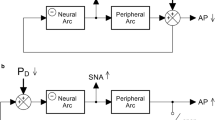
Summary
In anesthetized animals it has been shown previously, that the influence of electrical stimulation of efferent renal nerves on renal function with increasing stimulation frequencies can be graded; renin release is affected at low, sodium excretion at intermediate and vascular resistance at high stimulation frequencies.
Experiments in conscious dogs are reviewed, which present evidence for a similar functional dissociation under physiological conditions.
Moderate activations of the renal sympathetic nerves, which do not change renal blood flow 1) decrease sodium excretion independent of changes in angiotensin II, 2) interact with the pressure-dependent mechanism of renin release by resetting its threshold pressure and 3) modulate autoregulation by increasing the lower limits of glomerular filtration rate and renal blood flow-autoregulation.
These findings may contribute to our understanding of the role of the renal nerves in the pathophysiology of congestive heart failure and hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard C (1859) Lecons sur les propriétés physiologiques et les altérations pathologiques des liquides de l'organisme. JB Baillière et Fils, Paris, pp 171–176
Berne RM (1952) Hemodynamics and sodium excretion of denervated kidney in anesthetized and unanesthetized dog. Am J Physiol 171:148–158
Bradford JR (1889) The innervation of the renal blood vessels. J Physiol (Lond) 10:358–407
Cohnheim J, Roy CS (1883) Untersuchungen über die Cirkulation in den Nieren. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med 92:424–448
DiBona GF (1982) The functions of the renal nerves. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 94:76–181
Ehmke H, Persson P, Kirchheim H (1987) A physiological role for pressure-dependent renin release in long-term blood pressure control. Pflügers Arch 410:450–456
Ehmke H, Persson P, Fischer S, Hackenthal E, Kirchheim H (1989) Resetting of pressure-dependent renin release by intrarenal alpha1-adrenoceptors in conscious dogs. Pflügers Arch 413:261–266
Eide I, Loyning E, Kiil F (1973) Evidence for hemodynamic autoregulation of renin release. Circ Res 32:237–245
Farhi ER, Cant JR, Barger AC (1982) Interaction between intrarenal epinephrine receptors and the renal baroreceptor in the control of PRA in conscious dogs. Circ Res 50:477–485
Fahri ER, Cant JR, Barger AC (1983) Alterations of renal baroreceptor by salt intake in control of plasma renin activity in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 245:F119-F122
Fahri ER, Cant JR, Paganelli WC, Dzau VJ, Barger AC (1987) Stimulus-response curve of the renal baroreceptor: effect of converting enzyme inhibition and changes in salt intake. Circ Res 61:670–677
Finke R, Gross R, Hackenthal E, Huber J, Kirchheim H (1983) Threshold pressure for the pressure-dependent renin release in the autoregulating kidney of conscious dogs. Pflügers Arch 399:102–110
Gibbons GH, Dzau VJ, Farhi ER, Barger AC (1984) Interaction of signals influencing renin release. Ann Rev Physiol 46:291–308
Gottschalk CW, Moss NG, Colindres RE (1985) Neural control of renal function in health and disease. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G. The kidney: physiology and pathophysiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 613–644
Gross R, Ruffmann K, Kirchheim H (1979) The separate and combined influences of common carotid occlusion and nonhypotensive hemorrhage on kidney blood flow. Pflügers Arch 379:81–88
Gross R, Kirchheim H (1980) Effects of bilateral carotid occlusion and auditory stimulation on renal blood flow and sympathetic nerve activity in conscious dogs. Pflügers Arch 383:233–239
Gross R, Hackenberg HM, Hackenthal E, Kirchheim H (1981a) Interaction between perfusion pressure and sympathetic nerves in renin release by carotid baroreflex in conscious dogs. J Physiol (London) 313:237–250
Gross R, Kirchheim H, Ruffmann K (1981b) Effect of carotid occlusion and of perfusion pressure on renal function in conscious dogs. Circ Res 48:777–784
Guyton AC, Manning RD Jr, Hall JE, Norman RA Jr, Young DB, Pan Y (1984) The pathogenetic role of the kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6 (Suppl I):S151-S161
Kirchheim H (1976) Systemic arterial baroreceptor reflexes. Physiol Rev 56:100–176
Kirchheim H (1983) Regulation of renal hemodynamics in congestive heart failure. In: Vasodilators in Chronic Heart Failure. Ed by Just H and Bussmann WD, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 36–46
Kirchheim H, Finke R, Hackenthal E, Löwe W, Persson P (1985) Baroreflex sympathetic activation increases threshold pressure for the pressure dependent renin release in conscious dogs. Pflügers Arch 405:127–135
Kirchheim H, Ehmke H, Hackenthal E, Löwe W, Persson P (1987) Autoregulation of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration rate and renin release in conscious dogs. Pflügers Arch 410:441–449
Kirchheim H, Ehmke H, Persson P (1988) Physiology of the renal baroreceptor-mechanisms of renin release and its role in congestive heart failure Am J Cardiol 62:68E-71E
Morita H, Vatner SF (1985) Effects of hemorrhage on renal nerve activity in conscious dogs. Cir Res 57:788–793
Persson P, Ehmke H, Kirchheim H (1988a) Influence of the renin-angiotensin-system on the autoregulation of renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate in conscious dogs. Acta Physiol Scand 134:1–7
Persson P, Ehmke H, Nafz B, Kirchheim H (1988b) Einfluß des Sympathikus auf die renale Autoregulation am wachen Hund. Nieren- und Hochdruckkrankheiten 17 (Heft 9):336
Persson P, Ehmke H, Kögler U, Kirchheim H (1989) Modulation of natriuresis by sympathetic nerves and angiotensin II in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 256:F485-F489
Smith HW (1951) The Kidney. Structure and Function in Health and Disease. Oxford University Press, New York
Thames MD (1984) Renin release: Reflex control and adrenergic mechanisms. J Hypertension 2 (Suppl 1):57–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirchheim, H., Ehmke, H. & Persson, P. Sympathetic modulation of renal hemodynamics, renin release and sodium excretion. Klin Wochenschr 67, 858–864 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01717340
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01717340