Evaluation of the Monitoring Methodology in Head Injured Patients. In: Mendelow, A.D., et al. Brain Edema XI. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 76. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6346-7_93
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6346-7_93
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7257-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6346-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive