Abstract
Aging accompanied by several age-related complications, is a multifaceted inevitable biological progression involving various genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. The major factor in this process is oxidative stress, caused by an abundance of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). ROS and RNS pose a threat by disrupting signaling mechanisms and causing oxidative damage to cellular components. This oxidative stress affects both the ER and mitochondria, causing proteopathies (abnormal protein aggregation), initiation of unfolded protein response, mitochondrial dysfunction, abnormal cellular senescence, ultimately leading to inflammaging (chronic inflammation associated with aging) and, in rare cases, metastasis. RONS during oxidative stress dysregulate multiple metabolic pathways like NF-κB, MAPK, Nrf-2/Keap-1/ARE and PI3K/Akt which may lead to inappropriate cell death through apoptosis and necrosis. Inflammaging contributes to the development of inflammatory and degenerative diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and retinopathy. The body’s antioxidant systems, sirtuins, autophagy, apoptosis, and biogenesis play a role in maintaining homeostasis, but they have limitations and cannot achieve an ideal state of balance. Certain interventions, such as calorie restriction, intermittent fasting, dietary habits, and regular exercise, have shown beneficial effects in counteracting the aging process. In addition, interventions like senotherapy (targeting senescent cells) and sirtuin-activating compounds (STACs) enhance autophagy and apoptosis for efficient removal of damaged oxidative products and organelles. Further, STACs enhance biogenesis for the regeneration of required organelles to maintain homeostasis. This review article explores the various aspects of oxidative damage, the associated complications, and potential strategies to mitigate these effects.
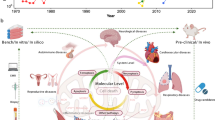
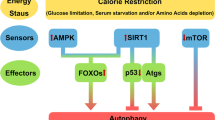
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addorisio SR, Shteynberg R, Dasilva M, Mixon J, Mucciarone K, Vu L et al (2022) Oxidative stress response in bacteria: a review. Fine Focus 8(1):36–46
Adebayo M, Singh S, Singh AP, Dasgupta S (2021) Mitochondrial fusion and fission: the fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis. FASEB J 35(6):e21620. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202100067R
Adwas AA, Elsayed A, Azab AE, Quwaydir FA (2019) Oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms in human body. J Appl Biotechnol Bioeng 6(1):43–47. https://doi.org/10.15406/jabb.2019.06.00173
Agrawal A, Koslover EF (2021) Optimizing mitochondrial maintenance in extended neuronal projections. PLoS Comput Biol 17(6):e1009073. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009073
Ahmad A, Ahsan H (2020) Biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in ophthalmic disorders. J Immunoass Immunochem 41(3):257–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/15321819.2020.1726774
Ahmad A, Khan M, Raza SS, Javed H, Ashafaq M, Islam F, Safhi MM, Islam F (2012) Ocimum sanctum attenuates oxidative damage and neurological deficits following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neurol Sci 33(6):1239–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-0940-1
Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C, Kroemer G, Kaufman RJ, Malhi H, Ren J (2022) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases. Hepatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32562
Akagawa M (2021) Protein carbonylation: molecular mechanisms, biological implications, and analytical approaches. Free Radic Res 55(4):307–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2020.1851027
Albensi BC (2019) What is nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) doing in and to the mitochondrion? Front Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00154
Ali SS, Ahsan H, Zia MK, Siddiqui T, Khan FH (2020) Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: classical team with new players. J Food Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13145
Ali S, Xia Q, Muhammad T, Liu L, Meng X, Bars-Cortina D, Khan AA, Huang Y, Dong L (2021) Glioblastoma therapy: rationale for a mesenchymal stem cell-based vehicle to carry recombinant viruses. Stem Cell Rev Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10207-w
Altemimi A, Lakhssassi N, Baharlouei A, Watson DG, Lightfoot DA (2017) Phytochemicals: extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants 6(4):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6040042
Aman Y, Schmauck-Medina T, Hansen M, Morimoto RI, Simon AK, Bjedov I, Palikaras K, Simonsen A, Johansen T, Tavernarakis N, Rubinsztein DC, Partridge L, Kroemer G, Labbadia J, Fang EF (2021) Autophagy in healthy aging and disease. Nature Aging 1(8):634–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-021-00098-4
Amarowicz R, Pegg RB (2019) Natural antioxidants of plant origin. Adv Food Nutr Res 90:1–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2019.02.011
Amos LA, Ma FY, Tesch GH, Liles JT, Breckenridge DG, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Han Y (2018) ASK 1 inhibitor treatment suppresses p38/JNK signalling with reduced kidney inflammation and fibrosis in rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Cell Mol Med 22(9):4522–4533. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13705
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Archer AE, Rogers RS, Von Schulze AT, Wheatley JL, Morris EM, McCoin CS, Thyfault JP, Geiger PC (2018) Heat shock protein 72 regulates hepatic lipid accumulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 315(4):R696–R707. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00073.2018
Asadipooya K, Uy EM (2019) Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), receptor for AGEs, diabetes, and bone: review of the literature. J Endocr Soc 3(10):1799–1818. https://doi.org/10.1210/js.2019-00160
Aseervatham GSB, Sivasudha T, Jeyadevi R, Arul Ananth D (2013) Environmental factors and unhealthy lifestyle influence oxidative stress in humans—an overview. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:4356–4369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1748-0
Atayik MC, Çakatay U (2022a) Melatonin-related signaling pathways and their regulatory effects in aging organisms. Biogerontology 23(5):529–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-022-09981-y
Atayik MC, Çakatay U (2022b) Mitochondria-targeted senotherapeutic interventions. Biogerontology 23(4):401–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-022-09973-y
Atila NE, Atila A, Kaya Z, Bulut YE, Oner F, Topal K, Bayraktutan Z, Bakan E (2021) The role of manganese, cadmium, chromium and selenium on subjective tinnitus. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:2844–2850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02420-4
Atta EM, Mohamed NH, Silaev AAA (2017) Antioxidants: an overview on the natural and synthetic types. Eur Chem Bull 6(8):365–375. https://doi.org/10.17628/ecb.2017.6.365-375
August PM, Maurmann RM, Saccomori AB, Scortegagna MC, Flores EB, Klein CP et al (2018) Effect of maternal antioxidant supplementation and/or exercise practice during pregnancy on postnatal overnutrition induced by litter size reduction: brain redox homeostasis at weaning. Int J Dev Neurosci 71:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2018.09.003
Aunan JR, Watson MM, Hagland HR, Søreide K (2016) Molecular and biological hallmarks of ageing. J Br Surg 103(2):e29–e46. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10053
Azzam EI, Jay-Gerin JP, Pain D (2012) Ionizing radiation-induced metabolic oxidative stress and prolonged cell injury. Cancer Lett 327(1–2):48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.012
Bailey CJ, Turner RC (1996) Metformin. N Engl J Med 334(9):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199602293340906
Baker J (2016) Exercise and intensity: implications for oxidative stress and muscle damage. MOJ Orthop Rheumatol 5(2):00174. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojor.2016.05.00174
Balch WE, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW (2008) Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science 319(5865):916–919. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1141448
Bandookwala M, Sengupta P (2020) 3-Nitrotyrosine: a versatile oxidative stress biomarker for major neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Neurosci 130(10):1047–1062. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2020.1713776
Barbosa ML, de Meneses AAPM, de Aguiar RPS, e Sousa JMDC, Cavalcante AADCM, Maluf SW (2020) Oxidative stress, antioxidant defense and depressive disorders: a systematic review of biochemical and molecular markers. Neurol Psychiatry Brain Res 36:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npbr.2020.02.006
Barnes PJ (2020) Oxidative stress-based therapeutics in COPD. Redox Biol 33:101544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101544
Bar-Zeev Y, Solt I (2018) Interventions for supporting women to stop smoking in pregnancy. Harefuah 157(12):783–786
Barzegar F, Kamankesh M, Mohammadi A (2019) Heterocyclic aromatic amines in cooked food: a review on formation, health risk-toxicology and their analytical techniques. Food Chem 280:240–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.12.058
Barzilai A, Yamamoto KI (2004) DNA damage responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair 3(8–9):1109–1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.03.002
Becher B, Spath S, Goverman J (2017) Cytokine networks in neuroinflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 17(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.123
Bhat G, Baba CS, Pandey A, Kumari N, Choudhuri G (2013) Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in nonobese Indian patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trop Gastroenterol 34(1):18–24. https://doi.org/10.7869/tg.2012.86
Bhattarai KR, Riaz TA, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2021) The aftermath of the interplay between the endoplasmic reticulum stress response and redox signaling. Exp Mol Med 53(2):151–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00560-8
Bhatti GK, Gupta A, Pahwa P, Khullar N, Singh S, Navik U et al (2022) Targeting mitochondrial bioenergetics as a promising therapeutic strategy in metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2022.05.002
