Summary
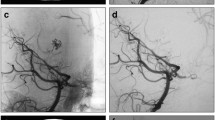
We studied the CT findings of 23 AVM cases confirmed by cerebral angiography and their clinical findings, and discussed mainly the lesions of ruptured AVM in the acute stage.
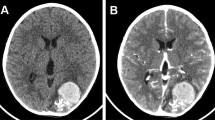
The 10 cases, in which CT was performed within 7 days after the onset of a ruptured AVM, presented with blood stained CSF except for two cases. All of the 10 cases showed intracerebral haemorrhages in the CT findings, and four of these cases were associated with ventricular rupture. In the plain CT of these 10 cases, high density in the cerebral cistern, such as seen in the acute stage of ruptured intracranial aneurysms, was not found except for 1 case.
In the enhanced CT within 7 days after the onset of ruptured AVM, no enhanced findings were found in eight cases. On the contrary, in 12 cases in which CT was performed later than the 8th day after the onset, enhanced findings were found in 11 cases.
It has been previously reported that SAH is seen in the lesion of ruptured AVM in the acute stage. From our CT findings of ruptured AVM in the acute stage, however, it was concluded that the lesion of a ruptured AVM in the acute stage does nat cause SAH but an intracerebral haematoma or ventricular rupture and that blood may enter the CSF only secondarily.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, B. A., Kendall, B. E., Symon, L.,et al., Angiographically occult arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.41 (1978), 1057–1064.
Hayward, R. D., Intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Observations after experience with computerized tomography. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.39 (1976), 1027–1033.
Kendall, B. E., Claveria, L. E., The use of computed axial tomography (CAT) for the diagnosis and management of intracranial angiomas. Neuroradiology12 (1976), 141–160.
Kramer, R. A., Wing, S. D., Computed tomography of angiographically occult cerebral vascular malformations. Radiology123 (1977), 649–652.
Lukin, R. R., Chambers, A. A., Tomsick, T. A., Cerebral vascular lesions. Infarction, hemorrhage, aneurysm, and arteriovenous malformation. Semin. Roentgenol.12 (1977), 77–89.
Mackenzie, I., The clinical presentation of the cerebral angioma. A review of 50 cases. Brain76 (1953), 184–214.
Maspes, P. E., Marini, G., Results of the surgical treatment of intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Vasc. Surg.4 (1970), 164–170.
Olivecrona, H., Riives, J., Arteriovenous aneurysm of the brain. Their diagnosis and treatment. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat.59 (1948), 567–602.
Paterson, J. H., McKissock, W., A clinical survey of intracranial angiomas with special reference to their mode of progression and surgical treatment. A report of 110 cases. Brain79 (1956), 233–266.
Paxton, R., Ambrose, J., The EMI scanner. A brief review of the first 650 patients. Brit. J. Radiol.47 (1974), 530–565.
Perret, G., Nishioka, H., Report on the cooperative study of intracranial aneurysm and subarachnoid hemorrhage, section VI arteriovenous malformation. J. Neurosurg.25 (1966), 467–490.
Pressman, S. D., Kirkwood, J. R., Davis, D. O., Computerized transverse tomography of vascular lesions of the brain. Amer. J. Roentgenol.124 (1975), 208–214.
Terbrugge, K., Scott, G., Ethier, R.,et al., Computed tomography in intracranial arteriovenous malformation. Radiology122 (1977), 703–705.
Tönnis, W., Schiefer, W., Walter, W., Signs and symptoms of supratentorial arteriovenous aneurysm. J. Neurosurg.15 (1958), 471–480.
Troupp, H., Marttila, I., Halonen, V., Arteriovenous malformations of the brain. Prognosis without operation. Acta neurochir. (Wien)22 (1970), 125–128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, S., Sonobe, M., Shirane, R. et al. Computer tomography of ruptured intracranial arteriovenous malformations in the acute stage. Acta neurochir 66, 87–94 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01809307
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01809307