Summary
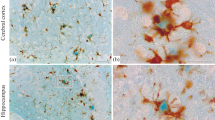
Immunocytochemical staining with monoclonal antibodies to the β-protein on tissue sections which have been pretreated with formic acid is not only a very specific but also a highly sensitive method for the detection of amyloid deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease victims. We report here a spectrum of morphological appearance of the brain amyloid deposits which are one of the main histopathological correlates of this disorder. Deposits of the β-protein are not only found in the well-known lesions [congophilic angiopathy and senile (neuritic) plaques] but are also seen under various morphological forms for which the word “plaques” does not appear an appropriate term: amyloid fibrils are found as large areas of diffuse infiltration of the neuropil, as ribbon-like infiltration in the subpial layer of the cerebral cortex, as granular deposits in the white matter, as diffuse deposits in the molecular layer of the cerebellum and the basal ganglia and as star-shaped deposits in the cerebellar Purkinje cell layer. The morphology of these deposits seems to depend on the cyto-and fibroarchitectonics of the brain region in which they are found, on the amount of amyloid deposited, and also on the type of staining technique used. It is only under specific circumstances that the deposition of amyloid in the neuropil is accompanied by the formation of paired helical filaments in nerve cell processes and their parent perikarya. In conclusion, our studies suggest that the extent of brain amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease is much wider than so far appreciated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderton BH, Breinburg D, Downes MJ, Green PJ, Tomlinson BE, Ulrich J, Wood JN, Kahn J (1982) Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature 298:84–86
Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Kim KS, Wisnewski HM (1989) Immunoreactivity of neuronal lipofuscin with monoclonal antibodies to the amyloid β-protein. Neurobiol Aging 10:125–132
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wiesniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 477:90–99
Binder LI, Frankfurter A, Rebhun LI (1985) The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol 101:1371–1378
Blessed G, Tomlinson BE, Roth M (1968) The association between quantitative mesures of dementia and of senile changes in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry 114:797–817
Corsellis JAN, Bruton CJ, Freeman-Browne D (1973) The aftermath of boxing. Psychol Med 3:270–303
Dickson DW, Farlo J, Davies P, Crystal H, Fuld P, Yen SH (1988) Alzheimer's disease. A double-labeling immunohistochemical study of senile plaques. Am J Pathol 132:86–101
Eanes ED, Glenner GG (1968) X-ray diffraction studies on amyloid filaments. J Histochem Cytochem 16:673–677
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Grundke-Iqbal I, Johnson AB, Wisniewski HM, Terry RD, Iqbal K (1979) Evidence that Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles originate from neurotubules. Lancet I:578–580
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung Y-C, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein τ (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4913–4917
Hershko A (1983) Ubiquitin: roles in protein modification and breakdown. Cell 34:11–12
Hirano A, Malamud N, Kurland LT (1961) Parkinsonismdementia complex. An endemic disease on the island of Guam. Brain 84:662–679
Hirano A, Malamud N, Elizan TS, Kurland LT (1966) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam: further pathologic studies. Arch Neurol 15:35–51
Ikeda K, Haga C, Kosaka K, Oyanagi S (1989) Senile qlaque-like structures-Observation of a probably unknown type of senile plaque by PAM electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol 78:137–142
Ikeda S, Allsop D, Glenner G (1989) The morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases: an immunohistochemical study using amyloid β protein antibody. Lab Invest 60:113–122
Jellinger K (1977) Cerebrovascular amyloidosis with cerebral hemorrhage. J Neurol 214:195–206
Kim KS, Miller DL, Sapienza VJ, Chen CMJ, Bai C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Currie JR, Wisniewski HM (1988) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive to synthetic cerebrovascular amyloid peptide. Neurosic Res Commun 2:121–130
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Kosik KS, Duffy LK, Dowling MM, Abraham C, McCluskey A, Selkoe DJ (1984) Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7941–7945
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down's syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
Mandybur TI, Bates SRD (1978) Fatal massive intracerebral hemorrhage complicating cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Arch Neurol 35:246–248
Merz PA, Wisniewski HM, Somerville RA, Bobin SA, Masters CL, Iqbal K (1983) Ultrastructural morphology of amyloid fibrils from neuritic and amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 60:113–124
Miller DL, Currie JR, Iqbal K, Potempska A, Styles J (1988) Relationships between the cerebral amyloid peptides and their precursors. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2:253 [abstr]
Mori H, Kondo J, Ihara Y (1987) Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science 235:1641–1644
Narang HK (1980) High-resolution electron microscopic analysis of the amyloid fibril in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:621–631
Ogomori K, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, Sato Y, Suetsugu M, Abe M (1989) β-protein amyloid is widely distributed in the central nervous system of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol 134:243–251
Okamoto K, Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Shoji M, Harigaya Y, Takatama M (1988) Immunogold electron microscopic study of cerebrovascular and senile plaque amyloid by use of anti-β protein antibody. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2:269 [abstr]
Perry G, Friedman R, Shaw G, Chau V (1987) Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3033–3036
Probst A, Brunnschweiler H, Lautenschlager C, Ulrich J (1987) A special type of senile plaque, possibly an initial stage. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:133–141
Rudelli RD, Wisniewski HM Kim KS, Wen GY (1988) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study of ependymal/choroidal pseudotangles (Biondi rings). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:320 [abstr 59]
Tagliavini F, Giaccone G, Frangione B, Bugiani O (1988) Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett 93:191–196
Terry RD, Wisniewski HM (1970) The ultrastructure of the neurofibrillary tangle and the senile plaque. Ciba Found Symp, pp. 145–168
Tomlinson BE (1986) Dementia and the deposition of amyloid in the brain. Neuropathology [Suppl] 3:1–12
Tomlinson BE, Henderson G (1976) Some quantitative cerebral findings in normal and demented people In: Terry RD, Gershon S (eds) Neurobiology of aging. Raven Press, New York, pp 183–204
Tomonaga M (1986) Amyloid angiopathy and dementia. Neuropathology [Suppl] 3:23–35
Vorbrodt AW, Wisniewski HM (1982) Plasmalemma-bound nucleoside diphosphatase as a cytochemical marker of central nervous system (CNS) mesodermal cells. J Histochem Cytochem 30:418–424
Wegiel J, Wisniewski HM, Wang KC, Kujawa M, Lach B (1988) The role of microglia in plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:338 [abstr 113]
Wisniewski HM, Terry RD (1973) Reexamination of the pathogenesis of the senile plaque. Prog Neuropathol 2:1–26
Wisniewski HM, Narang NK, Corsellis JAN, Terry RD (1976) Ultrastructural studies of the neuropil and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and post-traumatic dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 35:367 [abstr 136]
Wisniewski HM, Sinatra RS, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1981) Neurofibrillary and synaptic pathology in the aged brain. In: Johnson JE (ed) Aging and cell structure. vol 1. Plenum, New York, pp 105–142
Wisniewski HM, Moretz RC, Lossinsky AS (1981) Evidence for induction of localized amyloid deposits and neuritic plaques by an infectious agent. Ann Neurol 10:517–522
Wisniewski HM, Vorbrodt AW, Moretz RC, Lossinsky AS, Grundke-Iqbal I (1982) Pathogenesis of neuritic (senile) and amyloid plaque formation. Exp Brain Res [Suppl] 5:3–9
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Ihara Y (1988) A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by β protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol 76:541–549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by grants 5-AGO-4220-05 and 5-HD-22634-02 from the National Institutes of Heath
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wisniewski, H.M., Bancher, C., Barcikowska, M. et al. Spectrum of morphological appearance of amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 78, 337–347 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688170
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688170