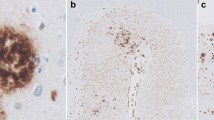
Abstract
In a consecutive autopsy series of 580 demented elderly subject, 256 with the clinical diagnosis of probable/possible Alzheimer's disease (AD), there were 10 cases aged between 80 and 99 years with moderate to severe dementia or confusional state in which neuropathological studies revealed abundant neurofibrillary tangles with predominant involvement of the allocortex (entorhinal region, subiculum, CA 1 sector of hippocampus, amygdala) but no or only very few senile plaques. Small numbers of diffuse deposits of βA4 amyloid protein were present in the entorhinal cortex of 3 and in the isocortex of 5 brains, while neuritic plaques were totally absent. Only a few cases of this “senile dementia with tangles only” or, more correctly, “neurofibrillary predominant type of AD” corresponding to the limbic stage of neuritic AD pathology have been described in the literature. This rare subtype occurring in very old (over 80 years of age) subjects that does not fall within the currently used neuropathological criteria for diagnosis of AD warrants further clinico-pathological documentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte T, Hyman BT (1992) Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 42:631–639
Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal K, Fried VA, Smith HT Wisniewski HM (1991) Abnormal phosphorylation of tau precedes ubiquination of neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 539:11–18
Bancher C, Braak H, Fischer P, Jellinger K (1993) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer lesions and intellectual status in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Neurosci Lett 162:179–182
Berg L, McKee DW, Miller JP, Barty J, Morris JC (1993) Neuropathological indices of Alzeimer's disease in demented and nondemented persons aged 80 years and older. Arch Neurol 50:349–358
Bouras C, Hof PR, Morrison JH (1993) Neurofibrillary tangle densities in the hippocampal formation in a non-demented population define subgroups of patients with differential early pathologic changes. Neurosci Lett 153:131–135
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Braak H, Braak E (1994) Pathology of Alzheimer's disease. In: Calne DB (ed) Neurodegenerative disease. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 585–613
Braak H, Duyckaerts C, Braak E, Piette F (1993) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes correlates with psychometrically assessed intellectual status. In: Corain B et al (eds) Alzheimer's disease. Advances in clinical and basic research, Wiley, Chichester, pp 131–137
Braak H, Braak E, Mandelkow EM (1994) A sequence of cytoskeleton changes related to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and neuropil threads. Acta Neuropathol 87:554–567
Braak H, Braak E, Yilzamer D, DeVos RAI, Jansen ENH, Bohl J, Jellinger K (1994) Amygdala pathology in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol 88:493–500
Chui HC, Tierney M, Zarow C, Lewis A, Sobel E, Perlmutter LS (1993) Neuropathologic diagnosis of Alzheimer disease: interrater reliability in the assessment of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 7:48–54
Crystal HA, Dickson DW, Sliwinski MJ, Lipton RB, Grober E, Marks-Nelson H, Antis P (1993) Pathological markers associated with normal aging and dementia in the elderly. Ann Neurol 34:566–573
Davis PB, White H, Price JL, McKeel D, Robins LN (1991) Retropective postmortem dementia assessment. Validation of a new clinical interview to assist neuropathologic study. Arch Neurol 48:613–617
Delacourte A (1993) The pathophysiological basis of Alzheimer's disease. Therapie 48:177–183
Delaere P, Duyckaerts C, He Y, Piette F, Hauw JJ (1991) Subtypes and differential laminar distributions of βA4 deposits in Alzheimer's disease: relationship with the intellectural status of 26 cases. Acta Neuropathol 81:328–335
Delaere P, He Y, Fayet G, Duyckaerts C, Hauw JJ (1993) β-A4 deposits are constant in the brain of the oldest old. Neurobiol Aging 14:191–194
Dickson DW, Crystall HA, Mattiace LA, Masur DM, Blau AD, Davies P, Yen SH, Aronson MK (1991) Identification of normal and pathological aging in prospectively studied nondemented elderly humans. Neurobiol Aging 13:179–189
