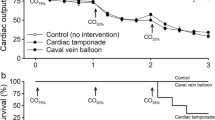
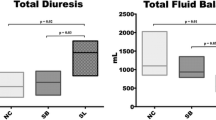
Abstract
Urological laparoscopy has gained increasing acceptance recently. Alterations in renal water and electrolyte homeostasis by carbon dioxide peritoneal insufflation, retroperitoneal insufflation and abdominal wall lifting were measured in 30 well-hydrated pigs over a 2-h period. Oliguria was observed after gaseous insufflation but not after lifting the abdominal wall. Return to normal urinary output was observed at 30 min after release of pneumoretroperitoneum, and 60 min after pneumoperitoneum. Creatinine clearance declined, while the clearance rates of potassium, sodium and urea remained unchanged during peritoneal and retroperitoneal insufflation. An elevated serum aldosterone concentration was found which may mediate the increased urinary excretion of potassium and decreased urinary excretion of sodium found during peritoneal insufflation. Renal function remained stable, despite an elevation of serum creatine kinase being elicited after lifting the abdominal wall. In conclusion, significant changes in water and electrolyte homeostasis occurred during gaseous, not gasless, laparoscopy in pigs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carey RM, Sen S (1986) Recent progress in the control of aldosterone secretion. Recent Prog Horm Res 42:251
Chang DT, Kirsch AJ, Sawczuk IS (1994) Oliguria during laparoscopic surgery. J Endourol 8:349
Chiu AW, Azadzoi KM, Hatzichristou DG, Siroky MB, Krane RJ, Babayan RK (1994) Effect of intra-abdominal pressure on renal tissue perfusion during laparoscopy. J Endourol 8:99
Diebel LN, Wilson RF, Dulchavsky SA, Saxe J (1992) Effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure on hepatic arterial, portal venous, and hepatic microcirculatory blood flow. J Trauma 33: 279
Doyle DJ, Mark PW (1989) Laparoscopy and vagal arrest. Anesthesia 44:448
Gaur DD, Agarwal DK, Purohit KC (1993) Retroperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy: initial case report. J Urol 149:103
Harman PK, Kron IL, McLachlan HD, Freedlender AE, Nolan SP (1982) Elevated intra-abdominal pressure and renal function. Ann Surg 196:594
Ichikawa I, Brener BM (1984) Glomerular actions of angiotensin II. Am J Med 76:43
Kashtan J, Green JF, Parson EQ, Holcroft JW (1981) Hemodynamic effects of increased abdominal pressure. J Surg Res 30:249
Kavoussi LR, Kerbl K, Capelouto CC, McDougall EM, Clayman RV (1993) Laparoscopic nephrectomy for renal neoplasms. Urology 42:603
Kavoussi LR, Sosa RE, Chandhoke PJ (1993) Complications of laparoscopic lymph node dissection. J Urol 149:322
Levens NR, Peach MJ, Vaughan ED Jr, Carey RM (1981) Demonstration of a primary anti-diuretic action of angiotensin II: effects of intrarenal converting enzymes inhibition in the conscious dog. Endocrinology 108:318
Mullet CE, Viale JP, Sagnard PE, Miellet CC, Ruynay LG, Counioux HC, Motin JP, Boulex JP, Dargent DM, Annat GJ (1993) Pulmonary CO2 elimination during surgical procedures using intra- or extraperitoneal CO2 insufflation. Anesth Analg 76:622
Pate JW, Estes JW (1968) Effects of elevated venous pressure on kidney function. Am Surg 34:729
Phillips J, Keith D, Hulka J, Hulka B, Keith L (1975) Gynecologic laparoscopy in 1975. J Reprod Med 16:105
Roith DL, Bark H, Nyska M, Glick, SM (1982) The effect of abdominal pressure on plasma antidiuretic hormone levels in the dog. J Surg Res 32:65
Schirmer HKA, Marshall RE, Jackson MP (1968) The effect of altered renal venous pressure on urine flow and cortical metabolism. J Urol 100:205
Schrier RW, Lieberman R, Ufferman RC (1977) Mechanisms of antidiuretic effect of beta adrenergic stimulation. J Clin Invest 51:97
Shenasky JH, Gillenwater JY (1972) The renal hemodynamic and functional effects of external counterpressure. Surg Gynecol Obst 134:253
Sosa RE, Weingram J, Poppas D, Lyons J (1992) Physiological consideration in laparoscopic surgery in urology. J Endourol 6:85
Wolf JS, Stoller ML (1994) The physiology of laparoscopy: basic principles, complications and other considerations. J Urol 152:294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, A.W., Chang, L.S., Birkett, D.H. et al. Changes in urinary output and electrolytes during gaseous and gasless laparoscopy. Urol. Res. 24, 361–366 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389794