Birch-Machin MA, Bowman A (2016) Oxidative stress and ageing. Br J Dermatol 175(S2):26–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14906
Bjørklund G, Chirumbolo S (2017) Role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in daily nutrition and human health. Nutrition 33:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.07.018
Bjørklund G, Shanaida M, Lysiuk R, Antonyak H, Klishch I, Shanaida V, Peana M (2022) Selenium: an antioxidant with a critical role in anti-aging. Molecules 27(19):6613. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196613
Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C (2021) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 397(10291):2284–2303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00218-X
Bloomer RJ (2007) Decreased blood antioxidant capacity and increased lipid peroxidation in young cigarette smokers compared to nonsmokers: impact of dietary intake. Nutr J 6(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-6-39
Boccatonda A, Tripaldi R, Davì G, Santilli F (2016) Oxidative stress modulation through habitual physical activity. Curr Pharm Des 22(24):3648–3680. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666160413123806
Boczek E, Gaglia G, Olshina M, Sarraf S (2019) The first Autumn School on Proteostasis: from molecular mechanisms to organismal consequences. Cell Stress Chaperones 24:481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-00998-w
Bouayed J, Bohn T (2010) Exogenous antioxidants—double-edged swords in cellular redox state: health beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects at high doses. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3(4):228–237. https://doi.org/10.4161/oxim.3.4.12858
Brioche T, Lemoine-Morel S (2016) Oxidative stress, sarcopenia, antioxidant strategies and exercise: molecular aspects. Curr Pharm Des 22(18):2664–2678
Calabrese EJ (2008) Neuroscience and hormesis: overview and general findings. Crit Rev Toxicol 38(4):249–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408440801981957
Calabrese EJ, Mattson MP (2017) How does hormesis impact biology, toxicology, and medicine? npj Aging Mech Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41514-017-0013-z
Calabrese V, Guagliano E, Sapienza M, Panebianco M, Calafato S, Puleo E, Pennisi G, Mancuso C, Allan Butterfield D, Stella AG (2007) Redox regulation of cellular stress response in aging and neurodegenerative disorders: role of vitagenes. Neurochem Res 32:757–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-006-9203-y
Calabrese V, Sultana R, Scapagnini G, Guagliano E, Sapienza M, Bella R, Kanski J, Pennisi G, Mancuso C, Stella AMG, Butterfield DA (2006) Nitrosative stress, cellular stress response, and thiol homeostasis in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(11-12):1975–1986
Camkurt MA, Fındıklı E, İzci F, Kurutaş EB, Tuman TC (2016) Evaluation of malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase and catalase activity and their diagnostic value in drug naïve, first episode, non-smoker major depression patients and healthy controls. Psychiatry Res 238:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.075
Cantoni O, Zito E, Guidarelli A, Fiorani M, Ghezzi P (2022) Mitochondrial ROS, ER stress, and Nrf2 crosstalk in the regulation of mitochondrial apoptosis induced by arsenite. Antioxidants 11(5):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11051034
Cao SS, Kaufman RJ (2012) Unfolded protein response. Curr Biol 22(16):R622–R626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.004
Capece D, Verzella D, Flati I, Arboretto P, Cornice J, Franzoso G (2022) NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2022.07.004
Carafa V, Rotili D, Forgione M, Cuomo F, Serretiello E, Hailu GS, Jarho E, Lahtela-Kakkonen M, Mai A, Altucci L (2016) Sirtuin functions and modulation: from chemistry to the clinic. Clin Epigenet. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-016-0224-3
Cardinali DP (2021) Melatonin and healthy aging. Vitam Horm 115:67–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2020.12.004
Carell T (2015) DNA repair. Angew Chem (Int Ed Engl) 54(51):15330–15333. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201509770
Cargnello M, Roux PP (2011a) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75(1):50–83. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00013-12
Cargnello M, Roux PP (2011b) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75(1):50–83. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.00031-10
Cargnello M, Roux PP (2012) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev MMBR 76(2):496
Carraro E, Schilirò T, Biorci F, Romanazzi V, Degan R, Buonocore D, Gilli G (2018) Physical activity, lifestyle factors and oxidative stress in middle age healthy subjects. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(6):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061152
Carroll D (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 188(4):773–782. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.111.131433
Cartier A, Côté M, Lemieux I, Pérusse L, Tremblay A, Bouchard C, Després JP (2009) Sex differences in inflammatory markers: what is the contribution of visceral adiposity? Am J Clin Nutr 89(5):1307–1314. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.27030
Castejon-Vega B, Cordero MD, Sanz A (2023) How the disruption of mitochondrial redox signalling contributes to ageing. Antioxidants 12(4):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040831
Catalá A, Díaz M (2016) Impact of lipid peroxidation on the physiology and pathophysiology of cell membranes. Front Physiol 7:423. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00423
Cerniuc C, Fischer T, Baumeister A, Bordewick Dell U (2019) Impact of intermittent fasting (5:2) on ketone body production in healthy female subjects. Ernährungs Umschau 66(1):2–9. https://doi.org/10.4455/eu.2019.002
Chandrasekaran A, Idelchik MDPS, Melendez JA (2017) Redox control of senescence and age-related disease. Redox Biol 11:91–102
Chang X, Zhang T, Zhang W, Zhao Z, Sun J (2020) Natural drugs as a treatment strategy for cardiovascular disease through the regulation of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5430407
Checa J, Aran JM (2020) Reactive oxygen species: drivers of physiological and pathological processes. J Inflamm Res. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S275595
Chen HK, Fernandez-Funez P, Acevedo SF, Lam YC, Kaytor MD, Fernandez MH et al (2003) Interaction of Akt-phosphorylated ataxin-1 with 14-3-3 mediates neurodegeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Cell 113(4):457–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00349-0
Chen WW, Zhang XIA, Huang WJ (2016) Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Med Rep 13(4):3391–3396. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.4948
Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, Li Y, Wang X, Zhao L (2018) Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 9(6):7204. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23208
Chen J, Yang J, Ma L, Li J, Shahzad N, Kim CK (2020) Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of methoxy, phenolic hydroxyl, and carboxylic acid groups of phenolic acids. Sci Rep 10(1):2611. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59451-z
Chen X, Ma W, Yao Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Wu X et al (2021) Serum deprivation-response protein induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through ASK1-JNK/p38 MAPK pathways. Cell Death Dis 12(5):425. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03711-x
Choi WS, Eom DS, Han BS, Kim WK, Han BH, Choi EJ, Oh TH, Markelonis GJ, Cho JW, Oh YJ (2004) Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK induced by oxidative stress is linked to activation of both caspase-8-and-9-mediated apoptotic pathways in dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 279(19):20451–20460. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311164200
Christen WG, Glynn RJ, Chew EY, Buring JE (2008) Vitamin E and age-related cataract in a randomized trial of women. Ophthalmology 115(5):822–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.06.040
Chung HY, Lee EK, Choi YJ, Kim JM, Kim DH, Zou Y, Kim CH, Lee J, Kim HS, Kim ND, Jung JH, Yu BP (2011) Molecular inflammation as an underlying mechanism of the aging process and age-related diseases. J Dent Res 90(7):830–840. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034510387794
Chung HY, Kim DH, Lee EK, Chung KW, Chung S, Lee B, Seo AY, Chung JH, Jung YS, Im E, Lee J (2019) Redefining chronic inflammation in aging and age-related diseases: proposal of the senoinflammation concept. Aging Dis 10(2):367. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.0324
Collier CA, Bruce CR, Smith AC, Lopaschuk G, Dyck DJ (2006) Metformin counters the insulin-induced suppression of fatty acid oxidation and stimulation of triacylglycerol storage in rodent skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291(1):E182–E189. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00272.2005
Cooper CE, Vollaard NB, Choueiri T, Wilson MT (2002) Exercise, free radicals and oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans 30(2):280–285. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0300280
Cornelius C, Perrotta R, Graziano A, Calabrese EJ, Calabrese V (2013) Stress responses, vitagenes and hormesis as critical determinants in aging and longevity: mitochondria as a ‘chi.’ Immun Ageing. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-4933-10-15
Crighton D, Wilkinson S, Ryan KM (2007) DRAM links autophagy to p53 and programmed cell death. Autophagy 3(1):72–74. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.3438
Crisóstomo L, Oliveira PF, Alves MG (2022) Antioxidants, oxidative stress, and non-communicable diseases. Antioxidants 11(6):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061080
D’Amico AM, Vasquez KM (2021) The multifaceted roles of DNA repair and replication proteins in aging and obesity. DNA Repair 99:103049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103049
Dandekar A, Mendez R, Zhang K (2015) Cross talk between ER stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation in health and disease. In: Stress responses: methods and protocols. pp 205–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2522-3_15
