Abstract
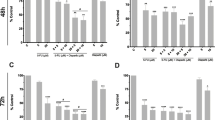
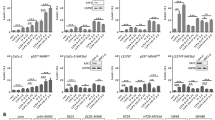
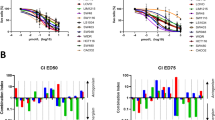
A common strategy to overcome acquired chemotherapy resistance is the combination of a specific anticancer drug (e.g., topoisomerase I inhibitor irinotecan) together with a putative sensitizer. The purpose of this study was to analyze the cytostatic/cytotoxic response of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cells to irinotecan, depending on the mismatch repair (MMR) and p53 status and to examine the impact of BV6, a bivalent antagonist of inhibitors of apoptosis c-IAP1/c-IAP2, alone or combined with irinotecan. Therefore, several MSH2- or MSH6-deficient cell lines were complemented for MMR deficiency, or MSH6 was knocked out/down in MMR-proficient cells. Upon irinotecan, MMR-deficient/p53-mutated lines repaired DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination less efficiently than MMR-proficient/p53-mutated lines and underwent elevated caspase-9-dependent apoptosis. Opposite, BV6-mediated sensitization was achieved only in MMR-proficient/p53-mutated cells. In those cells, c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 were effectively degraded by BV6, caspase-8 was fully activated, and both canonical and non-canonical NF-κB signaling were triggered. The results were confirmed ex vivo in tumor organoids from CRC patients. Therefore, the particular MMR+/p53mt signature, often found in non-metastasizing (stage II) CRC might be used as a prognostic factor for an adjuvant therapy using low-dose irinotecan combined with a bivalent IAP antagonist.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasland D, Gotzinger L, Hauck L et al (2018) Temozolomide induces senescence and repression of DNA repair pathways in glioblastoma cells via activation of ATR-CHK1, p21, and NF-kB. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-1733
Bhonde MR, Hanski ML, Budczies J et al (2006) DNA damage-induced expression of p53 suppresses mitotic checkpoint kinase hMps1: the lack of this suppression in p53MUT cells contributes to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 281(13):8675–8685
Bhonde MR, Hanski ML, Stehr J et al (2010) Mismatch repair system decreases cell survival by stabilizing the tetraploid G1 arrest in response to SN-38. Int J Cancer 126(12):2813–2825. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24893
Christmann M, Diesler K, Majhen D et al (2017) Integrin alphaVbeta3 silencing sensitizes malignant glioma cells to temozolomide by suppression of homologous recombination repair. Oncotarget 8(17):27754–27771. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10897
Fallik D, Borrini F, Boige V et al (2003) Microsatellite instability is a predictive factor of the tumor response to irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 63(18):5738–5744
Fedier A, Schwarz VA, Walt H, Carpini RD, Haller U, Fink D (2001) Resistance to topoisomerase poisons due to loss of DNA mismatch repair. Int J Cancer 93(4):571–576
Fulda S (2014) Regulation of cell migration, invasion and metastasis by IAP proteins and their antagonists. Oncogene 33(6):671–676. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.63
Fulda S, Vucic D (2012) Targeting IAP proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(2):109–124. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3627
Gryfe R, Kim H, Hsieh ET et al (2000) Tumor microsatellite instability and clinical outcome in young patients with colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med 342(2):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200001133420201
Guo J, Verma UN, Gaynor RB, Frenkel EP, Becerra CR (2004) Enhanced chemosensitivity to irinotecan by RNA interference-mediated down-regulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Clin Cancer Res 10(10):3333–3341. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0366
Hausner P, Venzon DJ, Grogan L, Kirsch IR (1999) The ``comparative growth assay”: examining the interplay of anti-cancer agents with cells carrying single gene alterations. Neoplasia 1(4):356–367
Hird AW, Aquila BM, Hennessy EJ, Vasbinder MM, Yang B (2015) Small molecule inhibitor of apoptosis proteins antagonists: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 25(7):755–774. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543776.2015.1041922
