Abstract
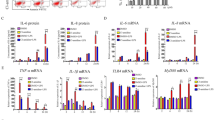
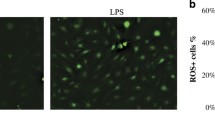
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process that ultimately results in tooth loss. Although the primary etiologic agent for periodontitis is bacteria, the majority of periodontal tissue destruction is thought to be caused by an inappropriate host response. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been known to be involved in periodontal tissue destruction. We treated human gingival fibroblasts with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) obtained fromE. coli and the periodontopathogensActinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans andPorphyromonas gingivalis, and examined their inflammatory responses in the presence and absence of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC). LPS enhanced ROS production, as well as, expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α, and the production and activation of MMP2. NAC suppressed all LPS-induced inflammatory responses examined, suggesting that LPS-induced ROS may play a major regulatory role in these responses in gingival fibroblasts. In addition, NAC prevented LPS-induced activation of p38 MAPK and JNK but not phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of IkB. These results indicate that NAC exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-stimulated gingival fibroblasts, functioning at least in part via down-regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK activation. Furthermore, this work suggests that antioxidants may be useful in adjunctive therapies that complement conventional periodontal treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. T., Staal, F. J., Gitler, C, Herzenberg, L. A., and Herzenberg, L. A., Separation of oxidant-initiated and redox- regulated steps in the NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 91, 11527–11531 (1994).
Andreakos, E., Sacre, S. M., Smith, C, Lundberg, A., Kiriakidis, S., Stonehouse, T., Monaco, C, Feldmann, M., and Foxwell, B. M., Distinct pathways of LPS-induced NF-kappa B activation and cytokine production in human myeloid and nonmyeloid cells defined by selective utilization of MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP.Blood, 103, 2229–2237 (2004).
Asehnoune, K., Strassheim, D., Mitra, S., Kim, J. Y, and Abraham, E., Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll- like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B.J. Immunol., 172, 2522–2529 (2004).
Bass, D. A., Parce, J. W., Dechatelet, L. R., Szejda, P., Seeds, M. C, and Thomas, M., Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation.J. Immunol., 130, 1910–1917 (1983).
Beyaert, R., Cuenda, A., Vanden Berghe, W., Plaisance, S., Lee, J. C, Haegeman, G, Cohen, P., and Fiers, W., The p38/ RK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway regulates interleukin-6 synthesis response to tumor necrosis factor.EMBOJ., 15, 1914–1923 (1996).
Birkedal-Hansen, H., Role of cytokines and inflammatory mediators in tissue destruction.J. Periodontal Res., 28, 500–510 (1993a).
Birkedal-Hansen, H., Role of matrix metalloproteinases in human periodontal diseases.J. Periodontol., 64, 474–484 (1993b).
Bodet, C, Andrian, E., Tanabe, S. I., and Grenier, D., Actinoba- cillus actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide regulates matrix metalloproteinase, tissue inhibitors of matrix metallo- proteinase, and plasminogen activator production by human gingival fibroblasts: A potential role in connective tissue destruction.J. Cell. Physiol., 212, 189–194 (2007).
Brennan, P. and O’Neill, L. A., Effects of oxidants and antioxidants on nuclear factor kappa B activation in three different cell lines: evidence against a universal hypothesis involving oxygen radicals.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1260, 167–175 (1995).
Brock, G R., Butterworth, C. J., Matthews, J. B., and Chappie, I. L. C, Local and systemic total antioxidant capacity in periodontitis and health.J. Clin. Periodontol., 31, 515–521 (2004).
Brook, M., Sully, G, Clark, A. R., and Saklatvala, J., Regulation of tumour necrosis factor alpha mRNA stability by the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 signalling cascade.FEBS Lett., 483, 57–61 (2000).
Chakraborti, S., Mandal, M., Das, S., Mandal, A., and Chakraborti, T., Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: an overview.Mol. Cell. Biochem., 253, 269–285 (2003).
Chapple, I. L. and Matthews, J. B., The role of reactive oxygen and antioxidant species in periodontal tissue destruction.Periodontol 2000., 43, 160–232 (2007).
Chappie, I. L. C, Brock, G, Eftimiade, C, and Matthews, J. B., Glutathione in gingival crevicular fluid and its relation to local antioxidant capacity in periodontal health and disease.Mol. Pathol., 55, 367–373 (2002).
Cho, S. Y, Park, S. J., Kwon, M. J., Jeong, T. S., Bok, S. H., Choi, W. Y, Jeong, W. I., Ryu, S. Y, Do, S. H., Lee, C. S., Song, J. C, and Jeong, K. S., Quercetin suppresses proinflammatory cytokines production through MAP kinases and NF-kappaB pathway in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage.Mol. Cell. Biochem., 243, 153–160 (2003).