Das TP, Suman S, Alatassi H, Ankem MK, Damodaran C (2016) Inhibition of AKT promotes FOXO3a-dependent apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis 7(2):e2111. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.403
Davinelli S, Scapagnini G (2022) The pharma-nutritional role of antioxidant phytochemicals in health and disease. Antioxidants 11(6):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061081
de Almeida AJPO, de Oliveira JCPL, da Silva Pontes LV, de Souza Júnior JF, Gonçalves TAF, Dantas SH et al (2022) ROS: basic concepts, sources, cellular signaling, and its implications in aging pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1225578
De Cabo R, Mattson MP (2019) Effects of intermittent fasting on health, aging, and disease. N Engl J Med 381(26):2541–2551. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1905136
de Cabo R, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Bernier M, Hall MN, Madeo F (2014) The search for antiaging interventions: from elixirs to fasting regimens. Cell 157(7):1515–1526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.031
De La Torre JC (2008) Pathophysiology of neuronal energy crisis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 5(3–4):126–132. https://doi.org/10.1159/000113681
De Rubis G, Paudel KR, Manandhar B, Singh SK, Gupta G, Malik R, Shen J, Chami A, MacLoughlin R, Chellappan DK, Oliver BGG, Hansbro PM, Dua K (2023) Agarwood oil nanoemulsion attenuates cigarette smoke-induced inflammation and oxidative stress markers in BCi-NS1.1 airway epithelial cells. Nutrients 15(4):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041019
Dejong K, Olyaei AMY, Lo JO (2019) Alcohol use in pregnancy. Clin Obstet Gynecol 62(1):142. https://doi.org/10.1097/GRF.0000000000000414
Delcroix-Gomez C, Delcroix MH, Jamee A, Gauthier T, Marquet P, Aubard Y (2022) Fetal growth restriction, low birth weight, and preterm birth: effects of active or passive smoking evaluated by maternal expired CO at delivery, impacts of cessation at different trimesters. Tob Induc Dis 20:70. https://doi.org/10.18332/tid/152111
Dembinska-Kiec A, Mykkänen O, Kiec-Wilk B, Mykkänen H (2008) Antioxidant phytochemicals against type 2 diabetes. Br J Nutr 99(E-S1):ES109–ES117. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711450896579X
Demirci-Çekiç S, Özkan G, Avan AN, Uzunboy S, Çapanoğlu E, Apak R (2022) Biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. J Pharm Biomed Anal 209:114477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2021.114477
Dever TE, Kinzy TG, Pavitt GD (2016) Mechanism and regulation of protein synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 203(1):65–107. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.186221
Dhanda S, Sunkaria A, Halder A, Sandhir R (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunctions contribute to energy deficits in rodent model of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 33:209–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0136-8
Di Francesco A, Di Germanio C, Bernier M, De Cabo R (2018) A time to fast. Science 362(6416):770–775. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau2095
Ding D, Lawson KD, Kolbe-Alexander TL, Finkelstein EA, Katzmarzyk PT, Van Mechelen W, Pratt M (2016) The economic burden of physical inactivity: a global analysis of major non-communicable diseases. Lancet 388(10051):1311–1324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30383-X
DiSabato DJ, Quan N, Godbout JP (2016) Neuroinflammation: the devil is in the details. J Neurochem 139:136–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13607
Dobson R, Giovannoni G (2019) Multiple sclerosis—a review. Eur J Neurol 26(1):27–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13819
Donkena KV, Young CY, Tindall DJ (2010) Oxidative stress and DNA methylation in prostate cancer. Obstet Gynecol Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/302051
Duan J, Yuan W, Jiang J, Wang J, Yan X, Liu F, Liu A (2023) ASK1 inhibitor NQDI 1 decreases oxidative stress and neuroapoptosis via the ASK1/p38 and JNK signaling pathway in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Mol Med Rep 27(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2023.12934
Dubois-Deruy E, Peugnet V, Turkieh A, Pinet F (2020) Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants 9(9):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090864
Duhig K, Chappell LC, Shennan AH (2016) Oxidative stress in pregnancy and reproduction. Obstet Med 9(3):113–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753495X16648495
Dutta D, Calvani R, Bernabei R, Leeuwenburgh C, Marzetti E (2012) Contribution of impaired mitochondrial autophagy to cardiac aging: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Circ Res 110(8):1125–1138. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.246108
Eguchi N, Vaziri ND, Dafoe DC, Ichii H (2021) The role of oxidative stress in pancreatic β cell dysfunction in diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 22(4):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041509
Eisenberg N, Zhou Q, Spinrad TL, Valiente C, Fabes RA, Liew J (2005) Relations among positive parenting, children’s effortful control, and externalizing problems: a three-wave longitudinal study. Child Dev 76(5):1055–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2005.00897.x
Enkhmaa B, Surampudi P, Anuurad E, Berglund L (2018) Lifestyle Changes: Effect of Diet, Exercise, Functional Food, and Obesity Treatment on Lipids and Lipoproteins. In K.R. Feingold (Eds.) et. al., Endotext. MDText.com, Inc
Estévez M, Xiong Y (2019) Intake of oxidized proteins and amino acids and causative oxidative stress and disease: recent scientific evidences and hypotheses. J Food Sci 84(3):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14460
Evans MA, Sano S, Walsh K (2020) Cardiovascular disease, aging, and clonal hematopoiesis. Annu Rev Pathol 15:419–438. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012419-032544
Farooq U, Notani D (2022) Transcriptional regulation of INK4/ARF locus by cis and trans mechanisms. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:948351. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.948351
Fasnacht M, Polacek N (2021) Oxidative stress in bacteria and the central dogma of molecular biology. Front Mol Biosci 8:671037. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.671037
Fernandes ACF, Vieira NC, de Santana AL, de Padua Gandra RL, Rubia C, Castro-Gamboa I et al (2020) Peanut skin polyphenols inhibit toxicity induced by advanced glycation end-products in RAW264. 7 macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol 145:111619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111619
Fernando DH, Forbes JM, Angus PW, Herath CB (2019) Development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of advanced glycation end products. Int J Mol Sci 20(20):5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205037
Ferreira JV, da Rosa Soares A, Pereira P (2022) Cell non-autonomous proteostasis regulation in aging and disease. Front Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.878296
Fischer R, Maier O (2015) Interrelation of oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease: role of TNF. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/610813
Fitter S, Vandyke K, Gronthos S, Zannettino AC (2012) Suppression of PDGF-induced PI3 kinase activity by imatinib promotes adipogenesis and adiponectin secretion. J Mol Endocrinol 48(3):229. https://doi.org/10.1530/jme-12-0003
Forman HJ, Zhang H (2021) Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20(9):689–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Frei B, Forte TM, Ames BN, Cross CE (1991) Gas phase oxidants of cigarette smoke induce lipid peroxidation and changes in lipoprotein properties in human blood plasma. Protective effects of ascorbic acid. Biochem J 277(1):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2770133
Furman D, Campisi J, Verdin E, Carrera-Bastos P, Targ S, Franceschi C et al (2019) Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat Med 25(12):1822–1832. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0675-0
Gal H, Majewska J, Krizhanovsky V (2022) The intricate nature of senescence in development and cell plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol 87:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.01.004
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB, Ostolaza H, Martín C (2020) Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci 21(17):6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
Ganguli S, DeLeeuw P, Satapathy SK (2019) A review of current and upcoming treatment modalities in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepat Med Evid Res 11:159. https://doi.org/10.2147/HMER.S188991
Ganguly P, Alam SF (2015) Role of homocysteine in the development of cardiovascular disease. Nutr J 14(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-14-6
Gao Q (2019) Oxidative stress and autophagy. In: Autophagy: biology and diseases: basic science. pp 179–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0602-4_9
Geto Z, Molla MD, Challa F, Belay Y, Getahun T (2020) Mitochondrial dynamic dysfunction as a main triggering factor for inflammation associated chronic non-communicable diseases. J Inflamm Res. https://doi.org/10.2147/jir.s232009
Ghemrawi R, Battaglia-Hsu SF, Arnold C (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disorders. Cells 7(6):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7060063
Ghezzi P, Bonetto V, Fratelli M (2005) Thiol–disulfide balance: from the concept of oxidative stress to that of redox regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(7–8):964–972. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2005.7.964
Giatromanolaki A, Kouroupi M, Balaska K, Koukourakis MI (2020) A novel lipofuscin-detecting marker of senescence relates with hypoxia, dysregulated autophagy and with poor prognosis in non-small-cell-lung cancer. In Vivo 34(6):3187–3193. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.12154
Giblin W, Skinner ME, Lombard DB (2014) Sirtuins: guardians of mammalian healthspan. Trends Genet 30(7):271–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2014.04.007
Giglia-Mari G, Zotter A, Vermeulen W (2011) DNA damage response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(1):a000745. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect
