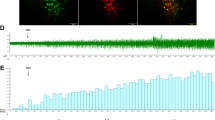
Abstract
Rationale
Peripheral neuropathic pain is a chronic condition that may produce plastic changes in several brain regions. The noradrenergic locus coeruleus (LC) is a crucial component of ascending and descending pain pathways, both of which are frequently compromised after nerve injury.
Objectives
The objective of the study was to examine whether chronic constriction injury (CCI), a model of neuropathic pain, alters noradrenergic activity in the rat LC.
Methods
Activity in the LC was assessed by electrophysiology and microdialysis, while protein expression was monitored in western blots and by immunohistochemistry.
Results
The pain threshold had dropped in injured rats 7 days after inducing neuropathy. While alpha-2-adrenoceptors mediate activity in the LC and in its terminal areas, no alterations in either spontaneous neuronal activity or extracellular noradrenaline levels were observed following CCI. Moreover, alpha-2-adrenoceptor activity in the LC of CCI rats remained unchanged after systemic administration of UK14,304, RX821002 or desipramine. Accordingly, extracellular noradrenaline levels in the LC were similar in CCI and control animals following local administration of clonidine or RX821002. In addition, there were no changes in the expression of the alpha-2-adrenoceptors, Gαi/z subunits or the regulators of G-protein signaling. However, pERK1/2 (phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2) expression augmented in the spinal cord, paragigantocellularis nucleus (PGi) and dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) following CCI.
Conclusions
Neuropathic pain is not accompanied by modifications in tonic LC activity after the onset of pain. This may indicate that the signals from the PGi and DRN, the excitatory and inhibitory afferents of the LC, cancel one another out.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston-Jones G, Bloom FE (1981) Norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats exhibit pronounced responses to non-noxious environmental stimuli. J Neurosci 1:887–900
Aston-Jones G, Ennis M, Pieribone VA, Nickell WT, Shipley MT (1986) The brain nucleus locus coeruleus: restricted afferent control of a broad efferent network. Science 234:734–737
Aston-Jones G, Akaoka H, Charlety P, Chouvet G (1991a) Serotonin selectively attenuates glutamate-evoked activation of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. J Neurosci 11:760–769
Aston-Jones G, Shipley MT, Chouvet G, Ennis M, van Bockstaele E, Pieribone V, Shiekhattar R, Akaoka H, Drolet G, Astier B et al (1991b) Afferent regulation of locus coeruleus neurons: anatomy, physiology and pharmacology. Prog Brain Res 88:47–75
Azami J, Wright DM, Roberts MH (1981) Effects of morphine and naloxone on the responses to noxious stimulation of neurones in the nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis. Neuropharmacology 20:869–876
Basbaum AI, Fields HL (1984) Endogenous pain control systems: brainstem spinal pathways and endorphin circuitry. Annu Rev Neurosci 7:309–338
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Berrocoso E, Mico JA, Ugedo L (2006) In vivo effect of tramadol on locus coeruleus neurons is mediated by alpha2-adrenoceptors and modulated by serotonin. Neuropharmacology 51:146–153
Berrocoso E, De Benito MD, Mico JA (2007) Role of serotonin 5-HT1A and opioid receptors in the antiallodynic effect of tramadol in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:97–105
Bricca G, Zhang J, Greney H, Dontenwill M, Stutzmann J, Belcourt A, Bousquet P (1993) Relevance of the use of [3H]-clonidine to identify imidazoline receptors in the rabbit brainstem. Br J Pharmacol 110:1537–1543
Brightwell JJ, Taylor BK (2009) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus contribute to neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 160:174–185
Cedarbaum JM, Aghajanian GK (1976) Noradrenergic neurons of the locus coeruleus: inhibition by epinephrine and activation by the alpha-antagonist piperoxane. Brain Res 112:413–419
Cedarbaum JM, Aghajanian GK (1978) Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by peripheral stimuli: modulation by a collateral inhibitory mechanism. Life Sci 23:1383–1392
Chapman V, Suzuki R, Dickenson AH (1998) Electrophysiological characterization of spinal neuronal response properties in anaesthetized rats after ligation of spinal nerves L5-L6. J Physiol 507(Pt 3):881–894
Chen SR, Chen H, Yuan WX, Pan HL (2011) Increased presynaptic and postsynaptic {alpha}2-adrenoceptor activity in the spinal dorsal horn in painful diabetic neuropathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337:285–292