Jacob S, Aguado M, Fallik D, Praz F (2001) The role of the DNA mismatch repair system in the cytotoxicity of the topoisomerase inhibitors camptothecin and etoposide to human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(17):6555–6562
Jaquith JB (2014) Targeting the inhibitor of apoptosis protein BIR3 binding domains. Pharm Patent Anal 3(3):297–312. https://doi.org/10.4155/ppa.14.16
Lee EW, Seong D, Seo J, Jeong M, Lee HK, Song J (2015) USP11-dependent selective cIAP2 deubiquitylation and stabilization determine sensitivity to smac mimetics. Cell Death Differ 22(9):1463–1476. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.234
Magrini R, Bhonde MR, Hanski ML et al (2002) Cellular effects of CPT-11 on colon carcinoma cells: dependence on p53 and hMLH1 status. Int J Cancer 101(1):23–31
Reich TR, Switzeny OJ, Renovanz M et al (2017) Epigenetic silencing of XAF1 in high-grade gliomas is associated with IDH1 status and improved clinical outcome. Oncotarget 8(9):15071–15084. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14748
Roig AI, Eskiocak U, Hight SK et al (2010) Immortalized epithelial cells derived from human colon biopsies express stem cell markers and differentiate in vitro. Gastroenterology 138(3):1012–1021. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.11.052
Shiovitz S, Bertagnolli MM, Renfro LA et al (2014) CpG island methylator phenotype is associated with response to adjuvant irinotecan-based therapy for stage III colon cancer. Gastroenterology 147(3):637–645. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.05.009
Steigerwald C, Rasenberger B, Christmann M, Tomicic MT (2018) Sensitization of colorectal cancer cells to irinotecan by the Survivin inhibitor LLP3 depends on XAF1 proficiency in the context of mutated p53. Arch Toxicol 92(8):2645–2648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2240-x
Tomicic MT, Kaina B (2013) Topoisomerase degradation, DSB repair, p53 and IAPs in cancer cell resistance to camptothecin-like topoisomerase I inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1835(1):11–27
Tomicic MT, Bey E, Wutzler P, Thust R, Kaina B (2002) Comparative analysis of DNA breakage, chromosomal aberrations and apoptosis induced by the anti-herpes purine nucleoside analogues aciclovir, ganciclovir and penciclovir. Mutat Res 505(1–2):1–11
Tomicic MT, Christmann M, Kaina B (2005) Topotecan-triggered degradation of topoisomerase I is p53-dependent and impacts cell survival. Cancer Res 65(19):8920–8926
van de Wetering M, Francies HE, Francis JM et al (2015) Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients. Cell 161(4):933–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.053
Varfolomeev E, Blankenship JW, Wayson SM et al (2007) IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131(4):669–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.030
Vilar E, Scaltriti M, Balmana J et al (2008) Microsatellite instability due to hMLH1 deficiency is associated with increased cytotoxicity to irinotecan in human colorectal cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 99(10):1607–1612. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604691
Volcic M, Karl S, Baumann B et al (2012) NF-kappaB regulates DNA double-strand break repair in conjunction with BRCA1-CtIP complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 40(1):181–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr687
Acknowledgements
We thank Anna Frumkina for conducting neutral comet assay. The work was financed by Dr. Mildred Scheel Stiftung für Krebsforschung to MTT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MTT: study design, experimental work, data analysis, paper writing. CS: experimental work. BR: technical assistance, experimental work. AB: contribution to a new model/methodology. MC: discussion and consulting.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomicic, M.T., Steigerwald, C., Rasenberger, B. et al. Functional mismatch repair and inactive p53 drive sensitization of colorectal cancer cells to irinotecan via the IAP antagonist BV6. Arch Toxicol 93, 2265–2277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02513-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02513-7