Abstract
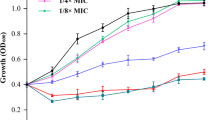
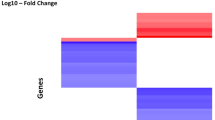
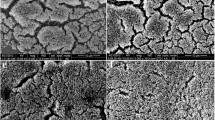
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important pathogens in humans and animals. The formation of biofilm by S. aureus is considered an important mechanism of antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, finding effective drugs against the biofilm produced by S. aureus has been a high priority. Licochalcone A (LAA), a natural plant product, was reported to have antibacterial activities and showed good activity against all 21 tested strains of S. aureus biofilm and planktonic cells. To detect the possible molecular mechanism of LAA against S. aureus biofilm or planktonic cells, Affymetrix GeneChips were used to determine the global comparative transcription of S. aureus biofilm and planktonic cells triggered by treatment with sub-bactericidal and sub-inhibitory concentrations of LAA, respectively. LAA significantly altered (greater than a 2- or less than −2-fold change) the expression of 693 genes in planktonic cells and 817 genes in biofilm. The levels of genes encoding autolysis-associated proteins, cell wall proteins, pathogenic factors, protein synthesis genes, and enzymes involved in capsule synthesis were significantly altered in LAA-treated S. aureus. Furthermore, some differences observed in the microarray analysis were verified by real-time RT–PCR. To our knowledge, this is the first observation of phenotype and expression profiles of S. aureus biofilm and planktonic cells in response to LAA treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah M, Chataigne G, Ferreira-Theret P, Benoliel C, Drider D, Dhulster P, Chihib NE (2014) Effect of growth temperature, surface type and incubation time on the resistance of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms to disinfectants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:2597–2607
Blickwede M, Wolz C, Valentin-Weigand P, Schwarz S (2005) Influence of clindamycin on the stability of coa and fnbB transcripts and adherence properties of Staphylococcus aureus Newman. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252(1):73–78. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.08.022
Cameron DR, Ward DV, Kostoulias X, Howden BP, Moellering RC, Eliopoulos GM, Peleg AY (2012) Serine/threonine phosphatase Stp1 contributes to reduced susceptibility to vancomycin and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 205(11):1677–1687
Chen M, Zhai L, Christensen SB, Theander TG, Kharazmi A (2001) Inhibition of fumarate reductase in Leishmania major and L. donovani by chalcones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45(7):2023–2029
Cheung AL, Zhang G (2002) Global regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus by the SarA protein family. Front Biosci 7:d1825–d1842
Chien Y-T, Manna AC, Projan SJ, Cheung AL (1999) SarA, a global regulator of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus, binds to a conserved motif essential for sar-dependent gene regulation. J Biol Chem 274(52):37169–37176
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2005) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Fifteenth informational supplement. Document M100-S15. CLSI/NCCLS, Wayne, PA, USA
Entenza J, Foster T, Eidhin DN, Vaudaux P, Francioli P, Moreillon P (2000) Contribution of clumping factor B to pathogenesis of experimental endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 68(9):5443–5446
Gao J, Stewart GC (2004) Regulatory elements of the Staphylococcus aureus protein A (Spa) promoter. J Bacteriol 186(12):3738–3748
Hutter B, Schaab C, Albrecht S, Borgmann M, Brunner NA, Freiberg C, Ziegelbauer K, Rock CO, Ivanov I, Loferer H (2004) Prediction of mechanisms of action of antibacterial compounds by gene expression profiling. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(8):2838–2844
Jang HJ, Chang MW, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2008) Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of triclosan on Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:695–707
Komatsuzawa H, Ohta K, Fujiwara T, Choi GH, Labischinski H, Sugai M (2001) Cloning and sequencing of the gene, fmtC, which affects oxacillin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 203(1):49–54
Kuroda M, Kuroda H, Oshima T, Takeuchi F, Mori H, Hiramatsu K (2003) Two-component system VraSR positively modulates the regulation of cell-wall biosynthesis pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 49(3):807–821
Lee JH, Cho HS, Kim Y, Kim JA, Banskota S, Cho MH, Lee J (2013) Indole and 7-benzyloxyindole attenuate the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4543–4552
Liang X, Zheng L, Landwehr C, Lunsford D, Holmes D, Ji Y (2005) Global regulation of gene expression by ArlRS, a two-component signal transduction regulatory system of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 187(15):5486–5492
Liu XL, Xu YJ, Go ML (2008) Functionalized chalcones with basic functionalities have antibacterial activity against drug sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Med Chem 43(8):1681–1687
