Abstract
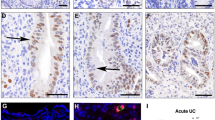
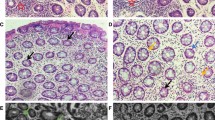
Stress (heat shock) proteins are ubiquitous intracellular proteins that can be inducedin vitro by physiological stress events that occur during inflammation. We have used an indirect immunoperoxidase method to locate 60-kDa stress proteins in biopsies taken from normal and inflamed colorectal mucosa. An anti-60-kDa monoclonal antibody (ML30) produced specific staining of surface epithelial cells localized to the site of the Golgi apparatus. In ulcerative colitis, there was an increased concentration of this stress protein compared with controls (P≤0.002) and also with a small group of active Crohn's colitis (P≤0.01), but no relationship between its concentration and disease activity. All biopsies also showed staining of goblet cells by ML30, suggesting a possible cross-reaction with mucin; electroblotting of crude but not purified mucin showed a faint 60-kDa band with ML30. We conclude that the 60-kDa stress protein is present in normal colorectal epithelial cells and is markedly inducedin vivo in ulcerative colitis. Further, we suggest that since the 60-kDa protein functions as a molecular chaperone, it may associate with colonic mucin aiding in its synthesis and/or secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindquist S: The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem 55:1151–1191, 1986
Polla BS: A role for heat shock proteins in inflammation? Immunol Today 9:134–137, 1988
Cheng MY, Hartl F-U, Martin J, Pollock RA, Kalousek F, Neupert W, Hallberg EM, Hallberg RL, Horwich AL: Mitochondrial heat-shock protein hsp60 is essential for assembly of proteins imported into yeast mitochondria. Nature 337:620–625, 1989
Tsoulfa G, Rook GAW, van Embden JDA, Young DB, Mehlert A, Isenberg DA, Hay FC, Lydyard PM: Raised serum IgG and IgA antibodies to mycobacterial antigens in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 48:118–123, 1989
Mojdehi G, Winrow VR, Rampton DS, Coates ARM, Blake DR: Cellular locale of heat-shock (stress) proteins in inflammatory tissues from patients with arthritis and ulcerative colitis. Br J Rheumatol 28(Abstr suppl 2):123, 1989
Mojdehi G, Winrow VR, Blake DR, Rampton DS: Immunohistological localisation of stress proteins in rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 98:A464, 1990
Saverymuttu SH, Camilleri M, Rees H, Lavender JP, Hodgson HJF, Chadwick VS: Indium 111-granulocyte scanning in the assessment of disease extent and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. A comparison with colonoscopy, histology and fecal indium 111-granulocyte excretion. Gastroenterology 90:1121–1128, 1986
Engers HD, Abe M, Bloom BR, Mehra V, Britton W, Buchanan TM, Khanolkar SK, Young DB, Closs O, Gillis T, Harboe M, Ivanyi J, Kolk AHJ, Shepard CC: Results of a World Health Organisation sponsored workshop on monoclonal antibodies toMycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun 48:603–605, 1985
Engers HD, Houba V, Bennedsen J, Buchanan TM, Chaparas SD, Kadival G, Closs O, David JR, van Embden JDA, Godal T, Mustafa SA, Ivanyi J, Young DB, Kaufmann SHE, Khomenko AG, Kolk AHJ, Kubin M, Louis JA, Minden P, Shinnick TM, Trnka L, Young RA: Results of a World Health Organisation sponsored workshop to characterise antigens recognised by mycobacteria-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun 51:718–720, 1986
Nakane PK, Pierce GB: Enzyme labeled antibodies for light and electron microscopic localisation of tissue antigens. J Cell Biol 33:307–318, 1967
Raouf A, Parker N, Iddon D, Ryder S, Langdon-Brown B, Milton JD, Walker R, Rhodes JM: Ion exchange chromatography of mucus glycoproteins in inflammatory bowel disease: Absence of a selective subclass defect. Gut 32:1139–1145, 1991
Makin CA: Monoclonal antibodies raised to colorectal carcinoma antigens. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 68:298–301, 1986
Mehlert A, Lamb J, Young D: Analysis of stress-related proteins involved in the immune response to mycobacterial infection. Biochem Soc Trans 16:721–722, 1988
Thole JER, Keulen WJ, Kolk AHJ, Groothuis DG, Berwald LG, Tiesjema RH, van Embden JDA: Characterisation, sequence determination, and immunogenicity of a 64-kilodalton protein ofMycobacterium bovis BCG expressed inEscherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun 55:1466–1475, 1987
Podolsky DK, Fournier DA, Lynch KE: Human colonic goblet cells: Demonstration of distinct subpopulations defined by mucin specific monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Invest 77:1263–1271, 1986
Evans DJ, Norton P, Ivanyi J: Distribution in tissue sections of the human GroEL stress-protein homologue. APMIS 98:437–441, 1990
Ohno K, Fukushima M, Fujiwara M, Narumiya S: Induction of 68000-dalton heat shock proteins by cyclopentenone prostaglandins. Its association with PG-induced G1 block in cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem 263:19764–19770, 1988
Santoro MG, Garaci E, Amici C: Prostaglandins with antiproliferative activity induce the synthesis of a heat shock protein in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8407–8411, 1989
Welch WJ: Phorbol ester, calcium ionophore, or serum added to quiescent rat embryo fibroblast cells all result in the elevated phosphorylation of two 28,000-dalton mammalian stress proteins. J Biol Chem 260:3058–3062, 1985
Keyse SM, Tyrrell RM: Heme oxygenase is the major 32-kDa stress protein induced in human skin fibroblasts by UVA radiation, hydrogen peroxide, and sodium arsenite. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:99–103, 1989
Robaye B, Hepburn A, Lecocq R, Fiers W, Boeynaems J-M, Dumont JE: Tumour necrosis factor-α induces the phosphorylation of 28-kDa stress proteins in endothelial cells: Possible role in protection against cytotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:301–308, 1989
Rampton DS, Hawkey CJ: Prostaglandins and ulcerative colitis. Gut 25:1399–1413, 1984
Simmonds NJ, Allen RE, Stevens TRJ, Van Someren RNM, Blake DR, Rampton DS: Chemiluminescence assay of reactive oxygen metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 103:186–196, 1992
Dudani AK, Gupta S: Immunological characterisation of a human homolog of the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Infect Immun 57:2786–2793, 1989
Ellis RJ, Hemmingsen SM: Molecular chaperones: Proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci 14:339–342, 1989
Rothman JE: Polypeptide chain binding proteins: Catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell 59:591–601, 1989
Bochkareva ES, Lissin NM, Girshovich AS: Transient association of newly synthesised unfolded proteins with the heat-shock GroEL protein. Nature 336:254–257, 1988
Wakefield AG, Sawyer AM, Dhillon AP, Pittilo RM, Rowles PM, Lewis AM, Pounder RE: Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease: Multifocal gastrointestinal infarction. Lancet 2:1057–1062, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
V.R. Winrow is supported by The Arthritis and Rheumatism Council for Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winrow, V.R., Mojdehi, G.M., Ryder, S.D. et al. Stress proteins in colorectal mucosa. Digest Dis Sci 38, 1994–2000 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297075
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297075