Abstract
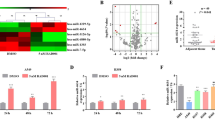
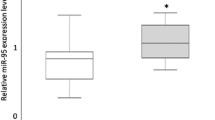
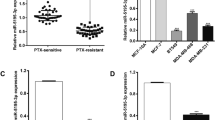
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Paclitaxel, either as monotherapy or combined with other agents, is the standard treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the most common type of lung cancer. However, both de novo and acquired resistance against paclitaxel frequently occurs and represents a huge clinical problem. The underlying mechanisms remain poorly characterized. Here, by comparing microRNA (miRNA) expression levels using miRNA arrays, we observed differential expression of miR-30a-5p in two independent lung cancer cell pairs (paclitaxel-resistant vs paclitaxel-sensitive A549 cell lines). Overexpression of miR-30a-5p sensitizes NSCLC cells to paclitaxel both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, miR-30a-5p increases paclitaxel sensitivity by promoting chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via downregulating BCL-2, a key apoptosis regulator. High miR-30a-5p expression is positively correlated with enhanced responsiveness to paclitaxel and predicts a more favorable clinical outcome in NSCLC patients. Moreover, miR-30a-5p expression is negatively correlated with BCL-2 expression in NSCLC tissues. These data indicate that miR-30a-5p may be useful to treat paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer and may also provide a biomarker to predict paclitaxel responsiveness in lung cancer.
Key messages
-
BCL-2 is a novel direct target of miR-30a-5p.
-
miR-30a-5p enhances NSCLC paclitaxel sensitivity in vitro and in vivo.
-
miR-30a-5p sensitizes NSCLC cells to paclitaxel by inducing apoptosis through BCL-2 inhibition.
-
miR-30a-5p negatively correlates with BCL-2 and predicts a favorable clinical outcome in NSCLC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29
Chang AY, Kim K, Glick J, Anderson T, Karp D, Johnson D (1993) Phase II study of taxol, merbarone, and piroxantrone in stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: the eastern cooperative oncology group results. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:388–394
Murphy WK, Fossella FV, Winn RJ, Shin DM, Hynes HE, Gross HM, Davilla E, Leimert J, Dhingra H, Raber MN et al (1993) Phase II study of taxol in patients with untreated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:384–388
Zheng H, Liu Z, Liu T, Cai Y, Wang Y, Lin S, Chen J, Wang J, Wang Z, Jiang B (2014) Fas signaling promotes chemoresistance in gastrointestinal cancer by up-regulating P-glycoprotein. Oncotarget 5:10763–10777
Vargas JR, Stanzl EG, Teng NN, Wender PA (2014) Cell-penetrating, guanidinium-rich molecular transporters for overcoming efflux-mediated multidrug resistance. Mol Pharm 11:2553–2565
Goncalves A, Braguer D, Kamath K, Martello L, Briand C, Horwitz S, Wilson L, Jordan MA (2001) Resistance to Taxol in lung cancer cells associated with increased microtubule dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11737–11742
He W, Zhang D, Jiang J, Liu P, Wu C (2014) The relationships between the chemosensitivity of human gastric cancer to paclitaxel and the expressions of class III β-tubulin, MAPT, and survivin. Med Oncol 31:950
Kavallaris M (2010) Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat Rev Cancer 10:194–204
Ingemarsdotter CK, Tookman LA, Browne A, Pirlo K, Cutts R, Chelela C, Khurrum KF, Leung EY, Dowson S, Webber L et al (2015) Paclitaxel resistance increases oncolytic adenovirus efficacy via upregulated CAR expression and dysfunctional cell cycle control. Mol Oncol 9:791–805
Choi JH, Sheu JJ, Guan B, Jinawath N, Markowski P, Wang TL, Shih IM (2009) Functional analysis of 11q13.5 amplicon identifies Rsf-1 (HBXAP) as a gene involved in paclitaxelresistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 69:1407–1415
Le XF, Bast RC Jr (2011) Src family kinases and paclitaxel sensitivity. Cancer Biol Ther 12:260–269
Peng X, Gong F, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Liu J, Yu M, Zhang S, Wang M, Xiao G, Liao H (2014) Autophagy promotes paclitaxel resistance of lung cancer cells: involvement of Warburg effect activated hypoxia-induced factor 1-α-mediated signaling. Cell Death Dis 5:e1367
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay D, Chakrabarti G (2015) MiR-16 targets Bcl-2 in paclitaxel-resistant lung cancer cells and overexpression of miR-16 along with miR-17 causes unprecedented sensitivity by simultaneously modulating autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal 27:189–203
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay D (2014) Chakrabarti G (2014) miR-17-5p downregulation contributes to paclitaxel resistance of lung cancer cells through altering beclin1 expression. PLoS One 9:e95716
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Database issue):D140–D144
Kanakkanthara A, Miller JH (2013) MicroRNAs: novel mediators of resistance to microtubule-targeting agents. Cancer Treat Rev 39:161–170
