Abstract
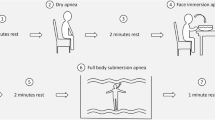
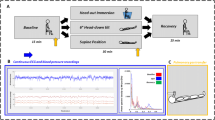
It has been documented that placing an ice-bag on the forehead causes similar cardiac and vascular responses as face immersion. There has been disagreement concerning the contribution of separate cold stimulation on the face and breathholding in the diving response. This study set out to unravel the extent to which these two factors contribute individually to the observed cardiovascular changes during the combined manoeuvre. It further aimed to reveal whether peripheral vascular responses to these stimuli are different in forearm and calf. We observed a significant rapid increase in the RR-interval, which was maintained until the end of the 25-s observation period and a homogeneous vasoconstriction in forearm and calf, despite minor changes in arterial blood pressure, during breathholding, placing the icebag on the forehead and the combined stimuli. Cardiac and peripheral vascular responses to the combined manoeuvre did not differ significantly from the responses elicitated by the two stimuli separately. This test is another example that illustrates the heterogeneous cardiovascular response involving both parasympathetic and sympathetic activation. Moreover, since the icebag on the forehead test is technically easy to perform and does not require the active co-operation of the patient, it may be a valid method to replace a full face immersion test accompanied by breathholding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison DJ (1979) Dangerous reflexes from the nose. Lancet 1:909
Brick I (1966) Circulatory responses to immersing the face in water. J Appl Physiol 22:33–36
Caputa M, Cabanac M (1979) Bradycardia during face cooling in man be produced by selective brain cooling. J Appl Physiol 46:905–907
Clement DL, Charlier P, De Meunynck G (1981) Diagnostic performance of ECG-triggered venous occlusion plethysmography. In: Dietrich EG (ed) Non-invasive cardiovascular diagnosis, 2nd edn. Littleton, Massachusetts, pp 313–318
Craig AB Jr (1963) Heart rate responses to apneic underwater diving and to breath holding in man. J Appl Physiol 18:854–862
Essandoh LK, Duprez DA, Shepherd JT (1987) Postural cardiovascular reflexes: comparison of responses of forearm and calf resistance vessels. J Appl Physiol 63:1801–1805
Follinsbee L (1974) Cardiovascular response to apneic immersion in cool and warm water. J Appl Physiol 36:226–232
Heistad DD, Abboud FM, Eckstein JW (1968) Vasoconstrictor response to simulated diving in man. J Appl Physiol 25:542–549
Kawakami Y, Natelson BH, DuBois AB (1967) Cardiovascular effects of face immersion and factors affecting diving reflex in man. J Appl Physiol 23:964–970
Kobayasi S, Ogawa T (1973) Effect of water temperature on bradycardia during nonapneic facial immersion in man. Jpn J Physiol 23:613–624
Moore TO, Lin YC, Lally DA, Hong SK (1972) Effects of temperature, immersion and ambient pressure on human apneic bradycardia. J Appl Physiol 3:36–41
Oppenshaw PJM, Woodroof GMF (1978) Effects of lung volume on the diving response in man. J Appl Physiol 45:783–785
Ross A, Steptoe A (1980) Attention of the diving reflex in man by mental stimulation. J Physiol 302:387–393
Rusch NJ, Shepherd JT, Webb RC, Vanhoutte PM (1981) Different behavior of the resistance vessels of the human calf and forearm during contralateral isometric exercise, mental stress and abnormal respiratory movement. Circ Res 48 [Suppl I]:118–130
Song SH, Lee WK, Chung YA, Hong SK (1969) Mechanism of apneic bradycardia in man. J Appl Physiol 27:323–327
Whayne TF, Killip T III (1967) Simulated diving in man: comparison of facial stimuli and response to arrhythmia. J Appl Physiol 22:800–807
Wolf S (1966) Sudden death and the oxygen-conserving reflex. Am Heart J 71:840–841
Zbrozyna AW, Westwood DM (1992) Cardiovascular responses elicited by simulated diving and their habituation in man. Clin Anton Res 2:225–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trouerbach, J., Duprez, D., De Buyzere, M. et al. Cardiovascular responses elicited by different simulated diving manoeuvres. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 68, 341–344 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571454
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571454