Cruz CD, Neto FL, Castro-Lopes J, McMahon SB, Cruz F (2005) Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation decreases nociceptive behaviour in monoarthritic rats. Pain 116:411–419
Dong WQ, Qiao JT, Skolnick M, Dafny N (1991) Focal dorsal raphe stimulation and pinnal electrical stimulation modulate spontaneous and noxious evoked responses in thalamic neurons. Int J Neurosci 57:123–140
Elam M, Svensson TH, Thoren P (1986) Locus coeruleus neurons and sympathetic nerves: activation by cutaneous sensory afferents. Brain Res 366:254–261
Ennis M, Aston-Jones G, Shiekhattar R (1992) Activation of locus coeruleus neurons by nucleus paragigantocellularis or noxious sensory stimulation is mediated by intracoerulear excitatory amino acid neurotransmission. Brain Res 598:185–195
Ernsberger P, Shen IH (1997) Membrane localization and guanine nucleotide sensitivity of medullary I1-imidazoline binding sites. Neurochem Int 30:17–23
Ernsberger P, Graves ME, Graff LM, Zakieh N, Nguyen P, Collins LA, Westbrooks KL, Johnson GG (1995) I1-imidazoline receptors. Definition, characterization, distribution, and transmembrane signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 763:22–42
Ferrari F, Fiorentino S, Mennuni L, Garofalo P, Letari O, Mandelli S, Giordani A, Lanza M, Caselli G (2011) Analgesic efficacy of CR4056, a novel imidazoline-2 receptor ligand, in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 4:111–125
Garzon J, Rodriguez-Munoz M, Lopez-Fando A, Sanchez-Blazquez P (2005a) Activation of mu-opioid receptors transfers control of Galpha subunits to the regulator of G-protein signaling RGS9-2: role in receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem 280:8951–8960
Garzon J, Rodriguez-Munoz M, Lopez-Fando A, Sanchez-Blazquez P (2005b) The RGSZ2 protein exists in a complex with mu-opioid receptors and regulates the desensitizing capacity of Gz proteins. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1632–1648
Georges F, Aston-Jones G (2003) Prolonged activation of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons by morphine withdrawal following clonidine: participation of imidazoline and norepinephrine receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1140–1149
Georges F, Caille S, Vouillac C, Le Moine C, Stinus L (2005) Role of imidazoline receptors in the anti-aversive properties of clonidine during opiate withdrawal in rats. Eur J Neurosci 22:1812–1816
Gilsbach R, Hein L (2008) Presynaptic metabotropic receptors for acetylcholine and adrenaline/noradrenaline. Handb Exp Pharmacol: 261–88
Hajos M, Engberg G, Elam M (1986) Reduced responsiveness of locus coeruleus neurons to cutaneous thermal stimuli in capsaicin-treated rats. Neurosci Lett 70:382–387
Hayashida K, Obata H, Nakajima K, Eisenach JC (2008) Gabapentin acts within the locus coeruleus to alleviate neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 109:1077–1084
Hollinger S, Hepler JR (2002) Cellular regulation of RGS proteins: modulators and integrators of G protein signaling. Pharmacol Rev 54:527–559
Holmberg M, Fagerholm V, Scheinin M (2003) Regional distribution of alpha(2C)-adrenoceptors in brain and spinal cord of control mice and transgenic mice overexpressing the alpha(2C)-subtype: an autoradiographic study with [(3)H]RX821002 and [(3)H]rauwolscine. Neuroscience 117:875–898
Jaggi AS, Singh N (2011) Role of different brain areas in peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1381:187–201
Jeanmonod D, Magnin M, Morel A (1993) Thalamus and neurogenic pain: physiological, anatomical and clinical data. Neuroreport 4:475–478
Jedema HP, Gold SJ, Gonzalez-Burgos G, Sved AF, Tobe BJ, Wensel T, Grace AA (2008) Chronic cold exposure increases RGS7 expression and decreases alpha(2)-autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons. Eur J Neurosci 27:2433–2443
Ji RR, Gereau RWt, Malcangio M, Strichartz GR (2009) MAP kinase and pain. Brain Res Rev 60:135–148
Jones SL (1991) Descending noradrenergic influences on pain. Prog Brain Res 88:381–394
Kawasaki Y, Kohno T, Zhuang ZY, Brenner GJ, Wang H, Van Der Meer C, Befort K, Woolf CJ, Ji RR (2004) Ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, protein kinase A, protein kinase C, and Src contribute to C-fiber-induced ERK activation and cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in dorsal horn neurons, leading to central sensitization. J Neurosci 24:8310–8321
Kim MA, Lee HS, Lee BY, Waterhouse BD (2004) Reciprocal connections between subdivisions of the dorsal raphe and the nuclear core of the locus coeruleus in the rat. Brain Res 1026:56–67
Korf J, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1973) Increased turnover of norepinephrine in the rat cerebral cortex during stress: role of the locus coeruleus. Neuropharmacology 12:933–938
