Summary
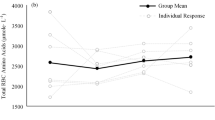
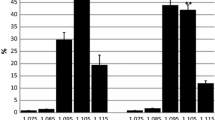
Red cell concentrations of hemoglobin (MCHC), H+, Na+, K+, Mg++, Cl− were measured in femoral venous blood of six untrained (UT), six endurance trained (TR) and three semitrained (ST) subjects during graded increasing work (4, 8, 12, 18 and 24 mkp/s, 10–15 min on each step) on a bicycle ergometer. Before exercise no significant differences were detected for the measured variables when comparing UT and TR. During exercise MCHC, [Na+], [K+] and [Mg++] remained constant indicating lack of water shift into the erythrocytes in spite of a marked acidosis (lowest pHBlood value 7.225). This lack resulted from an elevated extracellular osmolality. [H+]Ery and [Cl−]Ery maximally increased by 2.0×10−8 eq/kg H2O and 10 meq/l, respectively. The change was markedly greater in UT than in TR at equal load. However, if [H+]Ery and [Cl−]Ery were related to pH of whole blood, differences between groups almost disappeared and the ions were distributed as predictable from in vitro experiments (Fitzsimmons and Sendroy, 1961). Behaviour of H+ and Cl− may be of importance for oxygen dissociation under in vivo conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Beaumont, W., Rochelle, R. H.: Erythrocyte volume in acidified venous blood from exercising limbs. Pflügers Arch. 343, 41–48 (1973)
Böning, D.: Wirkungen eines akuten Sauerstoffmangels auf die Blutelektrolytkonzentrationen bei höhenangepa\ten und nicht-höhenangepa\ten Menschen. Pflügers Arch. 314, 217–230 (1970)
Böning, D., Schweigart, U., Kunze, M.: Diurnal variations of protein and electrolyte concentrations and acid-base status in plasma and red cells of normal man. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 32, 239–250 (1974)
Böning, D., Schweigart, U., Tibes, U., Hemmer, B.: Influences of exercise and endurance training on the oxygen dissociation curve of blood under in vivo and in vitro conditions. Europ. J. appl. Physiol. 34, 1–10 (1975)
de Bruin, S. H., Rollema, H. S., Janssen, L. H. M., van Os, G. A. J.: The interaction of chloride ions with human hemoglobin. Biochem. biophys. Res. Comm. 58, 210–215 (1974)
Costill, D. L., Fink, W. J.: Plasma volume changes following exercise and thermal dehydration. J. Appl. Physiol. 37, 521–525 (1974)
Dill, D. B., Edwards, H. T., Consolazio, W. V.: Blood as a physico-chemical system. XI. Man at rest. J. biol. Chem. 118, 635–648 (1937)
Dill, D. B., Talbott, J. H., Edwards, H. T.: Studies in muscular activity. VI. Response of several individuals to a fixed task. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 69, 267–305 (1930)
Eaton, J. W., Faulkner, J. A., Brewer, G. J.: Response of the human red cell to muscular activity. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 132, 886–887 (1969)
Fitzsimmons, E. J., Sendroy, J.: Distribution of electrolytes in human blood. J. biol. Chem. 236, 1595–1601 (1961)
Funder, J., Wieth, J. O.: Chloride and hydrogen ion distribution between human red cells and plasma. Acta physiol. scand. 68, 234–245 (1966)
Kilburn, K. H.: Muscular origin of elevated plasma potassium during exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 675–678 (1966)
Lundvall, J.: Tissue hyperosmolality as a mediator of vasodilatation and transcapillary fluid flux in exercising skeletal muscle. Acta physiol. scand. 86, Suppl. 379 (1972)
Netter, H.: Theoretische Biochemie. Physikalisch-chemische Grundlagen der LebensvorgÄnge. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1959
Nöcker, J., Lohmann, D., Schleusing, G.: Einflu\ von Training und Belastung auf den Mineralgehalt von Herz- und Skelettmuskel. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 17, 243–251 (1958)
Refsum, H. E., Meen, H. D., Strömme, S. B.: Whole blood, serum and erythrocyte magnesium concentrations after repeated heavy exercise of long duration. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 32, 123–127 (1973)
Shappell, S. D., Murray, J. A., Bellingham, A. J., Woodson, R. D., Detter, J. C., Lenfant, C.: Adaptation to exercise: role of hemoglobin affinity for oxygen and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate. J. appl. Physiol. 30, 827–837 (1971)
Van Slyke, D. D., Wu, H., McLean, F. C.: Studies of gas and elecrolyte equilibria in the blood. V. Factors controlling the electrolyte and water distribution in the blood. J. biol. Chem. 56, 765–849 (1923)
Tibes, U., Hemmer, B., Schweigart, U., Böning, D., Fotescu, D.: Exercise acidosis as cause of electrolyte changes in femoral venous blood of trained and untrained man. Pflügers Arch. 347, 145–158 (1974)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design. London-New York-Sydney: Mc-Graw-Hill 1971
Wissenschaftliche Tabellen, p. 508. Basel: Geigy 1960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Bundesinstitut für Sportwissenschaften, Köln
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Böning, D., Tibes, U. & Schweigart, U. Red cell hemoglobin, hydrogen ion and electrolyte concentrations during exercise in trained and untrained subjects. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 35, 243–249 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423283
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00423283