Abstract
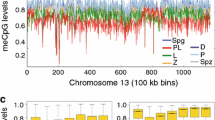
Genomic imprinting in mammals is thought to be mediated by differences in the methylation level of cytosine residues in the genome. These differences in DNA methylation are thought to be generated during the development of the germ line. To characterize the profile of global methylation of the mouse genome during male gametogenesis, we have quantified the relative level of methylation in individual cells during meiosis and spermatogenesis. A decrease in the level of DNA methylation is observed from meiotic cells to elongated spermatids. The erasure of the somatic pattern of methylation during spermatogenesis suggests the existence of a subsequent mechanism generating the parental specific methylation patterns leading to genomic imprinting of specific alleles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RLP, Bryans M, Rinaldi A, Smart A, Yesufu HMI (1990) Eukaryotic DNA methylases and their use forin vitro methylation.Phil Trans R Soc Lond 326: 189–198.
Bestor TH, Ingram VM (1983) Two DNA methyltransferases from murine erythroleukemia cells: purification, sequence specificity and mode of interaction with DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 5559–5563.
Boyes J, Bird A (1991) DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein.Cell 64: 1123–1134.
Clarke A (1990) Genetic imprinting in clinical genetics.Development Suppl: 131–139.
Chaillet JR, Vogt TF, Beier DR, Leder P (1991) Parental-specific methylation of an imprinted transgene is established during gametogenesis and progressively changes during embryogenesis.Cell 66: 77–83.
Driscoll DJ, Migeon BR (1990) Sex difference in methylation of single-copy genes in human meiotic germ cells: implications for X chromosome inactivation, parental imprinting, and origin of CpG mutations.Somat Cell Mol Genet 16: 267–282.
Ferraro M, Prantera G (1988) Human NORs show correlation between transcriptional activity, DNase I sensitivity and hypomethylation.Cytogenet Cell Genet 47: 58–61.
Grant M, Zuccotti M, Monk M (1992) Methylation of CpG sites of two X- linked genes coincides with X-inactivation in the female mouse embryo but not in the germ line.Nature Genetics 2: 161–166.
Groudine M, Conkin KF (1985) Chromatin structure andde novo methylation of sperm DNA: implications for activation of the paternal genome.Science 228: 1061–1068.
Gruenbaum G, Cedar H, Razin A (1982) Substrate and sequence specificity of a eukaryotic DNA methylase.Nature 295: 620–622.
Hall JG (1990) How imprinting is relevant to human disease?Development Suppl: 141–148.
Leonhardt H, Page AW, Weier HU, Beitor TH (1992) A targeting sequence directs DNA methyltransferase to sites of DNA replication in mammalian nuclei.Cell 71: 865–873.
Monk M, Adams RLP, Rinaldi A (1991) Decrease in DNA methylase activity during preimplantation development in the mouse.Development 112: 180–192.
Monk M, Boubelik M, Lehnert S (1987) Temporal and regional changes in DNA methylation in the embryonic, extraembryonic and germ cell lineages during mouse embryo development.Development 99: 371–382.
Oberlé I, Roussea F, Heitz Det al. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome.Science 252: 1097–1102.
Prantera G, Ferraro M (1990) Analysis of methylation and distribution of CpG sequences on human active and inactive X chromosomes byin situ nick-translation.Chromosoma 99: 18–22.
Razin A (1984) DNA methylation patterns: formation and biological functions. In: Razin A, Cedar H, Riggs AD, eds.DNA methylation. New York, Berlin, Heidelberg, Tokyo, Springer-Verlag. 127–146.
Razin A, Cedar H, Riggs AD (1984) Introduction and general overview. In: Razin A, Cedar H, Riggs AD, eds.DNA methylation. New York, Berlin, Heidelberg, Tokyo, Springer-Verlag. 1–10.
Razin A, Levine A, Kafri T, Roll M, Giloh H, Scarpa S, Carotti D (1988) Relationship between transient DNA hypomethylation and erythroid differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 9003–9006.
Razin A, Szyf M, Kafri T, Agostini S, Gomi T, Cantoni G (1986) Replacement of 5-methylcytosine by cytosine: a possible mechanism for transient DNA demethylation during differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2827–2831.
Reik W (1989) Genomic imprinting and genetic disorders in man.Trends Genet 5: 331–336.
Sandford J, Forrester L, Chapman V, Chandley A, Hastie N (1984) Methylation patterns of repetitive DNA sequences in germ cells ofMus musculus.Nucl Acids Res 12: 2823–2836.
Sapienza C, Tran TH, Paquette J, McGowan R, Peterson MB (1989) A methylation mosaic model for mammalian genome imprinting. In: Cohn WE & Moldave K, eds.Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology. San Diego, Academic Press, Inc. 145–156.
Solter D (1988) Differential imprinting and expression of maternal and paternal genomes.Annu Rev Genet 22: 127–146.
Swain JL, Stewart TA, Leder P (1987) Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting.Cell 50: 719–727.
Trasler JM, Hake LE, Johnson PA, Alcivar AA, Millette CF, Hecht NB (1990) DNA methylation and demethylation events during meiotic prophase in the mouse testis.Mol Cell Biol 10: 1828–1834.
Ueda T, Yamazaki K, Suzuki R, Fujimoto H, Sasaki M, Sakaki Y, Higashinakagawa T (1992) Parental methylation patterns of a transgenic locus in adult somatic tissues are imprinted during gametogenesis.Development 116: 831–839.
Wigler M, Levy D, Perucho M (1981) The somatic replication of DNA methylation.Cell 24: 33–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
del Mazo, J., Prantera, G., Torres, M. et al. DNA methylation changes during mouse spermatogenesis. Chromosome Res 2, 147–152 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01553493
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01553493