Abstract
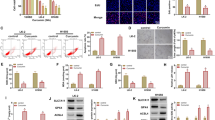
Cryptotanshinone, a well-known diterpene quinone from a widely used traditional Chinese herb named Salvia miltiorrhiza, has been reported for its therapeutical potentials on diverse activities. In this study, pharmacological effects of cryptotanshinone on acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells were investigated. IC50 values of 5.0 and 4.8 were obtained in CEM/ADR5000 and CCRF-CEM. Microarray-based mRNA expression revealed that cryptotanshinone regulated genes associated with cell cycle, DNA damage, reactive oxygen species (ROS), NFκB signaling and cellular movement. The involvement of these pathways in the mode of action of cryptotanshinone was subsequently validated by additional independent in vitro studies. Cryptotanshinone stimulated ROS generation and induced DNA damage. It arrested cells in G2/M phase of the cell cycle and induced apoptosis as measured by annexin V-FITC-conjugating fluorescence. The induction of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by cryptotanshinone was proved by loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and increased cleavage of caspase 3/7, caspase 9 and poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP). DNA-binding motif analysis of the microarray-retrieved deregulated genes in the promoter region revealed NFκB as potential transcription factor involved in cryptotanshinone’s mode of action. Molecular docking and Western blotting provided supportive evidence, suggesting that cryptotanshinone binds to IKK-β and inhibits the translocation of p65 from the cytosol to the nucleus. In addition, cryptotanshinone inhibited cellular movement as shown by a fibronectin-based cellular adhesion assay, indicating that this compound exerts anti-invasive features. In conclusion, cryptotanshinone exerts profound cytotoxicity, which is caused by multispecific modes of actions, including G2/M arrest, apoptosis and inhibition of cellular movement. The inhibitory activities of this compound may be explained by inhibition of NFκB, which orchestrates all these mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang KP, Tan HK, Selvaraja M, Kadir AA, Somchit MN, Akim AM, Zakaria ZA, Ahmad Z (2011) Cryptotanshinone attenuates in vitro oxLDL-induced pre-lesional atherosclerotic events. Planta Med 77:1782–1787. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1271119
Borst P, Schinkel AH (2013) P-glycoprotein ABCB1: a major player in drug handling by mammals. J Clin Invest 123:4131–4133. doi:10.1172/JCI70430
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V, Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S, Smulson M (1999) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol Chem 274:22932–22940. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.33.22932
Chen L, Wang HJ, Xie W, Yao Y, Zhang YS, Wang H (2014) Cryptotanshinone inhibits lung tumorigenesis and induces apoptosis in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep 9:2447–2452. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2093
Chiarini F, Lonetti A, Evangelisti C, Buontempo F, Orsini E, Evangelisti C, Cappellini A, Neri LM, McCubrey JA, Martelli AM (2015) Advances in understanding the acute lymphoblastic leukemia bone marrow microenvironment: from biology to therapeutic targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.08.015
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J (2003) Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J 17:1195–1214. doi:10.1096/fj.02-0752rev
Eberwine J, Yeh H, Miyashiro K, Cao Y, Nair S, Finnell R, Zettel M, Coleman P (1992) Analysis of gene expression in single live neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:3010–3014. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.7.3010
Eck SL, Perkins ND, Carr DP, Nabel GJ (1993) Inhibition of phorbol ester-induced cellular adhesion by competitive binding of NF-kappa B in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 13:6530–6536. doi:10.1128/MCB.13.10.6530
Efferth T (2001) The human ATP-binding cassette transporter genes: from the bench to the bedside. Curr Mol Med 1:45–65. doi:10.2174/1566524013364194
Fleury C, Mignotte B, Vayssière JL (2002) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochemie 84:131–141. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(02)01369-X
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2006) Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25:4798–4811. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209608
Ge Y, Cheng R, Zhou Y, Shen J, Peng L, Xu X, Dai Q, Liu P, Wang H, Ma X, Jia J, Chen Z (2012) Cryptotanshinone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of multidrug resistant human chronic myeloid leukemia cells by inhibiting the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biochem 368:17–25. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1338-3