Dickson DW, Davies P, Bevona C, Van Hoeven KH, Factor SM, Grober E, Aronson MK, Crystal HA (1994) Hippocampal sclerosis: a common pathological feature of dementia in very old (>= 80 years of age) humans. Acta Neuropathol 88:212–221
Duyckaerts C, Delaere P, Hauw JJ (1990) Rating of the lesions in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type: concordance between laboratories. J Neurol Sci 97:293–323
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-Mental State”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Giannakopoulos P, Hof PR, Surini M, Michell JP, Bouras C (1993) Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in the cerebral cortex of nonagenarian and centenarians. Acta Neuropathol 85:602–610
Goedert M (1993) Tau protein and the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci 16:460–465
Goodman L (1953) Alzheimer's disease. A clinico-pathologic analysis of twenty-three cases with a theory on pathogenesis. J Ment Nerv Dis 117:97–130
Hansen LA, Masliah E, Galasko D, Terry RD (1993) Plaqueonly Alzheimer disease is usually the Lewy body variant and vice versa. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52:648–654
Hauw JJ, Vignole P, Duyckaerts C (1986) Etude neuropathologique de douze centenaires. Rev Neurol (Paris) 142:107–115
Heyner RF, Wong-Riley MTT (1992) Entorhinal cortex of the human, monkey and rat: metabolic map as revealed by cytochrome oxidase. J Comp Neurol 326:451–469
Hof PR, Morrison JH (1994) The cellular basis of cortical disconnection in Alzheimer disease and related dementing conditions. In: Terry RD, Katzmann R, Bick KL (eds) Alzheimer disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 197–229
Honer WG, Dickson DW, Gleeson J, Davies P (1992) Regional synpatic pathology in alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 13:375–382
Hyman BT, Gomeszista T (1994) Alzheimer's disease is a laminar, regional, and neural system specific disease, not a global brain disease. Neurobiol Aging 15:353–355
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Kromer LJ, Damasio AR (1986) Perforant pathway changes and the memory impairment in Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol 20:37–40
Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR (1990) Memoryrelated neuronal systems in Alzheimer's disease: an anatomic study. Neurology 40:1721–1730
Iwatsubo T, Hasegawa M, Ihara Y (1994) Neuronal and glial tau-positive inclusions in diverse neurologic disease share common phosphorylation characteristics. Acta Neuropathol 88:129–136
Jellinger K, Braak H, Braak E, Fischer P (1991) Alzheimer lesions in the entorhinal region and isocortex in Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 640:203–209
Jones RSG (1993) Entorhinal-hippocampal connections: a speculative view of their function. Trends Neurosci 16:58–64
Kazee AM, Eskin TA, Lapham LW, Gabriel RR, McDaniel RD, Hamill RW (1993) Clinicopathologic correlates in Alzheimer's disease — assessment of clinical and pathologic diagnostic criteria. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 7: 152–164
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheinmer's disease. Arch Neurol 42: 1097–1105
Lassmann H, Weiler R, Fischer P, Bancher C, Jellinger K (1992) Synaptic pathology in Alzheimer's disease: immunological data for markers of synaptic and large dense core vesicles. Neuroscience 46: 1–8
Mukaetova-Ladinsky EB, Harrington CR, Roth M, Wischik CM (1993) Biochemical and anatomical redistribution of tau protein in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 143: 565–578
Mc Kee AC, Kosik KS, Kowall NW (1992) Neuritic pathology and dementaia in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 30: 156–165
Mc Keel DW, Ball MJ, Price JL, Smith DS, Miller JP, Berg L, Morris JC (1993) Interlaboratory histopathologic assessment of Alzheimer neuropathology — different methodologies yield comparable diagnostic results. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 7: 136–151