Fu J, Xu X, Kang L, Zhou L, Wang S, Lu J, Cheng L, Fan Z, Yuan B, Tian P et al (2014) miR-30a suppresses lung cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting Eya2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445:314–319
Tsukasa K, Ding Q, Miyazaki Y, Matsubara S, Natsugoe S, Takao S (2016) miR-30 family promotes migratory and invasive abilities in CD133(+) pancreatic cancer stem-like cells. Hum Cell 29:130–137
Sestito R, Cianfrocca R, Rosanò L, Tocci P, Semprucci E, Di Castro V, Caprara V, Ferrandina G, Sacconi A, Blandino G, Bagnato A (2016) miR-30a inhibits endothelin A receptor and chemoresistance in ovarian carcinoma. Oncotarget 7:4009–4023
Xu X, Fan Z, Kang L, Han J, Jiang C, Zheng X, Zhu Z, Jiao H, Lin J, Jiang K et al (2013) Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 123:630–645
Ji Q, Xu X, Xu Y, Fan Z, Kang L, Li L, Liang Y, Guo J, Hong T, Li Z et al (2016) miR-105/Runx2 axis mediates FGF2-induced ADAMTS expression in osteoarthritis cartilage. J Mol Med 94:681–694
Lee JH, Kim C, Sethi G, Ahn KS (2015) Brassinin inhibits BCL-2 signaling pathway through modulation of PIAS-3 and SOCS-3 expression and sensitizes human lung cancer xenograft in nude mice to paclitaxel. Oncotarget 6:6386–6405
Al-Dimassi S, Abou-Antoun T, El-Sibai M (2014) Cancer cell resistance mechanisms: a mini review. Clin Transl Oncol 16:511–516
Shajahan AN, Dobbin ZC, Hickman FE, Dakshanamurthy S, Clarke R (2012) Tyrosine-phosphorylated caveolin-1 (Tyr-14) increases sensitivity to paclitaxel by inhibiting BCL2 and BCLxL proteins via c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). J Biol Chem 287:17682–17692
Periti P, Mini E (1989) Drug resistance in cancer: an overview of the clinical aspects. J Chemother 1:5–9
Fan Z, Cui H, Yu H, Ji Q, Kang L, Han B, Wang J, Dong Q, Li Y, Yan Z et al (2016) MiR-125a promotes paclitaxel sensitivity in cervical cancer through altering STAT3 expression. Oncogene 5:e223
Shen Y, Wang P, Li Y, Ye F, Wang F, Wan X, Cheng X, Lu W, Xie X (2013) miR-375 is upregulated in acquired paclitaxel resistance in lung cancer. Br J Cancer 109:92–99
Li B, Ren S, Li X, Wang Y, Garfield D, Zhou S, Chen X, Su C, Chen M, Kuang P et al (2014) MiR-21 overexpression is associated with acquired resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 83:146–153
Yuan Y, Zheng S, Li Q, Xiang X, Gao T, Ran P, Sun L, Huang Q, Xie F, Du J, Xiao C (2016) Overexpression of miR-30a in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell line inhibits migration and invasion via targeting EYA2. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 48:220–228
Wen XP, Ma HL, Zhao LY, Zhang W, Dang CX (2015) MiR-30a suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression through AKT signaling pathway by targeting IGF1R. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 61:78–85
Li WF, Dai H, Ou Q, Zuo GQ, Liu CA (2016) Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol 37:5885–5895
Ji Q, Xu X, Zhang Q, Kang L, Xu Y, Zhang K, Li L, Liang Y, Hong T, Ye Q, Wang Y (2016) The IL-1β/AP-1/miR-30a/ADAMTS-5 axis regulates cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis. J Mol Med 94:771–785
Wang P, Zhang N, Liang J, Li J, Han S, Li J (2015) Micro-RNA-30a regulates ischemia-induced cell death by targeting heat shock protein HSPA5 in primary cultured cortical neurons and mouse brain after stroke. J Neurosci Res 93:1756–1768
Chen Z, Wang T, Liu Z, Zhang G, Wang J, Feng S, Liang J (2015) Inhibition of autophagy by MiR-30A induced by mycobacteria tuberculosis as a possible mechanism of immune escape in human macrophages. Jpn J Infect Dis 68:420–424
Qi F, He T, Jia L, Song N, Guo L, Ma X, Wang C, Xu M, Fu Y, Li L, Luo Y (2015) The miR-30 family inhibits pulmonary vascular hyperpermeability in the premetastatic phase by direct targeting of Skp2. Clin Cancer Res 21:3071–3080
Wan Q, Zhou Z, Ding S, He J (2015) The miR-30a negatively regulates IL-17-mediated signal transduction by targeting Traf3ip2. J Interf Cytokine Res 35:917–923
Wang LL, Zhang XH, Zhang X, Chu JK (2016) MiR-30a increases cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells through suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:1733–1739
Hata AN, Engelman JA, Faber AC (2015) The BCL2 family: key mediators of the apoptotic response to targeted anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Discov 5:475–487
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (81330053, 81372161, 81472589, 81630067, 81672602, 81502264, and 81572597) and Beijing Nova Program (Z141102001814055). Beijing Institute of Biotechnology and PLA General Hospital contribute to this work equally.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1023 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Jin, S., Ma, Y. et al. miR-30a-5p enhances paclitaxel sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer through targeting BCL-2 expression. J Mol Med 95, 861–871 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1539-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1539-z