Gill JG, Piskounova E, Morrison SJ (2016) Cancer, oxidative stress, and metastasis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 81:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2016.81.030791
Gladyshev VN (2014) The free radical theory of aging is dead. Long live the damage theory! Antioxid Redox Signal 20(4):727–731. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5228
Gladyshev VN, Kritchevsky SB, Clarke SG, Cuervo AM, Fiehn O, de Magalhães JP et al (2021) Molecular damage in aging. Nat Aging 1(12):1096–1106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-021-00150-3
Gocmez SS, Şahin TD, Yazir Y, Duruksu G, Eraldemir FC, Polat S, Utkan T (2019) Resveratrol prevents cognitive deficits by attenuating oxidative damage and inflammation in rat model of streptozotocin diabetes induced vascular dementia. Physiol Behav 201:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.12.012
Goh J, Wong E, Soh J, Maier AB, Kennedy BK (2023) Targeting the molecular & cellular pillars of human aging with exercise. FEBS J 290(3):649–668. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16337
Golpich M, Amini E, Mohamed Z, Azman Ali R, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Ahmadiani A (2017) Mitochondrial dysfunction and biogenesis in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and treatment. CNS Neurosci Ther 23(1):5–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12655
Gomes EC, Silva AN, de Oliveira MR (2012) Oxidants, antioxidants, and the beneficial roles of exercise-induced production of reactive species. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/756132
Gomes MJ, Martinez PF, Pagan LU, Damatto RL, Cezar MDM, Lima ARR et al (2017) Skeletal muscle aging: influence of oxidative stress and physical exercise. Oncotarget 8(12):20428. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14670
Gong L, Goswami S, Giacomini KM, Altman RB, Klein TE (2012) Metformin pathways: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 22(11):820. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283559b22
Gottlieb RA, Stotland A (2015) MitoTimer: a novel protein for monitoring mitochondrial turnover in the heart. J Mol Med (Berl) 93:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1230-6
Grabowska W, Sikora E, Bielak-Zmijewska A (2017) Sirtuins, a promising target in slowing down the ageing process. Biogerontology 18(4):447–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-017-9685-9
Gracia L, Lora G, Blair LJ, Jinwal UK (2019) Therapeutic potential of the Hsp90/Cdc37 interaction in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurosci 13:1263. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01263
Gu M, Mei XL, Zhao YN (2021) Sepsis and cerebral dysfunction: BBB damage, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy as key mediators and the potential therapeutic approaches. Neurotox Res 39:489–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-020-00270-5
Guo Z, Wang M, Ying X, Yuan J, Wang C, Zhang W, Tian S, Yan X (2023) Caloric restriction increases the resistance of aged heart to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating AMPK-SIRT1-PGC1a energy metabolism pathway. Sci Rep 13(1):2045. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-27611-6
Gustafsson ÅB, Dorn GW (2019) Evolving and expanding the roles of mitophagy as a homeostatic and pathogenic process. Physiol Rev 99(1):853–892. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00005.2018
Gutteridge JMC, Halliwell B (2018) Mini-review: oxidative stress, redox stress or redox success? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 502(2):183–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.045
Hajam YA, Rani R, Ganie SY, Sheikh TA, Javaid D, Qadri SS et al (2022) Oxidative stress in human pathology and aging: molecular mechanisms and perspectives. Cells 11(3):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030552
Halliwell B (2005) Free radicals and other reactive species in disease. In: eLS. Wiley, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1038/npg.els.0003913
Hardiman O, Al-Chalabi A, Chio A, Corr EM, Logroscino G, Robberecht W et al (2017) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim 3(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.71
Harman D (1956a) Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J Gerontol 11(3):298–300. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronj/11.3.298
Harman E (1956b) Protein oxidation in aging and age-related diseases. Gerontology 11:298–300. https://doi.org/10.1126/sageke.2002.37.cp14
Harman D (1992) Free radical theory of aging. Mutat Res 275(3–6):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-8734(92)90030-S
Harman D (2002) Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. Sci Aging Knowl Environ 2002(37):cp14. https://doi.org/10.1126/sageke.2002.37.cp14
Harrison DA (2012) The JAK/STAT pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(3):a011205. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a011205
Hartwig T, Zwicky P, Schreiner B, Yawalkar N, Cheng P, Navarini A et al (2018) Regulatory T cells restrain pathogenic T helper cells during skin inflammation. Cell Rep 25(13):3564–3572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.012
Hauck AK, Huang Y, Hertzel AV, Bernlohr DA (2019) Adipose oxidative stress and protein carbonylation. J Biol Chem 294(4):1083–1088. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R118.003214
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Tew KD (2020) Oxidative stress in cancer. Cancer Cell 38(2):167–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.06.001
He X, Tan C, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhou R, Cui D, You W, Zhao H, Ren J, Feng B (2016) Knock-in of large reporter genes in human cells via CRISPR/Cas9-induced homology-dependent and independent DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res 44(9):e85. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw064
He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS, Xu WW, Li B (2021) Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):425. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5
Hensel G, Kumlehn J (2019) Genome engineering using TALENs. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1900:195–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8944-7_13
Heslop KA, Rovini A, Hunt EG, Fang D, Morris ME, Christie CF et al (2020) JNK activation and translocation to mitochondria mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death induced by VDAC opening and sorafenib in hepatocarcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 171:113728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113728
Hetz C, Papa FR (2018) The unfolded protein response and cell fate control. Mol Cell 69(2):169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.017
Heun Y, Pircher J, Czermak T, Bluem P, Hupel G, Bohmer M et al (2019) Inactivation of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 drives vascular dysfunction in sepsis. EBioMedicine 42:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.034
Ho Zhi Guang M, Kavanagh EL, Dunne LP, Dowling P, Zhang L, Lindsay S et al (2019) Targeting proteotoxic stress in cancer: a review of the role that protein quality control pathways play in oncogenesis. Cancers 11(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010066
Horn A, Van der Meulen JH, Defour A, Hogarth M, Sreetama SC, Reed A et al (2017) Mitochondrial redox signaling enables repair of injured skeletal muscle cells. Sci Signal. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aaj1978
Houghton CA, Fassett RG, Coombes JS (2016) Sulforaphane and other nutrigenomic Nrf2 activators: can the clinician’s expectation be matched by the reality? Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7857186
Houtkooper RH, Pirinen E, Auwerx J (2012) Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):225–238. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3293
Huang X, Ahn DU (2019) Lipid oxidation and its implications to meat quality and human health. Food Sci Biotechnol 28:1275–1285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00631-7
Huang R, Zhou PK (2021) DNA damage repair: historical perspectives, mechanistic pathways and clinical translation for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6(1):254. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00648-7
Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou MC, Rahu N (2016) Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7432797
Hussain A, Dulay P, Rivera MN, Aramouni C, Saxena V (2019) Neoplastic pathogenesis associated with cigarette carcinogens. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.3955
Hwang J, Qi L (2018) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum: crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways. Trends Biochem Sci 43(8):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.06.005
Hwangbo DS, Lee HY, Abozaid LS, Min KJ (2020) Mechanisms of lifespan regulation by calorie restriction and intermittent fasting in model organisms. Nutrients 12(4):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041194
Ibraheem K, Yhmed AM, Qayyum T, Bryan NP, Georgopoulos NT (2019) CD40 induces renal cell carcinoma-specific differential regulation of TRAF proteins, ASK1 activation and JNK/p38-mediated, ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. Cell Death Discov 5(1):148. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-019-0229-8
Ikwegbue PC, Masamba P, Oyinloye BE, Kappo AP (2017) Roles of heat shock proteins in apoptosis, oxidative stress, human inflammatory diseases, and cancer. Pharmaceuticals 11(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11010002
Islam MT (2017) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol Res 39(1):73–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2016.1251711
Islam F, Ahmad A, Khan MM, Raza SS, Javed H, Ashafaq M, Islam F, Safhi MM (2012) Ocimum sanctum attenuates oxidative damage and neurological deficits following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Neurol Sci 33(6):1239–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-012-0940-1
Ismaiel A, Dumitraşcu DL (2019) Cardiovascular risk in fatty liver disease: the liver-heart axis-literature review. Front Med 6:202. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2019.00202