Li JX, Zhang Y (2011) Imidazoline I2 receptors: target for new analgesics? Eur J Pharmacol 658:49–56
Ma W, Eisenach JC (2003) Chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve induces the up-regulation of descending inhibitory noradrenergic innervation to the lumbar dorsal horn of mice. Brain Res 970:110–118
Mao J, Mayer DJ, Price DD (1993) Patterns of increased brain activity indicative of pain in a rat model of peripheral mononeuropathy. J Neurosci 13:2689–2702
Martin-Gomez JI, Ruiz J, Barrondo S, Callado LF, Meana JJ (2005) Opposite changes in imidazoline I2 receptors and alpha2-adrenoceptors density in rat frontal cortex after induced gliosis. Life Sci 78:205–209
Mateo Y, Fernandez-Pastor B, Meana JJ (2001) Acute and chronic effects of desipramine and clorgyline on alpha(2)-adrenoceptors regulating noradrenergic transmission in the rat brain: a dual-probe microdialysis study. Br J Pharmacol 133:1362–1370
Meana JJ, Herrera-Marschitz M, Goiny M, Silveira R (1997) Modulation of catecholamine release by alpha 2-adrenoceptors and I1-imidazoline receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 744:216–226
Molander C, Xu Q, Grant G (1984) The cytoarchitectonic organization of the spinal cord in the rat. I. The lower thoracic and lumbosacral cord. J Comp Neurol 230:133–141
Obata H, Li X, Eisenach JC (2005) alpha2-Adrenoceptor activation by clonidine enhances stimulation-evoked acetylcholine release from spinal cord tissue after nerve ligation in rats. Anesthesiology 102:657–662
Omiya Y, Yuzurihara M, Suzuki Y, Kase Y, Kono T (2008) Role of alpha2-adrenoceptors in enhancement of antinociceptive effect in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 592:62–66
Ortega JE, Fernandez-Pastor B, Callado LF, Meana JJ (2010) In vivo potentiation of reboxetine and citalopram effect on extracellular noradrenaline in rat brain by alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonism. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 20:813–822
Palazzo E, de Novellis V, Petrosino S, Marabese I, Vita D, Giordano C, Di Marzo V, Mangoni GS, Rossi F, Maione S (2006) Neuropathic pain and the endocannabinoid system in the dorsal raphe: pharmacological treatment and interactions with the serotonergic system. Eur J Neurosci 24:2011–2020
Parini A, Moudanos CG, Pizzinat N, Lanier SM (1996) The elusive family of imidazoline binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17:13–16
Parker RB, Waud DR (1971) Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 177:1–12
Paxinos G, Watson C (2009) The rat brain in stereotaxc coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Pertovaara A, Hamalainen MM (1994) Spinal potentiation and supraspinal additivity in the antinociceptive interaction between systemically administered alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist and cocaine in the rat. Anesth Analg 79:261–266
Pertovaara A, Kontinen VK, Kalso EA (1997) Chronic spinal nerve ligation induces changes in response characteristics of nociceptive spinal dorsal horn neurons and in their descending regulation originating in the periaqueductal gray in the rat. Exp Neurol 147:428–436
Pineda J, Ugedo L, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1993) Stimulatory effects of clonidine, cirazoline and rilmenidine on locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurones: possible involvement of imidazoline-preferring receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348:134–140
Pudovkina OL, Kawahara Y, de Vries J, Westerink BH (2001) The release of noradrenaline in the locus coeruleus and prefrontal cortex studied with dual-probe microdialysis. Brain Res 906:38–45
Randall LO, Selitto JJ (1957) A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 111:409–419
Renn CL, Dorsey SG (2005) The physiology and processing of pain: a review. AACN Clin Issues 16:277–290
Rodriguez-Munoz M, Bermudez D, Sanchez-Blazquez P, Garzon J (2007) Sumoylated RGS-Rz proteins act as scaffolds for Mu-opioid receptors and G-protein complexes in mouse brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:842–850
Ruiz-Ortega JA, Ugedo L (1997) The stimulatory effect of clonidine on locus coeruleus neurons of rats with inactivated alpha 2-adrenoceptors: involvement of imidazoline receptors located in the nucleus paragigantocellularis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355:288–294
Ruiz-Ortega JA, Ugedo L, Pineda J, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1995) The stimulatory effect of clonidine through imidazoline receptors on locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurones is mediated by excitatory amino acids and modulated by serotonin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 352:121–126
