Abstract
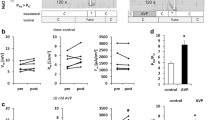
The effect of unilateral renal denervation on renal handling of water, sodium and potassium was studied with clearance and micropuncture techniques in sodium depleted anaesthetized rats in the nondiuretic state. In clearance experiments renal denervation resulted in a +140 and +320% increase in urine flow and potassium excretion, but sodium excretion of innervated (I) and denervated (D) kidneys was similar (I: 12.0±2.0, D: 14.0±3.6 nM·min−1·g−1; NS). However, upon the loop diuretic furosemide (1 mg·kg−1), a marked denervation natriuresis was observed (I: 2.8±0.9, D: 5.9±1.0 μM·min−1;P<0.05) and denervation diuresis and kaliuresis persisted, too (+95 and +60%, respectively). Micropuncture results revealed that fractional reabsorption of filtrate to late proximal puncture site was depressed by renal denervation from 62 to 49% while no change in time control rats was seen (64±2 vs. 64±1%; NS). In micropuncture experiments besides augmented urine flow (+82%) from D kidneys also a small denervation natriuresis was present (I: 21.6±6.4, D: 29.2±7.0 nM·min−1;P<0.05). It is concluded that the lack or marked attenuation of denervation natriuresis in sodium depleted rats were the result of an almost complete compensatory distal reabsorption of the excess sodium (but not of water and potassium) leaving the proximal tubule after denervation. The distal adaptive response can be overcome by furosemide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell-Reuss E, Colindres RE, Pastoriza-Munoz E, Mueller RA, Gottschalk CW (1975) Effects of acute unilateral renal denervation in the rat. J Clin Invest 56:208–217
Bello-Reuss E, Pastoriza-Munoz E, Colindres RE (1977) Acute unilateral denervation in rats with extracellular volume expansion. Am J Physiol 232:F26-F32
Bencsáth P, Asztalos B, Szalay L, Takács L (1979) Renal handling of sodium after chronic renal sympathectomy in the anaesthetized rat. Am J Physiol 236:F513-F518
Bencsáth P, Bonvalet JP, de Rouffignac C (1972) Tubular factors in denervation diuresis and natriuresis. In: Wirz H, Spinelli F (eds) Recent advances in renal physiology. Karger, Basel, pp 96–106
Bencsáth P, Fekete MI, Kanyicska B, Szénási G, Takács L (1982) Renal excretion of sodium after bilateral renal sympathectomy in the anaesthetized and conscious rat. J Physiol (London) 331:443–450
Bencsáth P, Szalay L, Demeczky L, Takács L (1971) Effects of chlorothiazide and furosemide on sodium and water excretion after unilateral splanchnicotomy in the dog. Nephron 8:329–343
Brubacher ES, Vander AJ (1968) Sodium deprivation and renin secretion in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol 214:15–21
DiBona GF (1982) The functions of the renal nerves. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 94:75–181
DiBona GF, Sawin LL (1983) Renal nerves in renal adaptation to dietary sodium restriction. Am J Physiol 245:F322-F328
Fejes-Tóth G, Szénási G, Zahajszky T, Takács L (1978) Urinary kallikrein excretion after renal sympathectomy in the rat. Renal Physiol Basel 1:219–222
Gordon D, Peart WS, Wilcox CS (1979) Requirement of the adrenergic nervous system for conservation of sodium by the rabbit kidney. J Physiol (London_ 293:24P
Gottshall RW, Davis JO, Shade RE, Spielman W, Johnson JA, Braverman B (1973) Effects of renal denervation on renin release in sodium-depleted dogs. Am J Physiol 225:344–349
Gottschalk CW (1979) Renal nerves and sodium excretion. Ann Rev Physiol 41:229–240
Gottschalk CW, Mylle M (1956) Micropuncture study of pressures in proximal tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney and their relation to ureteral and renal venous pressures. Am J Physiol 185:430–439
Hedeland H, Dymling JF, Hökfelt B (1969) Catecholamines, renin and aldosterone in postural hypotension. Acta Endocrinol 62:399–410
Schneider E, McLane-Vega L, Hanson R, Childers J, Gleason S (1978) Effect of chronic bilateral renal denervation on daily sodium excretion in the conscious dog. Fed Proc 37:645
Shear L (1968) Orthostatic hypotension. Treatment with sodium chloride and sodium retaining steroids. Arch Int Med 122: 467–471
Slaton PE, Biglieri EG (1967) Reduced aldosterone excretion in patients with autonomic insufficiency. J Clin Endocrinol 27: 37–45
Szénási G, Bencsáth P, Lehoczky E, Takács L (1981) Tubular transport and urinary excretion of phosphate after renal denervation in the anaesthetized rat. Am J Physiol 240:F481-F486
Szénási G, Bencsáth P, Takács L (1982) Water and sodium excretion in unilaterally denervated normal and sodium depleted anaesthetized rats before and after plasma volume repletion. Pflügers Arch 393:133–138
Wilcox CS, Aminoff MJ, Slater JDH (1977) Sodium homeostasis in patients with autonomic failure. Clin Sci Mol Med 53:321–328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szénási, G., Benesáth, P., Takács, L. et al. Proximal tubular transport and urinary excretion of sodium after renal denervation in sodium depleted rats. Pflugers Arch. 403, 146–150 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584092
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584092