Summary
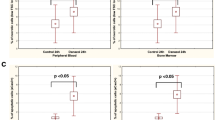
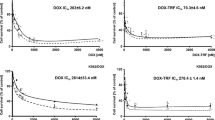
Leukemic cells from patients presenting with acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia and normal hematopoietic bone marrow cells from healthy donors for allogeneic bone marrow transplantation were incubated for 3 h with doxorubicin and epirubicin at different concentrations. The intracellular uptake at the end of the incubation was determined by photofluorometry in leukemic cells from 15 patients and in normal cells from 9 donors for bone marrow transplantation. Cytotoxicity in vitro against granulocyte/macrophage colony-forming units (CFU-GM) was determined in normal cells from 7 donors, and in vitro toxicity against leukemic cells was determined by a clonogenic technique in cells from 6 patients and by vital dye staining (DiSC) following 4 days' culture in cells from 15 patients. Epirubicin was significantly less toxic than doxorubicin to normal hematopoetic cells (72%±20% survival of cells for epirubicin vs 45%±13% for doxorubicin at a concentration of 0.2 μm;P≤0.005). As analyzed by the DiSC assay, 0.2 μm epirubicin was slightly more toxic to leukemic cells than was the same concentration of doxorubicin (47% vs 61% survival,P≤0.01), but the clonogenic assay revealed no difference in toxicity to leukemic cells. At a concentration of 0.2 μm, the mean intracellular uptake of epirubicin in leukemic cells was 0.43±0.26 nmol/mg protein as compared with 0.33±0.14 nmol/mg protein for doxorubicin (not significant). In normal cells, the uptake of epirubicin at a concentration of 0.2 μm was 0.47±0.25 nmol/mg protein as compared with 0.31±0.21 nmol/mg protein for doxorubicin (not significant). The reduced myelotoxicity observed in vitro together with the retained toxicity to leukemic cells indicates that the therapeutic index of epirubicin is better than that of doxorubicin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson B, Beran M, Peterson C, Tribukait B (1982) Significance of cellular pharmacokinetics for the cytotoxic effects of daunorubicin. Cancer Res 42: 178
Bonfante V, Villani F, Bonadonna G (1982) Toxic and therapeutic activity of 4′-epi-doxorubicin. Tumori 68: 105
Camaggi CM, Strocchi E, Tamassia V, Martoni A, Giovannini M, Iafelice G, Canova N, Marraro D, Martini A, Pannuti F (1982) Pharmacokinetic studies of 4′-epi-doxorubicin in cancer patients with normal and impaired renal function and with hepatic metastases. Cancer Treat Rep 66: 1819
Camaggi CM, Strocchi E, Martoni A, Angelelli B, Comparsi R, Pannati F (1985) Epirubicin plasma and blood pharmacokinetics after single i. v. bolus in advanced cancer patients. Drugs Exp Clin Res XI(4): 285
Casazza AM, Di Marco A, Bonadonna G, Bonfante V, Bertazzoli C, Bellini O, Pratesi G, Sala L, Ballerini L (1980) Effects of modification in position 4 of the chromophore or in position 4′ of the aminosugar, on the antitumor activity and toxicity of daunorubicin and doxorubicin. In: Crooke ST, Reich ST (eds) Anthracyclines; current status and new developments. Academic Press, New York, p 403
Cersosimo RJ, Hong WK (1986) Epirubicin: a review of the pharmacology, clinical activity and reverse effects of an Adriamycin analogue. J Clin Oncol 4: 425
Davis HL, Davis TE (1979) Daunorubicin and Adriamycin in cancer treatment: an analysis of their roles and limitations. Cancer Treat Rep 63: 809
Di Marco A, Casazza AM, Dasdia T, Necco A, Pratesi G, Rivolta P, Velcich A, Zaccara A, Zunino F (1977) Changes of activity of daunorubicin, Adriamycin and stereoisomers following the introduction or removal of hydroxyl groups in the amino sugar moiety. Chem Biol Interact 19: 291
Iscove NN, Senn JS, Till JE (1971) Colony formation by normal leukemic bone marrow cells in culture. Effect of conditioned medium from human leukocytes. Blood 37: 1
Lowry OM, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. Biol Chem 193: 265
Paul C, Peterson C, Gahrton G, Lockner D (1979) Uptake of free and DNA-bound daunorubicin and doxorubicin in human leukemic cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2: 49
Pike BL, Robinson WA (1970) Human bone marrow colony growth in agar-gel. J Cell Physiol 76: 77
Robert J, Vrignaud P, Nguyen-Ngoc T, Iliadis A, Mauriac L, Hurteloup P (1985) Comparative pharmacokinetics and metabolism of doxorubicin and epirubicin in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rep 69: 633
Sampi K, Masaoka T, Shirakawa S, Shirai T, Abe T, Shibata H, Umeda M, Kobayashi T, Sugiyama H, Toki H, Kozuru M, Tamura K, Oguro M, Hirota Y (1987) A phase II study of epirubicin in acute leukemia: a cooperative group study. Anticancer Res 7: 29
Schwartz H, Kanter P (1979) Biochemical parameters of growth inhibition of human leukemia cells by antitumor anthracycline agents. Cancer Treat Rep 63: 821
Sundman-Engberg B, Tidefelt U, Liliemark J, Paul C (1990) Intracellular concentrations of anti-cancer drugs in leukemic cells in vitro vs in vivo. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 25: 252
Tidefelt U, Sundman-Engberg B, Paul C (1989) Comparison of the intracellular pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin and 4′-epi-doxorubicin in patients with acute leukemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 24: 225
Lum BL, Billingham ME, Bristow MR, Brown BW, Howes AE, Aston DA, Meyers FJ, Carter SK, Hannigan JF, Torti FM (1986) Epirubicin and doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: Assessment by multiple endomyocardial biopsy and dose-injury slope analysis: An NCOG study. Proc Annu Meet Am Assoc Cancer Res 27: 175
Weenen H, Lankelma J, Penders PGM, McVie JG, Ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Planque MM de, Pinedo HM (1983) Pharmacokinetics of 4′-epi-doxorubicin in man. Invest New Drugs 1: 059
Weisenthal L, Kurnick N, Lippman M (1983) Comparison of dye exclusion assays with a clonogenic assay in the determination of drug-induced cytotoxicity. Cancer Res 43: 258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tidefelt, U., Sundman-Engberg, B. & Paul, C. Intracellular uptake and cytotoxic effect in vitro of doxorubicin and epirubicin in human leukemic and normal hematopoietic cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 29, 7–12 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686328
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686328