Abstract
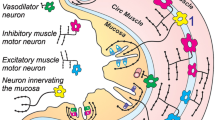
The quantitative distribution of neuropeptide Y (NPY) immunoreactivity has been determined along the length of the gastrointestinal tract in three mammalian species; rat, pig, and guinea pig. The peptide was shown to be present in all regions studied and in all three species. Exceptionally high concentrations were found in the region of the lower esophageal sphincter. Pretreatment of rats with 6-hydroxydopamine depleted NPY concentrations by 30–40%, indicating that NPY is colocalized in part with adrenergic nerves. Characterization of the NPY immunoreactivity by high-pressure liquid chromatography revealed a single major peak. NPY immunoreactivity derived from rat extracts eluted consistently earlier from the column than synthetic porcine standard, indicating minor species differences. Pharmacological studies using longitudinal muscle from guinea pig terminal ileum demonstrated that NPY caused a dose-dependent inhibition of the electrically stimulated, neurally mediated contraction of longitudinal smooth muscle. This suggested that NPY may act presynaptically to inhibit cholinergic transmission. The effects of various NPY fragments were also tested on the same preparation. The C-terminal fragments were active but were considerably less potent than NPY, while the free acid form of NPY and N-terminal fragment (1–19) were completely inactive. Thus, this study has demonstrated the presence of NPY in the gastrointestinal tract of various species, particularly within the lower esophageal sphincter. The pharmacological actions of the peptide suggest a role in the control of nonvascular smooth muscle tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tatemoto K, Carlquist M, Mutt V: Neuropeptide Y-a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature 296:659–660, 1982
Tatemoto K: Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2514–2518, 1982
Loren I, Alumets J, Hakanson R, Sundler F: Immunoreactive pancreatic polypeptide (PP) occurs in the central and peripheral nervous system: preliminary immunocytochemical observations. Cell Tissue Res 200:179–186, 1979
Lundberg JM, Hokfelt T, Anggard A, Kimmel J, Goldstein M, Markey M: Coexistence of an avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP) immunorective substance and catecholamine in some peripheral and central neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 110:107–109, 1980
Sundler F, Moghimzadeh E, Hakanson R, Ekelund M, Emson P: Nerve fibers in the gut and pancreas of the rat displaying neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity. Cell Tissue Res 230:487–493, 1983
Furness JB, Costa M, Emson PC, Hakanson R, Moghimzadeh E, Sundler F, Taylor IL, Chance RE: Distribution, pathways and reactions to drug treatment of nerves with neuropeptide Y-and pancreatic polypeptide-like immunoreactivity in the guinea pig digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res 234:71–92, 1983
Tatemoto K, Siimesmaa S, Jornvall H, Allen JM, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Mutt V: Isolation and characterization of neuropeptide Y from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett 179:181–184, 1985
Allen JM, Yeats JC, Adrian TE, Bloom SR: Radioimmunoassay of neuropeptide Y (NPY). Regul Peptides 8:61–70, 1984
Lundberg JM, Tatemoto K, Terenius L, Hellstrom PM, Mutt V, Hokfelt T, Hamberger B: Localization of peptide YY (PYY) in gastrointestinal endocrine cells and effects on intestinal blood flow and motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4471–4475, 1982
El-Salhy M, Grimelius L, Wilander E, Ryberg B, Terenius L, Lundberg JM, Tatemoto K: Immunocytochemical identification of polypeptide YY (PYY) cells in the human gastrointestinal tract. Histochemistry 77:15–23, 1983
Aggestrup S, Uddman R, Jensen SL, Sundler F, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O, Host JJ, Hakanson R, Ekman R, Sorensen HR: Regulatory peptides in the lower esophageal sphincter of man. Regul Peptides 10:167–178, 1985
Kostrzewa RM, Jacobwitz DM: Pharmacological actions of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Rev 76:199–288, 1974
Lee Y, Shiosaka S, Emson PC, Powell JF, Smith AD, Tohyama M: Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactive structures in the rat stomach with special reference to the noradrenaline neuron system. Gastroenterology 89:118–126, 1985
Lundberg JM, Tatemoto K: Pancreatic polypep ide family (APP, BPP, NPY, and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand 116:393–402, 1982
Allen JM, Bircham PMM, Edwards AV, Tatemoto K, Bloom SR: Neuropeptide Y (NPY) reduces myocardial perfusion and inhibits the force of contraction of the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Regul Peptides 6:247–253, 1983
Hellstrom PM, Olerup O, Tatemoto K: Neuropeptide Y may mediate effects of sympathetic nerve stimulations on colonic motility and blood flow in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 124:613–624, 1985
Allen JM, Polak JM, Rodrigo J, Darcy K, Bloom SR: Localization of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in nerves of the rat cardiovascular system and effect of 6-hydroxydopamine. Cardiovasc Res 19:570–577, 1985
Uddman R, Alumets J, Hakanson R, Sundler F, Walles B: Peptidergic (enkephalin) innervation of the mammalian esophagus. Gastroenterology 78:732–737, 1980
North RA, Katayama Y, Williams JT: On the mechanism and site of action of enkephalin on single myenteric neurons. Brain Res 165:67–77, 1979
Szerb JC: Correlation between acetylcholine release and neuronal activity in the guinea pig ileum myenteric plexus: Effect of morphine. Neuroscience 7:327–340, 1980
North RA: Electrophysiology of the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience 7:315–325, 1982
Allen JM, Adrian TE, Tatemoto K, Polak JM, Hughes J, Bloom SR: Two novel related peptide, neuropeptide Y (NPY) and peptide YY (PYY) inhibit contraction of the electrically field stimulated mouse vas deferens. Neuropeptides 3:71–77, 1982
Ohhashi T, Jacobwitz DM: The effects of pancreatic polypeptides and neuropeptide Y on the rat vas deferens. Peptide 4:381–386, 1983
Lundberg JM, Stjarne L: Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of [3H]noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation in the rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand 120:477–479, 1984
Stjernquist M, Emson P, Owman Ch, Sjoberg N-O, Sundler F, Tatemoto K: Neuropeptide Y in the female reproductive tract of the rat. Distribution of nerve fibres and motor effects. Neurosci Lett 39:279–284, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, J.M., Hughes, J. & Bloom, S.R. Presence, distribution, and pharmacological effects of neuropeptide Y in mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Digest Dis Sci 32, 506–512 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296034
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296034