Iurlaro R, Muñoz-Pinedo C (2016) Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J 283(14):2640–2652. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13598
Jaalouk D, Matar Boumosleh J, Helou L, Abou Jaoude M (2019) Dietary patterns, their covariates, and associations with severity of depressive symptoms among university students in Lebanon: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr 58:997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1614-4
Jackson SP, Bartek J (2009) The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 461(7267):1071–1078. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08467
Jakubczyk K, Dec K, Kałduńska J, Kawczuga D, Kochman J, Janda K (2020) Reactive oxygen species-sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski 48(284):124–127
Jan R (2019) Understanding apoptosis and apoptotic pathways targeted cancer therapeutics. Adv Pharm Bull 9(2):205. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2019.024
Jangid P, Rai U, Sharma RS, Singh R (2022) The role of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on female fertility: a review. Int J Environ Health Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2022.2030676
Javed F, He Q, Davidson LE, Thornton JC, Albu J, Boxt L et al (2010) Brain and high metabolic rate organ mass: contributions to resting energy expenditure beyond fat-free mass. Am J Clin Nutr 91(4):907–912. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28512
Jones DP (2006) Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(9–10):1865–1879. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.1865
Jung KJ, Lee EK, Kim SJ, Song CW, Maruyama N, Ishigami A et al (2015) Anti-inflammatory activity of SMP30 modulates NF-κB through protein tyrosine kinase/phosphatase balance. J Mol Med 93:343–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1219-1
Kabir A, Miah S, Islam A (2018) Factors influencing eating behavior and dietary intake among resident students in a public university in Bangladesh: a qualitative study. PLoS ONE 13(6):e0198801. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198801
Kam TI, Mao X, Park H, Chou SC, Karuppagounder SS, Umanah GE et al (2018) Poly(ADP-ribose) drives pathologic α-synuclein neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 362(6414):eaat8407. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat8407
Kamal H, Tan GC, Ibrahim SF, Shaikh MF, Mohamed IN, Mohamed RMP et al (2020) Alcohol use disorder, neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: interplay between oxidative stress, neuroimmune response and excitotoxicity. Front Cell Neurosci 14:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00282
Kane AE, Sinclair DA (2018) Sirtuins and NAD+ in the development and treatment of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res 123(7):868–885. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312498
Kannan K, Jain SK (2000) Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 7(3):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-4680(00)00053-5
Kar S, Shahshahan HR, Kambis TN, Yadav SK, Li Z, Lefer DJ, Mishra PK (2019) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates homocysteine-induced cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. Front Physiol 10:598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00598
Karin M, Greten FR (2005) NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 5(10):749–759. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1703
Karstoft K, Brinkløv CF, Thorsen IK, Nielsen JS, Ried-Larsen M (2017) Resting metabolic rate does not change in response to different types of training in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol 8:132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00132
Karstoft K, Safdar A, Little JP (2018) Optimizing exercise for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol 9:237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00237
Kaur J (2014) A comprehensive review on metabolic syndrome. Cardiol Res Pract. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/943162
Kawamura T, Muraoka I (2018) Exercise-induced oxidative stress and the effects of antioxidant intake from a physiological viewpoint. Antioxidants 7(9):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7090119
Kealy RD, Lawler DF, Ballam JM, Mantz SL, Biery DN, Greeley EH et al (2002) Effects of diet restriction on life span and age-related changes in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 220(9):1315–1320. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.2002.220.1315
Kehm R, Baldensperger T, Raupbach J, Höhn A (2021) Protein oxidation-formation mechanisms, detection and relevance as biomarkers in human diseases. Redox Biol 42:101901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101901
Kehrer JP, Robertson JD, Smith CV (2010) Free radicals and reactive oxygen species. In: Comprehensive toxicology: second edition. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-046884-6.00114-7
Kelishadi R, Mirghaffari N, Poursafa P, Gidding SS (2009) Lifestyle and environmental factors associated with inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance in children. Atherosclerosis 203(1):311–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.06.022
Kennel KB, Greten FR (2021) Immune cell-produced ROS and their impact on tumor growth and metastasis. Redox Biol 42:101891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101891
Kenyon J, Gerson SL (2007) The role of DNA damage repair in aging of adult stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 35(22):7557–7565. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm1064
Keshari AK, Verma AK, Kumar T, Srivastava R (2015) Oxidative stress: a review. Int J Sci Technol 3(7):155
Kim KH, Kim YH, Son JE, Lee JH, Kim S, Choe MS et al (2017) Intermittent fasting promotes adipose thermogenesis and metabolic homeostasis via VEGF-mediated alternative activation of macrophage. Cell Res 27(11):1309–1326. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.126
Kim JE, Leem J, Lee HG, Lee KW (2018) Reactive oxygen species-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by α-amyrin and β-amyrin in human cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020554
Klaips CL, Jayaraj GG, Hartl FU (2018) Pathways of cellular proteostasis in aging and disease. J Cell Biol 217(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201709072
Kloeber JA, Lou Z (2022) Critical DNA damaging pathways in tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 85:164–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.04.012
Klotz DM, Hewitt SC, Ciana P, Raviscioni M, Lindzey JK, Foley J et al (2002) Requirement of estrogen receptor-α in insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)-induced uterine responses and in vivo evidence for IGF-1/estrogen receptor cross-talk. J Biol Chem 277(10):8531–8537. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109592200
Kma L, Baruah TJ (2022) The interplay of ROS and the PI3K/Akt pathway in autophagy regulation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 69(1):248–264. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2104
Knuever J, Poeggeler B, Gáspár E, Klinger M, Hellwig-Burgel T, Hardenbicker C et al (2012) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone controls mitochondrial biology in human epidermis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(3):978–986. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-1096
Konovalova J, Gerasymchuk D, Parkkinen I, Chmielarz P, Domanskyi A (2019) Interplay between microRNAs and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236055
Korovila I, Hugo M, Castro JP, Weber D, Höhn A, Grune T, Jung T (2017) Proteostasis, oxidative stress and aging. Redox Biol 13:550–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.07.008
Koundouros N, Poulogiannis G (2018) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling and redox metabolism in cancer. Front Oncol 8:160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00160
Kovalic AJ, Satapathy SK, Chalasani N (2018) Targeting incretin hormones and the ASK-1 pathway as therapeutic options in the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol Int 12:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9854-1
Kowalska M, Piekut T, Prendecki M, Sodel A, Kozubski W, Dorszewska J (2020) Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA oxidative damage in physiological and pathological aging. DNA Cell Biol 39(8):1410–1420. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.5347
Kruk J, Aboul-Enein HY, Kładna A, Bowser JE (2019) Oxidative stress in biological systems and its relation with pathophysiological functions: the effect of physical activity on cellular redox homeostasis. Free Radic Res 53(5):497–521. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2019.1612059
Kumar SB, Dada R, Gupta NP (2018a) Environmental toxicants–induced male reproductive toxicity. In: Bioenvironmental issues affecting men’s reproductive and sexual health. pp 305–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801299-4.00019-0
Kumar S, Mishra V, Thaker R, Gor M, Perumal S, Joshi P et al (2018b) Role of environmental factors & oxidative stress with respect to in vitro fertilization outcome. Indian J Med Res 148(Suppl 1):S125. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1864_17
Lakshmi BVS, Sudhakar M, Aparna M (2013) Protective potential of black grapes against lead induced oxidative stress in rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35(3):361–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2013.01.008
Lam D, Rao SK, Ratra V, Liu Y, Mitchell P, King J et al (2015) Cataract. Nat Rev Dis Prim 1(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.14
Larsen MK, Matchkov VV (2016) Hypertension and physical exercise: the role of oxidative stress. Medicina 52(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2016.01.005
Lawson M, Jomova K, Poprac P, Kuča K, Musílek K, Valko M (2017a) Free radicals and antioxidants in human disease. In: Nutritional antioxidant therapies: treatments and perspectives. Springer, Cham, pp 283–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67625-8_12
Lawson RP, Mathys C, Rees G (2017b) Adults with autism overestimate the volatility of the sensory environment. Nat Neurosci 20(9):1293. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4615v