Creemers, L. B., Jansen, I. D., Docherty, A. J., Reynolds, J. J., Beertsen, W., and Everts, V, Gelatinase A (MMP-2) and cysteine proteinases are essential for the degradation of collagen in soft connective tissue.Matrix Biol., 17, 35–46 (1998).
De la Fuente, M. and Victor, V. M., Anti-oxidants as modulators of immune function.Immunol. Cell Biol., 78, 49–54 (2000).
Di Paola, R., Mazzon, E., Zito, D., Maiere, D., Britti, D., Genovese, T., and Cuzzocrea, S., Effects of Tempol, a membrane- permeable radical scavenger, in a rodent model periodontitis.J. Clin. Periodontol., 32, 1062–1068 (2005).
Galli, A., Svegliati-Baroni, G, Ceni, E., Milani, S., Ridolfi, F., Salzano, R., Tarocchi, M., Grappone, C, Pellegrini, G, Benedetti, A., Surrenti, C, and Casini, A., Oxidative stress stimulates proliferation and invasiveness of hepatic stellate cells via a MMP2-mediated mechanism.Hepatology, 41, 1074–1084 (2005).
Graves, D. T. and Cochran, D., The contribution of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor to periodontal tissue destruction.J. Periodontol., 74, 391–401 (2003).
Gustafsson, A. and Asman, B., Increased release of free oxygen radicals from peripheral neutrophils in adult periodontitis after Fc delta-receptor stimulation.J. Clin. Periodontol., 23, 38–44 (1996).
Haddad, J. J., L-Buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine, an irreversible inhibitor of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase, augments LPS-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis: evidence for the implication of an IkappaB-alpha/NF-kappaB insensitive pathway.Eur. Cytokine Netw., 12, 614–624 (2001).
Haffajee, A. D. and Socransky, S. S., Microbiology of periodontal diseases: introduction.Periodontol. 2000, 38, 9–12 (2005).
Hall, T. J., Schaeublin, M., Jeker, H, Fuller, K., and Chambers, T. J., The role of reactive oxygen intermediates in osteoclastic bone resorption.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 207, 280–287 (1995).
Heumann, D. and Roger, T., Initial responses to endotoxins and Gram-negative bacteria.Clin. Chim. Acta, 323, 59–72 (2002).
Hidding, U., Mielke, K., Waetzig, V, Brecht, S., Hanisch, U., Behrens, A., Wagner, E., and Herdegen, T., The c-Jun N- terminal kinases in cerebral microglia: immunological functions in the brain.Biochem. Pharmacol., 64, 781–788 (2002).
Hsu, H. Y and Wen, M. H., Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression.J. Biol. Chem., 277, 22131–22139 (2002).
Janssen-Heininger, Y M., Poynter, M. E., and Baeuerle, P. A., Recent advances towards understanding redox mechanisms in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB.Free Radic. Biol. Med., 28, 1317–1327 (2000).
Karin, M., Signal transduction from cell surface to nucleus in development and disease.FASEBJ., 6, 2581–2590 (1992).
Kim, S. H., Kim, J., and Sharma, R. P., Inhibition of p38 and ERK MAP kinases blocks endotoxin-induced nitric oxide production and differentially modulates cytokine expression.Pharmacol. Res., 49, 433–439 (2004).
Kimura, S., Yonemura, T., and Kaya, H., Increased oxidative product formation by peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes in human periodontal diseases.J. Periodontal Res., 28, 197–203 (1993).
Korostoff, J. M., Wang, J. F, Sarment, D. P., Stewart, J. C, Feldman, R. S., and Billings, P. C, Analysis of in situ protease activity in chronic adult periodontitis patients: expression of activated MMP-2 and a 40 kDa serine protease.J. Periodontol., 71, 353–360 (2000).
Lee, N. K., Choi, Y G, Baik, J. Y, Han, S. Y, Jeong, D. W., Bae, Y. S., Kim, N., and Lee, S. Y, A crucial role for reactive oxygen species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.Blood, 106, 852–859 (2005).
Mastronarde, J. G, Monick, M. M., Mukaida, N., Matsushima, K., and Hunninghake, G W., Activator protein-1 is the preferred transcription factor for cooperative interaction with nuclear factor-kappaB in respiratory syncytial virus-induced interleukin-8 gene expression in airway epithelium.J. Infect. Dis., 177, 1275–1281 (1998).
Mathy-Hartert, M., Deby-Dupont, G P., Reginster, J. Y, Ayache, N., Pujol, J. P., and Henrotin, Y E., Regulation by reactive oxygen species of interleukin-1 beta, nitric oxide and prostaglandin E(2) production by human chondrocytes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 10, 547–555 (2002).