Gillet JP, Efferth T, Remacle J (2007) Chemotherapy-induced resistance by ATP-binding cassette transporter genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775:237–262. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2007.05.002
Gottesman MM (2002) Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med 53:615–627. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.53.082901.103929
Guo Y, Li Y, Xue L, Severino RP, Gao S, Niu J, Qin LP, Zhang D, Brömme D (2014) Salvia miltiorrhiza: an ancient Chinese herbal medicine as a source for anti-osteoporotic drugs. J Ethnopharmacol 155:1401–1416. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.07.058
Hamm R, Chen YR, Seo EJ, Zeino M, Wu CF, Müller R, Yang NS, Efferth T (2014) Induction of cholesterol biosynthesis by archazolid B in T24 bladder cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 91:18–30. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.06.018
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2012) NF-κB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev 26:203–234. doi:10.1101/gad.183434.111
Hu T, To KK, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu L, Shen J, Chan RL, Li M, Yeung JH, Cho CH (2014) Reversal of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated multidrug resistance in colon cancer cells by cryptotanshinone and dihydrotanshinone of Salvia miltiorrhiza. Phytomedicine 21:1264–1272. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2014.06.013
Jacamo R, Chen Y, Wang Z, Ma W, Zhang M, Spaeth EL, Wang Y, Battula VL, Mak PY, Schallmoser K, Ruvolo P, Schober WD, Shpall EJ, Nguyen MH, Strunk D, Bueso-Ramos CE, Konoplev S, Davis RE, Konopleva M, Andreeff M (2014) Reciprocal leukemia-stroma VCAM-1/VLA-4-dependent activation of NF-κB mediates chemoresistance. Blood 123:2691–2702. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-06-511527
Jena NR, Mishra PC (2012) Formation of ring-opened and rearranged products of guanine: mechanisms and biological significance. Free Radic Biol Med 53:81–94. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.04.008
Jin YC, Kim CW, Kim YM, Nizamutdinova IT, Ha YM, Kim HJ, Seo HG, Son KH, Jeon SJ, Kang SS, Kim YS, Kam SC, Lee JH, Chang KC (2009) Cryptotanshinone, a lipophilic compound of Salvia miltiorrriza root, inhibits TNF-alpha-induced expression of adhesion molecules in HUVEC and attenuates rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 614:91–97. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.038
Juliano RL, Haskill S (1993) Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 120:577–585. doi:10.1083/jcb.120.3.577
Kim EJ, Jung SN, Son KH, Kim SR, Ha TY, Park MG, Jo IG, Park JG, Choe W, Kim SS, Ha J (2007) Antidiabetes and antiobesity effect of cryptotanshinone via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol 72:62–72. doi:10.1124/mol.107.034447
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163. doi:10.1152/physrev.00013.2006
Kryston TB, Georgiev AB, Pissis P, Georgakilas AG (2011) Role of oxidative stress and DNA damage in human carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 711:193–201. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.12.016
Lam FF, Yeung JH, Chan KM, Or PM (2008) Mechanisms of the dilator action of cryptotanshinone on rat coronary artery. Eur J Pharmacol 578:253–260. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.09.040
Lee SY, Choi DY, Woo ER (2005) Inhibition of osteoclast differentiation by tanshinones from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge. Arch Pharm Res 28:909–913. doi:10.1007/BF02973876
Lee WY, Cheung CC, Liu KW, Fung KP, Wong J, Lai PB, Yeung JH (2010) Cytotoxic effects of tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza on doxorubicin-resistant human liver cancer cells. J Nat Prod 73:854–859. doi:10.1021/np900792p
Liu T, Ortiz JA, Taing L, Meyer CA, Lee B, Zhang Y, Shin H, Wong SS, Ma J, Lei Y, Pape UJ, Poidinger M, Chen Y, Yeung K, Brown M, Turpaz Y, Liu XS (2011) Cistrome: an integrative platform for transcriptional regulation studies. Genome Biol 12:R83. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-8-r83
Liu Z, Xu S, Huang X, Wang J, Gao S, Li H, Zhou C, Ye J, Chen S, Jin ZG, Liu P (2015) Cryptotanshinone, an orally bioactive herbal compound from Danshen, attenuates atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice: role of LOX-1. Br J Pharmacol. doi:10.1111/bph.13068
Lockyer JM, Colladay JS, Alperin-Lea WL, Hammond T, Buda AJ (1998) Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated adhesion molecule expression in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 82:314–320. doi:10.1161/01.RES.82.3.314