Sanchez-Blazquez P, Boronat MA, Olmos G, Garcia-Sevilla JA, Garzon J (2000) Activation of I(2)-imidazoline receptors enhances supraspinal morphine analgesia in mice: a model to detect agonist and antagonist activities at these receptors. Br J Pharmacol 130:146–152
Scheinin M, Lomasney JW, Hayden-Hixson DM, Schambra UB, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Fremeau RT Jr (1994) Distribution of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype gene expression in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 21:133–149
Segal M (1979) Serotonergic innervation of the locus coeruleus from the dorsal raphe and its action on responses to noxious stimuli. J Physiol 286:401–415
Shimizu K, Asano M, Kitagawa J, Ogiso B, Ren K, Oki H, Matsumoto M, Iwata K (2006) Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in medullary and upper cervical cord neurons following noxious tooth pulp stimulation. Brain Res 1072:99–109
Singewald N, Philippu A (1998) Release of neurotransmitters in the locus coeruleus. Prog Neurobiol 56:237–267
Svensson TH, Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1975) Inhibition of both noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in brain by the alpha-adrenergic agonist clonidine. Brain Res 92:291–306
Swett JE, Woolf CJ (1985) The somatotopic organization of primary afferent terminals in the superficial laminae of the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 231:66–77
Talley EM, Rosin DL, Lee A, Guyenet PG, Lynch KR (1996) Distribution of alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 372:111–134
Tseng TJ, Hsieh YL, Hsieh ST (2007) Reversal of ERK activation in the dorsal horn after decompression in chronic constriction injury. Exp Neurol 206:17–23
Urban R, Szabo B, Starke K (1995) Involvement of alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular effects of moxonidine. Eur J Pharmacol 282:19–28
Van Bockstaele EJ, Colago EE, Aicher S (1998) Light and electron microscopic evidence for topographic and monosynaptic projections from neurons in the ventral medulla to noradrenergic dendrites in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res 784:123–138
Van Steenwinckel J, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, Pommier B, Mauborgne A, Dansereau MA, Kitabgi P, Sarret P, Pohl M, Melik Parsadaniantz S (2011) CCL2 released from neuronal synaptic vesicles in the spinal cord is a major mediator of local inflammation and pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 31:5865–5875
Viisanen H, Pertovaara A (2007) Influence of peripheral nerve injury on response properties of locus coeruleus neurons and coeruleospinal antinociception in the rat. Neuroscience 146:1785–1794
Wang QP, Nakai Y (1994) The dorsal raphe: an important nucleus in pain modulation. Brain Res Bull 34:575–585
West CH, Ritchie JC, Boss-Williams KA, Weiss JM (2009) Antidepressant drugs with differing pharmacological actions decrease activity of locus coeruleus neurons. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:627–641
Xu M, Wei H, Kontinen VK, Kalso E, Pertovaara A (2000) The dissociation of sedative from spinal antinociceptive effects following administration of a novel alpha-2-adrenoceptor agonist, MPV-2426, in the locus coeruleus in the rat. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 44:648–655
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mrs Raquel Rey-Brea, Mr Jesus Gallego-Gamo and Mrs Beatriz Fraile for their excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by grants from the “Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria” (PI070687, PI10/01221, PI080417); MICINN (SAF 2009–08460); CIBERSAM (G09, G18, G16); Junta de Andalucía, Consejería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa (CTS-510, CTS-4303); Cátedra Externa del Dolor Fundación Grünenthal-University of Cadiz; FP7-PEOPLE-2010-RG (268377); the Basque Government (IT199/07); and an FPU fellowship (AP2007-02397). The authors would also like to thank Conselho de Reitores das Universidades Portuguesas (CRUP) for financing the collaboration between the Spanish and Portuguese authors (project Acção Integrada E-42/07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alba-Delgado, C., Borges, G., Sánchez-Blázquez, P. et al. The function of alpha-2-adrenoceptors in the rat locus coeruleus is preserved in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Psychopharmacology 221, 53–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2542-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2542-7