Abstract
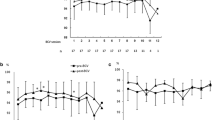
We have studied the hemodynamic effects of an intravenous single dose of nitroglycerin in 13 patients with secondary pulmonary hypertension and Cor Pulmonale, during the acute course of respiratory failure and under assisted ventilation. We observed a significant decrease in systolic, diastolic and mean pulmonary arterial pressures, and in pulmonary resistance and systolic right ventricular work index, without any change in right or left pre-loads. The systolic arterial pressure decreased slightly, without any change in cardiac index or diastolic pressure. The arterial and mixed venous oxygen contents, and the pulmonary shunting (Qs/Qt) were unchanged. These results suggest that nitroglycerin may be a useful therapy in patients in the acute stages of pulmonary hypertension resulting from chronic lung disease and under assisted ventilation. In addition, the lack of change in cardiac index, intrapulmonary shunting and oxygen content suggests that this decrease in pulmonary resistance is not linked with any deleterious effect in oxygen transfer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahmy NR (1978) Nitroglycerin as a hypotensive drug during general anesthesia. Anesthesiology 49:17–20
Kadowitz PJ, Higashida R, Hyman AL (1973) Effects of systemic vasodilatators on pulmonary venous tone. Am J Cardiol 43:405–408
Konietzko N, Schlehe H, Harisch B, Matthys H (1975) Effect of isosorbide dinitrate on hemodynamics and respiration of patients with coronary artery disease and of patients with Cor pulmonale. Respiration 32:368–377
Kopman EA, Weygandt GR, Bauer S, Ferguson JB (1978) Arterial hypoxemia following administration of sublingual nitroglycerin. Am Heart J 96:444–447
Mookherjee S, Fuleihan D, Warner RA, Vardan S, Obeid AI (1978) Effects of sublingual nitroglycerin on resting pulmonary gas exchange and hemodynamics in man. Circulation 57:106–110
Rubin LJ, Peter RH (1979) The effects of oral hydralazine on rest and exercise hemodynamics in pulmonary hypertension secondary to chronic lung disease. Clin Res 27:793A
Simonneau G, Escourrou P, Legrand A, Cerrina J, Duroux P, Lockart A (1980) Hemodynamic effects of Nifedipine in acute respiratory failure complicating chronic obstructive lung disease. Intensive Care Med 6:61 (Abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fourrier, F., Chopin, C., Durocher, A. et al. Intravenous nitroglycerin in acute respiratory failure of patients with chronic obstructive lung disease, secondary pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale. Intensive Care Med 8, 85–88 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01694872
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01694872