Manna AC, Ingavale SS, Maloney M, Van Wamel W, Cheung AL (2004) Identification of sarV (SA2062), a new transcriptional regulator, is repressed by SarA and MgrA (SA0641) and involved in the regulation of autolysis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 186(16):5267–5280
McAleese F, Wu SW, Sieradzki K, Dunman P, Murphy E, Projan S, Tomasz A (2006) Overexpression of genes of the cell wall stimulon in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus exhibiting vancomycin-intermediate-S. aureus-type resistance to vancomycin. J Bacteriol 188:1120–1133
Novick RP (2003) Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol Microbiol 48(6):1429–1449
Otto M (2012) Staphylococcal infections: mechanisms of biofilm maturation and detachment as critical determinants of pathogenicity. Annu Rev Med 64(1):175–188. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042711-140023
Quiel A, Jürgen B, Piechotta G, Le Foll AP, Ziebandt AK, Kohler C, Köster D, Engelmann S, Erck C, Hintsche R, Wehland J, Hecker M, Schweder T (2010) Electrical protein array chips for the detection of staphylococcal virulence factors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1619–1627
Resch A, Rosenstein R, Nerz C, Götz F (2005) Differential gene expression profiling of Staphylococcus aureus cultivated under biofilm and planktonic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(5):2663–2676
Rice K, Peralta R, Bast D, de Azavedo J, McGavin MJ (2001) Description of staphylococcus serine protease (ssp) operon in Staphylococcus aureus and nonpolar inactivation of sspA-encoded serine protease. Infect Immun 69(1):159–169
Rohde H, Knobloch JK, Horstkotte MA, Mack D (2001) Correlation of Staphylococcus aureus icaADBC genotype and biofilm expression phenotype. J Clin Microbiol 39(12):4595–4596
Sadykov MR, Bayles KW (2012) The control of death and lysis in staphylococcal biofilms: a coordination of physiological signals. Curr Opin Microbiol 15(2):211–215
Shibata S (2000) A drug over the millennia: pharmacognosy, chemistry, and pharmacology of licorice. Yakugaku Zasshi 120(10):849–862
Smith K, Gould KA, Ramage G, Gemmell CG, Hinds J, Lang S (2010) Influence of tigecycline on expression of virulence factors in biofilm-associated cells of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54(1):380–387
Utaida S, Dunman P, Macapagal D, Murphy E, Projan S, Singh V, Jayaswal R, Wilkinson B (2003) Genome-wide transcriptional profiling of the response of Staphylococcus aureus to cell-wall-active antibiotics reveals a cell-wall-stress stimulon. Microbiology 149(10):2719–2732
Wang D, Yu L, Xiang H, Fan J, He L, Guo N, Feng H, Deng X (2008) Global transcriptional profiles of Staphylococcus aureus treated with berberine chloride. FEMS Microbiol Lett 279(2):217–225
Wang D, Jin Q, Xiang H, Wang W, Guo N, Zhang K, Tang X, Meng R, Feng H, Liu L, Wang X, Liang J, Shen F, Xing M, Deng X, Yu L (2011) Transcriptional and functional analysis of the effects of magnolol: inhibition of autolysis and biofilms in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26833
Wann ER, Gurusiddappa S, Höök M (2000) The fibronectin-binding MSCRAMM FnbpA of Staphylococcus aureus is a bifunctional protein that also binds to fibrinogen. J Biol Chem 275(18):13863–13871
Wu T-Y, Khor T, Saw C, Loh S, Chen A, Lim S, Park J, Cai L, Kong A-N (2011) Anti-inflammatory/anti-oxidative stress activities and differential regulation of Nrf2-mediated genes by non-polar fractions of tea Chrysanthemum zawadskii and licorice Glycyrrhiza uralensis. AAPS J 13(1):1–13
Xing M, Shen F, Liu L, Chen Z, Guo N, Wang X, Wang W, Zhang K, Wu X, Wang X, Li Y, Sun S, Yu L (2012) Antimicrobial efficacy of the alkaloid harmaline alone and in combination with chlorhexidine digluconate against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus grown in planktonic and biofilm cultures. Lett Appl Microbiol 54(5):475–482
You YO, Choi NY, Kang SY, Kim KJ (2013) Antibacterial activity of Rhus javanica against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:549207
Yu L, Xiang H, Fan J, Wang D, Yang F, Guo N, Jin Q, Deng X (2008) Global transcriptional response of Staphylococcus aureus to rhein, a natural plant product. J Biotechnol 135(3):304–308
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Important National Science and Technology Specific Projects (2012ZX10003002), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 31172364; No. 31271951; No. 31000822), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-09-0434; NCET-13-0245), Fundamental Research Program of Shen Zhen (JCYJ20130401172016183; JCYJ20120616142424467), and Shenzhen Promotion Plan Basic Research Laboratory in 2012 (ZDSY20120616141302982).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Fengge Shen and Xudong Tang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 904 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, F., Tang, X., Wang, Y. et al. Phenotype and expression profile analysis of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms and planktonic cells in response to licochalcone A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 359–373 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6076-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6076-x