Mathy-Hartert, M., Martin, G, Devel, P., Deby-Dupont, G, Pujol, J. P., Reginster, J. Y, and Henrotin, Y, Reactive oxygen species downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory genes by human chondrocytes.Inflamm. Res., 52, 111–118 (2003).
McCulloch, C. A. and Bordin, S., Role of fibroblast sub- populations in periodontal physiology and pathology.J. Periodontal Res., 26, 144–154 (1991).
Means, T. K., Golenbock, D. T., and Fenton, M. J., Structure and function of Toll-like receptor proteins.Life. Sci., 68, 241–258 (2000).
Minden, A. and Karin, M., Regulation and function of the JNK subgroup of MAP kinases.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1333, F85-F104 (1997).
Morse, D., Pischke, S. E., Zhou, Z., Davis, R. J., Flavell, R. A., Loop, T., Otterbein, S. L, Otterbein, L. E., and Choi, A. M., Suppression of inflammatory cytokine production by carbon monoxide involves the JNK pathway and AP-1.J. Biol. Chem., 278, 36993–36998 (2003).
Nagase, H. and Woessner, J. F. Jr., Matrix metalloproteinases.J. Biol. Chem., 274, 21491–21494 (1999).
Okada, H. and Murakami, S., Cytokine expression in periodontal health and disease.Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med., 9, 248–266 (1998).
Park, S. Y, Kim, Y H., Jun, J. H., Kim, G. S., Min, B. M., and Baek, J. H., P. gingivalis and A. actinomycetemcomitans LPS differentially regulate the expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in gingival fibroblast and periodontal ligament fibroblast.Int. J. Oral Biol., 29, 7–16 (2004).
Rajagopalan, S., Meng, X. P., Ramasamy, S., Harrison, D. G, and Galis, Z. S., Reactive oxygen species produced by macrophage-derived foam cells regulate the activity of vascular matrix metalloproteinases in vitro. Implications for atherosclerotic plaque stability.J. Clin. Invest, 98, 2572–2579 (1996).
Ryan, K. A., Smith, M. F. Jr., Sanders, M. K., and Ernst, P. B., Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species differentially regulate Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of NF-kappa B and interleukin-8 expression.Infect. Immun., 72, 2123–2130 (2004).
Sanchez-Tillo, E., Comalada, M., Xaus, J., Farrera, C, Valledor, A. F, Caelles, C, Lloberas, J., and Celada, A., JNK1 is required for the induction of MKP1 expression in macrophages during proliferation and LPS-dependent activation.J. Biol. Chem., 282, 12566–12573 (2007).
Schreck, R., Albermann, K., and Baeuerle, P. A., Nuclear factor kappa B: an oxidative stress-responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review).Free Radic. Res. Commun., 17, 221–237 (1992).
Schubert, S. Y, Neeman, I., and Resnick, N., A novel mechanism for the inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in vascular endothelial cells by natural antioxidants.FASEB J., 16, 1931- 1933 (2002).
Seger, R. and Krebs, E. G, The MAPK signaling cascade.FASEB J., 9, 726–735 (1995).
Strassheim, D., Asehnoune, K., Park, J. S., Kim, J. Y, He, Q., Richter, D., Mitra, S., Arcaroli, J., Kuhn, K., and Abraham, E., Modulation of bone marrow-derived neutrophil signaling by H2O2: disparate effects on kinases, NF-kappaB, and cytokine expression.Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 286, C683-C692 (2004).
Tiranathanagul, S., Yongchaitrakul, T, Pattamapun, K., and Pavasant, P., Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans lipo- polysaccharide activates matrix metalloproteinase-2 and increases receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand expression in human periodontal ligament cells.J. Penodontol., 75, 1647–1654 (2004).
Victor, V. M. and De la Fuente, M., N-acetylcysteine improves in vitro the function of macrophages from mice with endotoxin- induced oxidative stress.Free Radic. Res., 36, 33–45 (2002).
Victor, V. M., Rocha, M., and De la Fuente, M., N-acetylcysteine protects mice from lethal endotoxemia by regulating the redox state of immune cells.Free Radic. Res., 37, 919–929 (2003).
Winyard, P. G and Blake, D. R., Antioxidants, redox-regulated transcription factors, and inflammation.Adv. Pharmacol., 38, 403–421 (1997).
Woo, C. H., Lim, J. H., and Kim, J. H., Lipopolysaccharide induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-p38 kinase-activator protein-1 pathway in Raw 264.7 cells.J. Immunol., 173, 6973–6980 (2004).
Zafarullah, M., Li, W. Q., Sylvester, J., and Ahmad, M., Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions.Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 60, 6–20 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.Y., Jun, JH., Lee, HL. et al. N-acetyicysteine prevents lps-lnduced pro-inflammatory cytokines and mmp2 production in gingival fibroblasts. Arch. Pharm. Res. 30, 1283–1292 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980269
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980269