McKhann GD, Drachmann DA, Folstein MF et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Sevices Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Mena R, Wischik CM, Novak M, Milstein C, Cuello AC (1991) A progressive deposition of paired helical filaments (PHF) in the brain characterizes the evolution of dementia in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50: 474–490
Mirra SS, Heyman A McKeel D Sumi SM, Crain BJ, Brownlee LM, Vogel FS, Hughes JP, Van Belle G, Berg L (1991) The Consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer's disease (CERAD). II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 41: 479–486
Mirra SS, Gearing M, McKeel DW, Crain BJ, Hughes JP, Van Belle G, Heyman A, (1994) Interlaboratory comparison of neuropathology assessment in Alzheimer's disease: a study of the consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer's disease (CERAD). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 53: 303–315
Mizutani T, Amano N, Sasaki H (1990) Senile dementia of Alzheimer type characterized by laminar neuronal loss exclusively in the hippocampus, parahippocampus and medial occipital cortex Acta Neuropathol 80: 575–580
Mizutani T, Shimada H (1992) Neuropathological background of twenty-seven centenarian brains. J Neurol Sci 108: 168–177
Morris JC, McKeel DWJr, Storandt M, Rubin EM, Price JL, Grant EA, Ball MJ, Berg L (1991) Very mild Alzheimer's disease: informant-based clinical, psychometric, and pathological distinction from normal aging. Neurology 41: 469–478
Paulus W, Bancher C, Jellinger K, (1992) Interrater reliability in the neuropathologic diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 42: 329–332
Price JL, Davis PB, Morris JC, White DL (1992) The distribution of tangles, plaques and related immnohistochemical markers in healthy aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 12: 295–312
Reusche E (1991) Silver staining of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in paraffine sections. Pathol Res Pract 187: 1045–1049
Roberts GW, Nash M, Ince PG, Roystom MC, Gentleman SM (1993) On the origin of Alzheimer's disease: a hypothesis. Neuroreport 4: 7–9
Scheff SW, Price DA (1993) Synapse loss in the temporal lobe in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 33: 190–199
Schnitzler JG (1911) Zur Abgrenzung der sogenanten Alzheimer'schen Krankheit. Z Ges Neurol Psychiatr 7: 34–37
Scott SA, DeKosky ST, Sparks DL, Knox CA, Scheff SW (1992) Amygdala cell loss and atrophy in Alzheimers disease. Ann Neurol 32: 555–563
Sparks DL, Liu H, Scheff SW et al (1993) Temporal sequence of plaque formation in the cerebral cortex of nondemented individuals. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 52: 135–142
Terry RD, Hansen LA, DeTeresa R, Davies P, Tobias H, Katzman R (1987) Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type without neocortical neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46: 262–268
Terry RD, Masliah E, Hansen LA (1994) Structural basis of the cognitive alteractions in Alzheimer's disease. In: Terry RD, Katzmann R, Bick KL (eds) Alzheimer disease. Raven Press, New York pp 179–196
Tierney MC, Fischer H, Lewis AJ, et al (1988) The NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease: clinicopathological study of 57 cases. Neurology 38: 356–364
Ulrich J, Spillantini MG, Godert M, Dukas L, Stähelin HB (1992) Abundant neurofibrillary tangles without senile plaques in a subset of patients with senile dementia. Neurodegeneration 1: 257–284
Van Hoesen GW, Hyman BT, Damasio AR (1991) Entorhinal cortex pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Hippocampus 1: 1–8
Vereecken THLG, Vogels OJM, Nieuwenhuys R (1994) Neuron loss and shrinkage in the amygdala in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 15: 45–54
Wisniewski K, Jervis GA, Moretz RC, Wisniewski HM (1979) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. Ann Neurol 5: 288–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bancher, C., Jellinger, K.A. Neurofibrillary tangle predominant form of senile dementia of Alzheimer type: a rare subtype in very old subjects. Acta Neuropathol 88, 565–570 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296494
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296494