Lucas DM, Still PC, Pérez LB, Grever MR, Kinghorn AD (2010) Potential of plant-derived natural products in the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma. Curr Drug Targets 11:812–822. doi:10.2174/138945010791320809
Luo F, Gu J, Chen L, Xu X (2014) Systems pharmacology strategies for anticancer drug discovery based on natural products. Mol BioSyst 10:1912–1917. doi:10.1039/c4mb00105b
Mei Z, Zhang F, Tao L, Zheng W, Cao Y, Wang Z, Tang S, Le K, Chen S, Pi R, Liu P (2009) Cryptotanshinone, a compound from Salvia miltiorrhiza modulates amyloid precursor protein metabolism and attenuates beta-amyloid deposition through upregulating alpha-secretase in vivo and in vitro. Neurosci Lett 452:90–95. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.01.013
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791. doi:10.1002/jcc.21256
Mothana RAA, Jansen R, Gruenert R, Bednarski PJ, Lindequist U (2009) Antimicrobial and cytotoxic abietane diterpenoids from the roots of Meriandera benghalensis (Roxb.) Benth. Pharmazie 64:613–615. doi:10.1691/ph.2009.9543
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:143–183. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.47.120505.105122
Park IJ, Yang WK, Nam SH, Hong J, Yang KR, Kim J, Kim SS, Choe W, Kang I, Ha J (2014) Cryptotanshinone induces G1 cell cycle arrest and autophagic cell death by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase signal pathway in HepG2 hepatoma. Apoptosis 19:615–628. doi:10.1007/s10495-013-0929-0
Prasad S, Ravindran J, Aggarwal BB (2010) NF-kappaB and cancer: how intimate is this relationship. Mol Cell Biochem 336:25–37. doi:10.1007/s11010-009-0267-2
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM (2006) Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:219–234. doi:10.1038/nrd1984
Tang S, Shen XY, Huang HQ, Xu SW, Yu Y, Zhou CH, Chen SR, Le K, Wang YH, Liu PQ (2011) Cryptotanshinone suppressed inflammatory cytokines secretion in RAW264.7 macrophages through inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Inflammation 34:111–118. doi:10.1007/s10753-010-9214-3
Tang Y, Chen Y, Chu Z, Yan B, Xu L (2014) Protective effect of cryptotanshinone on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 723:494–500. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.019
Wang Y, Wang S, Li Y, Jiang J, Zhou C, Li C, Li D, Lu L, Liu P, Huang M, Shen X (2014) Therapeutic effect of Cryptotanshinone on collagen-induced arthritis in rats via inhibiting nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway. Transl Res. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2014.12.004
Wong RS (2011) Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:87. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-30-87
Woods D, Turchi JJ (2013) Chemotherapy induced DNA damage response: convergence of drugs and pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 14:379–389. doi:10.4161/cbt.23761
Wrighton CJ, Hofer-Warbinek R, Moll T, Eytner R, Bach FH, de Martin R (1996) Inhibition of endothelial cell activation by adenovirus-mediated expression of IkBa, an inhibitor of the transcription factor NF-kB. J Exp Med 183:1013–1022. doi:10.1084/jem.183.3.1013
Yeh PY, Chuang SE, Yeh KH, Song YC, Cheng AL (2003) Involvement of nuclear transcription factor-kappa B in low-dose doxorubicin-induced drug resistance of cervical carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 66:25–33. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(03)00250-8
Yoo KY, Park SY (2012) Terpenoids as potential anti-Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Molecules 17:3524–3538. doi:10.3390/molecules17033524
Youns M, Hoheisel JD, Efferth T (2010) Traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) for molecular targeted therapies of tumours. Curr Drug Discov Technol 7:37–45. doi:10.2174/157016310791162730
Acknowledgments
We thank the microarray unit of the DKFZ Genomics and Proteomics Core Facility for providing the Illumina Whole-Genome Expression Beadchips and related services as well as the Cytometry Core Facility at the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB, Mainz, Germany) for technical support. We are thankful to the National Science Council (Taiwan) and German Academic Exchange Service for providing a scholarship to Ching-fen Wu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, CF., Klauck, S.M. & Efferth, T. Anticancer activity of cryptotanshinone on acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Arch Toxicol 90, 2275–2286 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1616-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1616-4