Lee TH, Kang TH (2019) DNA oxidation and excision repair pathways. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):6092. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236092
Lee KH, Cha M, Lee BH (2020) Neuroprotective effect of antioxidants in the brain. Int J Mol Sci 21(19):1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197152
Lennicke C, Cochemé HM (2020) Redox signalling and ageing: insights from Drosophila. Biochem Soc Trans 48(2):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20190052
Leslie LA, Younes A (2013) Targeting oncogenic and epigenetic survival pathways in lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 54(11):2365–2376. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2013.780288
Leyane TS, Jere SW, Houreld NN (2022) Oxidative stress in ageing and chronic degenerative pathologies: molecular mechanisms involved in counteracting oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci 23(13):7273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23137273
Li M, Sharma A, Yin C, Tan X, Xiao Y (2017) Metformin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and improves the induction of autophagy in HFD-induced obese mice. Mol Med Rep 16(1):680–686. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6637
Li Z, Cheng J, Huang L, Li W, Zhao Y, Lin W (2021) Aging diagnostic probe for research on aging and evaluation of anti-aging drug efficacy. Anal Chem 93(41):13800–13806. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02391
Li J, Yang D, Li Z, Zhao M, Wang D, Sun Z et al (2022) PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2022.101817
Liguori I, Russo G, Curcio F, Bulli G, Aran L, Della-Morte D, Gargiulo G, Testa G, Cacciatore F, Bonaduce D, Abete P (2018) Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv Aging 13:757–772. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S158513
Lin YY, Lee SD (2018) Cardiovascular benefits of exercise training in postmenopausal hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 19(9):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092523
Lin J, Cook NR, Albert C, Zaharris E, Gaziano JM, Van Denburgh M et al (2009) Vitamins C and E and beta carotene supplementation and cancer risk: a randomized controlled trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(1):14–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djn438
Lindsey ME, Tarr MA (2000) Quantitation of hydroxyl radical during Fenton oxidation following a single addition of iron and peroxide. Chemosphere 41(3):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00296-9
Lingappan K (2018) NF-κB in oxidative stress. Curr Opin Toxicol 7:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2017.11.002
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D, Sun SC (2017a) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Liu YC, Wilkins M, Kim T, Malyugin B, Mehta JS (2017b) Cataracts. Lancet 390(10094):600–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30544-5
Liu XF, Zhou DD, Xie T, Hao JL, Malik TH, Lu CB, Qi J, Pant OP, Lu CW (2018) The Nrf2 signaling in retinal ganglion cells under oxidative stress in ocular neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Biol Sci 14(9):1090–1098. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.25996
Liu P, Wang Y, Li X (2019) Targeting the untargetable KRAS in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 9(5):871–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2019.03.002
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z et al (2020) PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis 11(9):797. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
Liu J, Xu P, Liu D, Wang R, Cui S, Zhang Q et al (2021) TCM regulates PI3K/Akt signal pathway to intervene atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4854755
López-Lluch G, Navas P (2016) Calorie restriction as an intervention in ageing. J Physiol 594(8):2043–2060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2017.08.002
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153(6):1194–1217
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2023) Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.001
Lu Y, Ma J, Zhao J, Song Z, Zhou C, Liu X et al (2020) The role of MKP-5 in adipocyte-macrophage interactions during obesity. Obes Facts 13(1):86–101. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505343
Lu Y, Liu Y, Zheng M (2022) The role and regulation of apoptosis signal-regulated kinase 1 in liver disease. Mol Biol Rep 49(11):10905–10914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07783-6
Madian AG, Myracle AD, Diaz-Maldonado N, Rochelle NS, Janle EM, Regnier FE (2011) Determining the effects of antioxidants on oxidative stress induced carbonylation of proteins. Anal Chem 83(24):9328–9336. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac201856g
Magallón M, Navarro-García MM, Dasí F (2019) Oxidative stress in COPD. J Clin Med 8(11):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111953
Magallón M, Pastor S, Carrión AE, Bañuls L, Pellicer D, Castillo S et al (2021) Oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in rare respiratory diseases. J Clin Med 10(6):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10061268
Magrì A, Lipari CLR, Risiglione P, Zimbone S, Guarino F, Caccamo A, Messina A (2023) ERK1/2-dependent TSPO overactivation associates with the loss of mitophagy and mitochondrial respiration in ALS. Cell Death Dis 14(2):122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05643-0
Man AWC, Li H, Xia N (2020) Impact of lifestyles (diet and exercise) on vascular health: oxidative stress and endothelial function. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1496462
Manning BD, Toker A (2017) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating the network. Cell 169(3):381–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.001
Mao Z, Bostick RM (2021) Associations of dietary, lifestyle, other participant characteristics, and oxidative balance scores with plasma F 2-isoprostanes concentrations in a pooled cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02754-2v
Martin DE, Hall MN (2005) The expanding TOR signaling network. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(2):158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.008
Martín AR, Villegas I, la Casa C, Alarcón De La Lastra C (2004) Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in grapes, suppresses oxidative damage and stimulates apoptosis during early colonic inflammation in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 67(7):1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2003.12.024
Martínez Leo EE, Peñafiel AM, Hernández Escalante VM, Cabrera Araujo ZM (2021) Ultra-processed diet, systemic oxidative stress, and breach of immunologic tolerance. Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111419
Martínez-Cué C, Rueda N (2020) Cellular senescence in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00016
Mas-Bargues C, Escrivá C, Dromant M, Borrás C, Viña J (2021) Lipid peroxidation as measured by chromatographic determination of malondialdehyde. Human plasma reference values in health and disease. Arch Biochem Biophys 709:108941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2021.108941
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ, Márquez J (2012) Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: an update. Arch Toxicol 86:1649–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0906-3
Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2008) Redox control of cell fate by MAP kinase: physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780(11):1325–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.12.011
Mattson MP (2008) Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev 7(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2007.08.007
Mayer IA, Arteaga CL (2016) The PI3K/AKT pathway as a target for cancer treatment. Annu Rev Med 67:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-062913-051343
Maynard S, Fang EF, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Croteau DL, Bohr VA (2015) DNA damage, DNA repair, aging, and neurodegeneration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5(10):a025130. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a025130
McKay TB, Lyon D, Sarker-Nag A, Priyadarsini S, Asara JM, Karamichos D (2015) Quercetin attenuates lactate production and extracellular matrix secretion in keratoconus. Sci Rep 5(1):9003. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09003
Mehdi MM, Solanki P, Singh P (2021) Oxidative stress, antioxidants, hormesis and calorie restriction: the current perspective in the biology of aging. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 95:104413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2021.104413
Mena S, Ortega A, Estrela JM (2009) Oxidative stress in environmental-induced carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 674(1–2):36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2008.09.017
Mendoza-Chamizo B, Løbner-Olesen A, Charbon G (2018) Coping with reactive oxygen species to ensure genome stability in Escherichia coli. Genes 9(11):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9110565
Meng X, Cui J, He G (2021) Bcl-2 is involved in cardiac hypertrophy through PI3K-Akt pathway. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6615502
Mercken EM, Carboneau BA, Krzysik-Walker SM, de Cabo R (2012) Of mice and men: the benefits of caloric restriction, exercise, and mimetics. Ageing Res Rev 11(3):390–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2011.11.005
Mesinovic J, Zengin A, De Courten B, Ebeling PR, Scott D (2019) Sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther 12:1057. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S186600
Miądlikowska E, Rzepka-Wrona P, Miłkowska-Dymanowska J, Białas AJ, Piotrowski WJ (2022) Serum biomarkers of lung fibrosis in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features—what do we already know? J Clin Med 11(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11010079
Miettinen TP, Björklund M (2017) Mitochondrial function and cell size: an allometric relationship. Trends Cell Biol 27(6):393–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2017.02.006
Mirończuk-Chodakowska I, Witkowska AM, Zujko ME (2018) Endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants in the human body. Adv Med Sci 63(1):68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2017.05.005
