Abstract
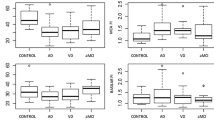
Primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type and multi-infarct dementia exhibit differences in cerebrovascular blood flow velocity profiles, which were investigated by means of transcranial Doppler sonography. The pulsatility indices, as angle-independent parameters of peripheral vascular resistance, measured in middle cerebral and basilar arteries of patients with multi-infarct dementia (MID), were significantly increased (p<0.005) with respect to cases of primary degenerative dementia of the Alzheimer type and to healthy age-matched controls. Approximately 75% of all MID patients exhibited small vessel disease rather than thromboembolism from the extracranial arteries and the heart, as judged by extracranial and transcranial Doppler sonographies, computerized cerebral tomographies, EEGs, and, if necessary, 2-D echocardiographies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaslid R., Markwalder T. M., and Nornes H. (1982) Noninvasive transcranial ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries.J. Neurosurg. 57, 769–774.
American Psychiatric Association (1987)Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (3rd ed., rev. ed). American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC, pp. 103–123.
Arnolds B. and von Reutern G. M. (1986) Transcranial Doppler sonography: Examination technique and normal reference values.Ultrasound Med. Biol. 12, 115–123.
Biedert S., Foerstl H., and Hewer W. (1990) Transcranial Doppler sonography in the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and multi-infarct dementia.J. Cardiovasc. Technol. 9, 153–155.
Bishop C. C. R., Powell S., Rutt D., and Browse N. L. (1986) Transcranial Doppler measurement of middle cerebral artery flow velocity: A validation study.Stroke 17, 913–915.
Corsellis J. A. N. (1969) The pathology of dementia.Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2, 695–702.
Deutsch G. and Tweedy J. R. (1987) Cerebral blood flow in severity-matched Alzheimer and multi-infarct patients.Neurology 37, 431–438.
Foerstl H., Biedert S., and Hewer W. (1989) Multiinfarct and Alzheimer-type dementia investigated by transcranial Doppler sonography.Biol. Psychiatry 26, 590–594.
Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., and McHugh P. R. (1975) “Mini-Mental-State.” A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician.J. Psychiatr. Res. 12, 189–198.
Hachinski V. C., Lassen N. A., and Marshall J. (1974) Multi-infarct dementia: A cause of mental deterioration in the elderly.Lancet 2, 207–209.
Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J. (Ross Russell R. W., and Symon L. (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia.Arch. Neurol. 32, 632–637.
Hennerici M., Rautenberg W., Sitzer G., and Schwartz A. (1987) Transcranial Doppler ultrasound for the assessment of intracranial arterial flow velocity. Part I.Surg. Neurol. 27, 429–448.
Liston E. H. and LaRue A. (1983) Clinical differentiation of primary degenerative and multi-infarct dementia: A critical review of the evidence. Part II: Pathological studies.Biol. Psychiatry 18, 1467–1484.
Mattle H., Grolimund P., Huber P., Sturzenegger M., and Zurbruegg H. R. (1988) Transcanial Doppler sonographic findings in middle cerebral artery disease.Arch. Neurol. 45, 289–295.
McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., and Stadlan E. M. (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Report of the NINCDSADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease.Neurology 34, 939–944.
Rogers R. L., Meyer J. S., Mortel K. F., Mahurin R. K., and Judd B. W. (1986) Decreased cerebral blood flow precedes multi-infarct dementia, but follows senile dementia of Alzheimer type.Neurology 36, 1–6.
St. Clair D. and Whalley L. J. (1983) Hypertension, multi-infarct dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.Br. J. Psychiat. 143, 274–276.
Shaw T. G., Mortel K. F., Meyer J. S., Rogers R. L., Hardenberg J., and Cutaia M. M. (1984) Cerebral blood flow changes in benign aging and cerebrovascular disease.Neurology 34, 855–866.
Shiraishi J., Inaoka H., Okuda J., and Kaneko Z. (1979) Cerebral circulation in the aged with organic dementia.Jpn. J. Geriatr. 16, 7–16.
Tierney M. C., Fisher R. H., Lewis A. J., Zorzitto M. L., Snow W. G., Reid D. W., and Nieuwstraten P. (1988) The NINCDS-ADRDA work group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer’s disease: A clinicopathologic study of 57 cases.Neurology 38, 359–364.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biedert, S., Förstl, H. & Hewer, W. The value of transcranial Doppler sonography in the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer disease vs multi-infarct dementia. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 19, 15–23 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160165
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160165