Abstract
Rationale and objectives
Among the changes caused by repeated exposure to drugs of abuse, structural rearrangements play a critical role, setting the stage for maladaptive responses to environmental challenges and sustaining drug-taking and drug-seeking behaviors. Given that adolescents are more vulnerable to drug abuse than adults and based on our recent data showing that a single exposure to cocaine during adolescence is sufficient to change the adolescent brain, we decided to investigate whether acute cocaine exposure may alter actin remodeling in reward-related brain regions.
Methods
Accordingly, we decided to evaluate if F-actin/G-actin ratio was altered by a single injection of cocaine (20 mg/kg) at postnatal day 35. We also evaluated whether the first administration of cocaine influences such a ratio in response to a second injection (10 mg/kg) provided 24 h or 7 days later.
Results
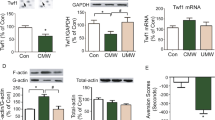
Within the medial prefrontal cortex, a single cocaine injection increases the F-actin/G-actin ratio. This effect lasts 1 week, and it is not affected by the second injection of cocaine, indicating a persistent effect of the first exposure. In the nucleus accumbens, cocaine reduces the F-actin/G-actin ratio 24 h later. Seven days later, instead, such a ratio is markedly increased: notably, the additional exposure to the psychostimulant normalizes the F-actin/G-actin ratio.
Conclusions
These results suggest that a single cocaine injection during adolescence causes possible changes in actin dynamics and influences the response to a second challenge of the psychostimulant, indicating that early cocaine priming might affect mechanisms regulating synaptic structural plasticity in specific brain regions


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch M, Castro J, Saneyoshi T, Matsuno H, Sur M, Hayashi Y (2014) Structural and molecular remodeling of dendritic spine substructures during long-term potentiation. Neuron 82:444–459
Bramham CR (2008) Local protein synthesis, actin dynamics, and LTP consolidation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18:524–531
Caffino L, Calabrese F, Giannotti G, Barbon A, Verheij MM, Racagni G, Fumagalli F (2015a) Stress rapidly dysregulates the glutamatergic synapse in the prefrontal cortex of cocaine-withdrawn adolescent rats. Addict Biol 20:158–169
Caffino L, Giannotti G, Malpighi C, Racagni G, Fumagalli F (2015b) Short-term withdrawal from developmental exposure to cocaine activates the glucocorticoid receptor and alters spine dynamics. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:1832–1841
Chapman RH, Stern JM (1978) Maternal stress and pituitary-adrenal manipulations during pregnancy in rats: effects on morphology and sexual behavior of male offspring. J Comp Physiol Psychol 92:1074–1083
Cingolani LA, Goda Y (2008) Actin in action: the interplay between the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic efficacy. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:344–356
Collins SL, Izenwasser S (2004) Chronic nicotine differentially alters cocaine-induced locomotor activity in adolescent vs. adult male and female rats. Neuropharmacology 46:349–362
Dietz DM, Dietz KC, Nestler EJ, Russo SJ (2009) Molecular mechanisms of psychostimulant-induced structural plasticity. Pharmacopsychiatry 42(Suppl 1):S69–S78
Doremus-Fitzwater, T. L., Spear, L. P., 2016. Reward-centricity and attenuated aversions: An adolescent phenotype emerging from studies in laboratory animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
Giannotti G, Caffino L, Calabrese F, Racagni G, Riva MA, Fumagalli F (2014) Prolonged abstinence from developmental cocaine exposure dysregulates BDNF and its signaling network in the medial prefrontal cortex of adult rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:625–634
Gourley SL, Olevska A, Gordon J, Taylor JR (2013) Cytoskeletal determinants of stimulus-response habits. J Neurosci 33:11811–11816
Holtmaat A, Svoboda K (2009) Experience-dependent structural synaptic plasticity in the mammalian brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:647–658
Hotulainen P, Hoogenraad CC (2010) Actin in dendritic spines: connecting dynamics to function. J Cell Biol 189:619–629
Kalivas PW, O'Brien C (2008) Drug addiction as a pathology of staged neuroplasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:166–180
Korpi ER, den Hollander B, Farooq U, Vashchinkina E, Rajkumar R, Nutt DJ, Hyytia P, Dawe GS (2015) Mechanisms of action and persistent neuroplasticity by drugs of abuse. Pharmacol Rev 67:872–1004
Luo L (2002) Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:601–635
Maldonado AM, Kirstein CL (2005) Cocaine-induced locomotor activity is increased by prior handling in adolescent but not adult female rats. Physiol Behav 86:568–572
Nyberg F (2014) Structural plasticity of the brain to psychostimulant use. Neuropharmacology 87:115–124
Okamoto K, Nagai T, Miyawaki A, Hayashi Y (2004) Rapid and persistent modulation of actin dynamics regulates postsynaptic reorganization underlying bidirectional plasticity. Nat Neurosci 7:1104–1112
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, Fifth edn. Academic Press, New York
Rocha BA, Fumagalli F, Gainetdinov RR, Jones SR, Ator R, Giros B, Miller GW, Caron MG (1998) Cocaine self-administration in dopamine-transporter knockout mice. Nat Neurosci 1:132–137
Shen HW, Toda S, Moussawi K, Bouknight A, Zahm DS, Kalivas PW (2009) Altered dendritic spine plasticity in cocaine-withdrawn rats. J Neurosci 29:2876–2884
Star EN, Kwiatkowski DJ, Murthy VN (2002) Rapid turnover of actin in dendritic spines and its regulation by activity. Nat Neurosci 5:239–246
Toda S, Shen HW, Peters J, Cagle S, Kalivas PW (2006) Cocaine increases actin cycling: effects in the reinstatement model of drug seeking. J Neurosci 26:1579–1587
Toda S, Shen H, Kalivas PW (2010) Inhibition of actin polymerization prevents cocaine-induced changes in spine morphology in the nucleus accumbens. Neurotox Res 18:410–415
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Zardi Gori Foundation for funding this project through a grant to FF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caffino, L., Giannotti, G., Racagni, G. et al. A single cocaine exposure disrupts actin dynamics in the cortico-accumbal pathway of adolescent rats: modulation by a second cocaine injection. Psychopharmacology 234, 1217–1222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4559-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4559-z