Misgeld T, Schwarz TL (2017) Mitostasis in neurons: maintaining mitochondria in an extended cellular architecture. Neuron 96(3):651–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.055
Mishra R, Bisht SS (2011) Antioxidants and their characterization. J Pharm Res 4(8):2744–2746
Mitsuishi Y, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2012) The Keap1–Nrf2 system in cancers: stress response and anabolic metabolism. Front Oncol 2:200. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2012.00200
Młynarczyk M, Falkowska M, Micun Z, Obuchowska I, Kochanowicz J, Socha K, Konopińska J (2022) Diet, oxidative stress, and blood serum nutrients in various types of glaucoma: a systematic review. Nutrients 14(7):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071421
Moelling K, Schad K, Bosse M, Zimmermann S, Schweneker M (2002) Regulation of Raf-Akt cross-talk. J Biol Chem 277(34):31099–31106. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m111974200
Moghadam ZM, Henneke P, Kolter J (2021) From flies to men: ROS and the NADPH oxidase in phagocytes. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:628991. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.628991
Mohora M, Greabu M, Totan A, Mitrea N, Battino M (2009) Redox-sensitive signaling factors and antioxidants. Farmacia 57(4):399–410
Moldakozhayev A, Gladyshev VN (2023) Metabolism, homeostasis, and aging. Trends Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2023.01.003
Moldogazieva NT, Mokhosoev IM, Feldman NB, Lutsenko SV (2018) ROS and RNS signalling: adaptive redox switches through oxidative/nitrosative protein modifications. Free Radic Res 52(5):507–543. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2018.1457217
Moon H, Ro SW (2021) MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 13(12):3026. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123026
Moraes L, Dries SS, Seibert BS, Linden R, Perassolo MS (2023) Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in ethanol users. Braz J Med Biol Res 56:e12465. https://doi.org/10.1590/1414-431X2023e12465
Morsi M, Kobeissy F, Magdeldin S, Maher A, Aboelmagd O, Johar D, Bernstein L (2019) A shared comparison of diabetes mellitus and neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Biochem 120(9):14318–14325. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26261
Most J, Redman LM (2020) Impact of calorie restriction on energy metabolism in humans. Exp Gerontol 133:110875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110875
Müller MJ, Geisler C, Blundell J, Dulloo A, Schutz Y, Krawczak M et al (2018) The case of GWAS of obesity: does body weight control play by the rules? Int J Obes 42(8):1395–1405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0081-6
Muniz FWMG, Nogueira SB, Mendes FLV, Rösing CK, Moreira MMSM, de Andrade GM, de Sousa Carvalho R (2015) The impact of antioxidant agents complimentary to periodontal therapy on oxidative stress and periodontal outcomes: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol 60(9):1203–1214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.05.007
Naganna CM, Prasad KY, Mahendra VP, Ganesan P, Kumar R (2023) Vanillic acid potentiates insulin secretion and prevents pancreatic β-cells cytotoxicity under H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Mol Biol Rep 50(2):1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08046-0
Neha K, Haider MR, Pathak A, Yar MS (2019) Medicinal prospects of antioxidants: a review. Eur J Med Chem 178:687–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.010
Neves J, Sousa-Victor P (2020) Regulation of inflammation as an anti-aging intervention. FEBS J 287(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15061
Newman JC, Verdin E (2017) β-Hydroxybutyrate: a signaling metabolite. Annu Rev Nutr 37:51–76. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071816-064916
Ngoi NY, Liew AQ, Chong SJ, Davids MS, Clement MV, Pervaiz S (2021) The redox-senescence axis and its therapeutic targeting. Redox Biol 45:102032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.102032
Nguyen GT, Green ER, Mecsas J (2017) Neutrophils to the ROScue: mechanisms of NADPH oxidase activation and bacterial resistance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017(7):373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00373
Niedzielska E, Smaga I, Gawlik M, Moniczewski A, Stankowicz P, Pera J, Filip M (2016) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 53:4094–4125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9337-5
Norat P, Soldozy S, Sokolowski JD, Gorick CM, Kumar JS, Chae Y et al (2020) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurological disorders: exploring mitochondrial transplantation. npj Regen Med 5(1):22. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41536-020-00107-x
Nowotny K, Jung T, Höhn A, Weber D, Grune T (2015) Advanced glycation end products and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomolecules 5(1):194–222. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5010194
Oakes SA, Papa FR (2015) The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol 10:173–194. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104649
Obeng E (2020) Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals—a review. Braz J Biol 81:1133–1143. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.228437
Obsilova V, Honzejkova K, Obsil T (2021) Structural insights support targeting ASK1 kinase for therapeutic interventions. Int J Mol Sci 22(24):13395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413395
Oda K, Ikeda Y, Kawana K, Osuga Y, Fujii T (2015) mTOR signaling in endometrial cancer: from a molecular and therapeutic point of view. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep 4:1–10
Ogier JM, Nayagam BA, Lockhart PJ (2020) ASK1 inhibition: a therapeutic strategy with multi-system benefits. J Mol Med 98:335–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01878-y
Ottens F, Franz A, Hoppe T (2021) Build-UPS and break-downs: metabolism impacts on proteostasis and aging. Cell Death Differ 28(2):505–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00682-y
Padma VV, Baskaran R, Divya S, Priya LB, Saranya S (2016) Modulatory effect of Tinospora cordifolia extract on Cd-induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Integr Med Res 5(1):48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imr.2015.12.005
Pani G (2010) P66SHC and ageing: ROS and TOR? Aging (Albany NY) 2(8):514. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100182
Papaconstantinou J, Hsieh CC (2010) Activation of senescence and aging characteristics by mitochondrially generated ROS: how are they linked? Cell Cycle 9(19):3831–3833. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.19.13324
Park S, Park SY (2021) Can antioxidants be effective therapeutics for type 2 diabetes? Yeungnam Univ J Med 38(2):83–94. https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00563
Park SY, Kwak YS, Park SY, Kwak YS (2016) Impact of aerobic and anaerobic exercise training on oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in athletes. J Exerc Rehabil 12(2):113–117. https://doi.org/10.12965/jer.1632598.299
Pawlyk AC, Giacomini KM, McKeon C, Shuldiner AR, Florez JC (2014) Metformin pharmacogenomics: current status and future directions. Diabetes 63(8):2590–2599. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1367
Pereira HABS, Dionizio AS, Fernandes MS, Araujo TT, Cestari TM, Buzalaf CP et al (2016) Fluoride intensifies hypercaloric diet-induced ER oxidative stress and alters lipid metabolism. PLoS ONE 11(6):e0158121. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158121
Persynaki A, Karras S, Pichard C (2017) Unraveling the metabolic health benefits of fasting related to religious beliefs: a narrative review. Nutrition 35:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2016.10.005
Piacenza L, Zeida A, Trujillo M, Radi R (2022) The superoxide radical switch in the biology of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. Physiol Rev 102(4):1881–1906. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00005.2022
Pickering RJ, Rosado CJ, Sharma A, Buksh S, Tate M, de Haan JB (2018) Recent novel approaches to limit oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications. Clin Transl Immunol 7(4):e1016. https://doi.org/10.1002/cti2.1016
Pisoschi AM, Pop A (2015) The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: a review. Eur J Med Chem 97:55–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
Pisoschi AM, Pop A, Iordache F, Stanca L, Predoi G, Serban AI (2021) Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants—an overview on their chemistry and influences on health status. Eur J Med Chem 209:112891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112891
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Ploumi C, Daskalaki I, Tavernarakis N (2017) Mitochondrial biogenesis and clearance: a balancing act. FEBS J 284(2):183–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13820
Poprac P, Jomova K, Simunkova M, Kollar V, Rhodes CJ, Valko M (2017) Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38(7):592–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.005
Postma DS, Bush A, van den Berge M (2015) Risk factors and early origins of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 385(9971):899–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60446-3
Powers SK, Radak Z, Ji LL (2016) Exercise-induced oxidative stress: past, present and future. J Physiol 594(18):5081–5092. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP270646
Prineas JW, Parratt JD (2021) Multiple sclerosis: microglia, monocytes, and macrophage-mediated demyelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 80(10):975–996. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nlab083
Pu ZQ, Yu TF, Liu D, Jin CW, Sadiq E, Qiao X et al (2021) NR4A1 enhances MKP7 expression to diminish JNK activation induced by ROS or ER-stress in pancreatic β cells for surviving. Cell Death Discov 7(1):133. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00521-0
Qin S, Yin J, Huang S, Lin J, Fang Z, Zhou Y, Huang K (2019) Astragaloside IV protects ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury by preventing mitochondrial oxidative stress and the activation of mitochondrial pathway apoptosis in rats. Front Pharmacol 10:894. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00894
