Abstract
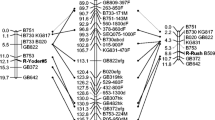
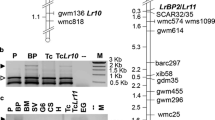
A total of 1,110 decamer primers were screened for RAPD markers linked to a dominant allele in hazelnut (Corylus avellana) that confers resistance to eastern filbert blight caused by Anisogramma anomala. Twenty RAPD markers linked in coupling, and five markers linked in repulsion, were found. A seedling population was used to construct a linkage map of the region flanking the resistance locus. The map spans 46.6 cM, with 14 markers on one side of the resistance locus and eight on the other side. Eleven markers showed less than 3% recombination with resistance, including three that showed no recombination. Seven of these 11 markers are sufficiently robust to allow their use in marker-assisted selection. These include AA12850 which shows no recombination, and six markers on one side of the resistance locus: 173500, 152800, 122825, 2751130, H19650 and O161250. Marker 268580, which flanks the resistance locus on the other side, is also suitable for use in marker-assisted selection, but shows 5.8% recombination with resistance. Other markers are less suitable for marker-assisted selection because of sensitivity to changes in primer or MgCl2 concentration, or the long time required for electrophoresis to separate bands of similar size. The 16 markers closest to the resistance locus were cloned and sequenced. The W07365 marker, which showed no recombination with the resistance locus but is difficult to score, includes a CT microsatellite repeat. The sequence information will allow the design of SCAR primers and eventual map-based cloning of the resistance allele.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coyne CJ, Mehlenbacher SA, Hampton RO, Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB (1996) Use of ELISA to rapidly screen hazelnut for resistance to eastern filbert blight. Plant Dis 80:1327–1330
Davis JW, Mehlenbacher SA (1997) Identification of RAPD markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in hazelnut. Acta Hortic 445:553–556
Davis J, Henderson D, Kobayashi M, Clegg MT (1998) Genealogical relationships among cultivated avocado as revealed through RFLP analyses. J Hered 89:319–323
Johnson KB, Pscheidt JW, Pinkerton JN (1993) Evaluation of chlorothalonil, fenarimol, and flusilazole for control of eastern filbert blight. Plant Dis 77:831–837
Johnson KB, Mehlenbacher SA, Stone JK, Pscheidt JW, Pinkerton JN (1996) Eastern filbert blight of European hazelnut - it’s becoming a manageable disease. Plant Dis 80:1308–1316
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson I, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SL, Newbers L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental populations. Genomics 1:182–195
Lunde CF, Mehlenbacher SA, Smith DC (2000) Survey of hazelnut cultivars for response to eastern filbert blight inoculation. HortScience 35:729–731
Mehlenbacher SA, Thompson MM, Cameron HR (1991) Occurrence and inheritance of resistance to eastern filbert blight in ‘Gasaway’ hazelnut. HortScience 26:410–411
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genome regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9829–9832
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Theiling KM, Griesbach JA (1992) Distribution and characteristics of the eastern filbert blight epidemic in western Oregon. Plant Dis 76:1179–1182
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Stone JK, Ivors KL (1998a) Factors affecting the release of ascospores of Anisogramma anomala. Phytopathology 88:122–128
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Stone JK, Ivors KL (1998b) Maturation and seasonal discharge pattern of ascospores of Anisogramma anomala. Phytopathology 88:1165–1173
Pinkerton JN, Johnson KB, Aylor DE, Stone JK (2001) Spatial and temporal increase of eastern filbert blight in European hazelnut orchards in the Pacific Northwest. Phytopathology 91:1214–1223
Stone JK, Johnson KB, Pinkerton JN, Pscheidt JW (1992) Natural infection period and susceptibility of vegetative seedlings of European hazelnut to Anisogramma anomala. Plant Dis 76:348–352
Wagner DB, Furnier GR, Saghai-Maroof MA, Williams SM, Dancik BP, Allard RW (1987) Chloroplast DNA polymorphisms in lodgepole and jack pines and their hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2097–2100
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Acknowledgements
I thank Ruth Martin for considerable help in cloning and sequencing, and advice on other aspects of this study. This research was supported by the Oregon Hazelnut Commission and a Specific Cooperative Agreement with the United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.B. Neale
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehlenbacher, S.A., Brown, R.N., Davis, J.W. et al. RAPD markers linked to eastern filbert blight resistance in Corylus avellana . Theor Appl Genet 108, 651–656 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1476-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1476-9