Qin J, Cao M, Hu X, Tan W, Ma B, Cao Y, Chen Z, Li Q, Hu G (2023) Dual inhibitors of ASK1 and PDK1 kinases: design, synthesis, molecular docking and mechanism studies of N-benzyl pyridine-2-one containing derivatives as anti-fibrotic agents. Eur J Med Chem 247:115057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.115057
Qu B, Jia Y, Liu Y, Wang H, Ren G, Wang H (2015) The detection and role of heat shock protein 70 in various nondisease conditions and disease conditions: a literature review. Cell Stress Chaperones 20(6):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-015-0618-8
Quetglas-Llabrés MM, Monserrat-Mesquida M, Bouzas C, Gómez C, Mateos D, Ripoll-Vera T et al (2022) Inflammatory and oxidative stress markers related to adherence to the Mediterranean diet in patients with metabolic syndrome. Antioxidants 11(5):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11050901
Radak Z, Torma F, Berkes I, Goto S, Mimura T, Posa A et al (2019) Exercise effects on physiological function during aging. Free Radic Biol Med 132:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.444
Radi E, Formichi P, Battisti C, Federico A (2014) Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 42(s3):S125–S152. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-132738
Rahal A, Kumar A, Singh V, Yadav B, Tiwari R, Chakraborty S, Dhama K (2014) Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: the interplay. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/761264
Rahman HH, Niemann D, Munson-McGee SH (2022) Association between asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and lung cancer in the US population. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23631-3
Rajendran P, Nandakumar N, Rengarajan T, Palaniswami R, Gnanadhas EN, Lakshminarasaiah U, Gopas J, Nishigaki I (2014) Antioxidants and human diseases. Clin Chim Acta 436:332–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2014.06.004
Rambold AS, Pearce EL (2017) Mitochondrial dynamics at the interface of immune cell metabolism and function. Trends Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.08.006
Rao TP, Sakaguchi N, Juneja LR, Wada E, Yokozawa T (2005) Amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) extracts reduce oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Med Food 8(3):362–368. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2005.8.362
Rascio F, Spadaccino F, Rocchetti MT, Castellano G, Stallone G, Netti GS, Ranieri E (2021) The pathogenic role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer onset and drug resistance: an updated review. Cancers 13(16):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13163949
Rattan SI (2008) Hormesis in aging. Ageing Res Rev 7(1):63–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2007.03.002
Rattan SI (2018) Biogerontology: research status, challenges and opportunities. Acta Biomed 89(2):291. https://doi.org/10.23750/abm.v89i2.7403
Rattan SI (2022) Physiological hormesis and hormetins in biogerontology. Curr Opin Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2022.01.001
Rauschenberger L, Behnke J, Grotemeyer A, Knorr S, Volkmann J, Ip CW (2022) Age-dependent neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in a genetic A30P/A53T double-mutated α-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 171:105798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105798
Reddy D, Kumavath R, Tan TZ, Ampasala DR, Kumar AP (2020) Peruvoside targets apoptosis and autophagy through MAPK Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways in human cancers. Life Sci 241:117147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117147
Redman LM, Smith SR, Burton JH, Martin CK, Il’yasova D, Ravussin E (2018) Metabolic slowing and reduced oxidative damage with sustained caloric restriction support the rate of living and oxidative damage theories of aging. Cell Metab 27(4):805–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.019
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochem Biophys Acta 1863(12):2977–2992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012
Reeg S, Grune T (2015) Protein oxidation in aging: does it play a role in aging progression? Antioxid Redox Signal 23(3):239–255. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2014.6062
Ren J, Bi Y, Sowers JR, Hetz C, Zhang Y (2021) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in cardiovascular diseases. Nat Rev Cardiol 18(7):499–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00511-w
Rodrigues SDO, Cunha CMCD, Soares GMV, Silva PL, Silva AR, Gonçalves-de-Albuquerque CF (2021) Mechanisms, pathophysiology and currently proposed treatments of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmaceuticals 14(10):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14100979
Rodríguez-Cano AM, González-Ludlow I, Suárez-Rico BV, Montoya-Estrada A, Piña-Ramírez O, Parra-Hernández SB, Reyes-Muñoz E, Estrada-Gutierrez G, Calzada-Mendoza CC, Perichart-Perera O (2022) Ultra-processed food consumption during pregnancy and its association with maternal oxidative stress markers. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071415
Rodríguez-Rodríguez P, Ramiro-Cortijo D, Reyes-Hernández CG, López de Pablo AL, Carmen González M, Arribas SM (2018) Implication of oxidative stress in fetal programming of cardiovascular disease. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00602
Ros M, Carrascosa JM (2020) Current nutritional and pharmacological anti-aging interventions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1866(3):165612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165612
Rose MR, Flatt T, Graves JL, Greer LF, Martinez DE, Matos M, Mueller LD, Shmookler Reis RJ, Shahrestani P (2012) What is aging? Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00134
Rossner P Jr, Milcova A, Libalova H, Novakova Z, Topinka J, Balascak I, Sram RJ (2009) Biomarkers of exposure to tobacco smoke and environmental pollutants in mothers and their transplacental transfer to the foetus. Part II. Oxidative damage. Mutat Res 669(1–2):20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.04.010
Sagoo MK, Gnudi L (2020) Diabetic nephropathy: an overview. In: Diabetic nephropathy: methods and protocols. pp 3–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9841-8_1
Saha S, Buttari B, Panieri E, Profumo E, Saso L (2020) An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225474
Saidi AO, Akintayo CO, Atuma CL, Mahmud H, Sabinari IW, Oniyide AA et al (2022) Melatonin supplementation preserves testicular function by attenuating lactate production and oxidative stress in high fat diet-induced obese rat model. Theriogenology 187:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.02.029
Salles GBC, Boiago MM, Silva AD, Morsch VM, Gris A, Mendes RE et al (2019) Lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in broiler breast fillets with white striping myopathy. J Food Biochem 43(4):e12792. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12792
Salvestrini V, Sell C, Lorenzini A (2019) Obesity may accelerate the aging process. Front Endocrinol 10:266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00266
Samadian F, Dalili N, Jamalian A (2016) Lifestyle modifications to prevent and control hypertension. Iran J Kidney Dis 10(5):237
Sanchez T (2018) Effects of mercury, lead, arsenic and zinc to human renal oxidative stress and functions: a review. Arch Med. https://doi.org/10.21767/2473-6457.10027
Sánchez-Rodríguez MA, Zacarías-Flores M, Correa-Muñoz E, Arronte-Rosales A, Mendoza-Núñez VM (2021) Oxidative stress risk is increased with a sedentary lifestyle during aging in Mexican women. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9971765
Sangeetha T, Chen Y, Sasidharan S (2020) Oxidative stress and aging and medicinal plants as antiaging agents. J Complement Med Res 11(3):01. https://doi.org/10.5455/jcmr.2020.11.03.01
Santoro A, Martucci M, Conte M, Capri M, Franceschi C, Salvioli S (2020) Inflammaging, hormesis and the rationale for anti-aging strategies. Ageing Res Rev 64:101142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101142
Santos JPMD, Maio MCD, Lemes MA, Laurindo LF, Haber JFDS, Bechara MD et al (2022) Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and organokines: what is now and what will be in the future. Int J Mol Sci 23(1):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010498
Sarkar S, Chakraborty D, Bhowmik A, Ghosh MK (2019) Cerebral ischemic stroke: cellular fate and therapeutic opportunities. Front Biosci Landmark 24(3):415–430. https://doi.org/10.2741/4727
Savaş A, Oz E, Oz F (2021) Is oven bag really advantageous in terms of heterocyclic aromatic amines and bisphenol-A? Chicken meat perspective. Food Chem 355:129646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129646
Savić N, Schwank G (2016) Advances in therapeutic CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Transl Res 168:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2015.09.008
Scarpulla RC, Vega RB, Kelly DP (2012) Transcriptional integration of mitochondrial biogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 23(9):459–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2012.06.006
Schaur RJ, Siems W, Bresgen N, Eckl PM (2015) 4-Hydroxy-nonenal—a bioactive lipid peroxidation product. Biomolecules 5(4):2247–2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5042247
Schiavone S, Jaquet V, Trabace L, Krause KH (2013) Severe life stress and oxidative stress in the brain: from animal models to human pathology. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(12):1475–1490. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4720v
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24(10):R453–R462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Schröder K (2020) NADPH oxidases: current aspects and tools. Redox Biol 34:101512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101512
Schumacher B, Pothof J, Vijg J, Hoeijmakers JH (2021) The central role of DNA damage in the ageing process. Nature 592(7856):695–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03307-7
Schuster AK, Erb C, Hoffmann EM, Dietlein T, Pfeiffer N (2020) The diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma. Dtsch Arztebl Int 117(13):225. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2020.0225
Seixas AF, Quendera AP, Sousa JP, Silva AF, Arraiano CM, Andrade JM (2022) Bacterial response to oxidative stress and RNA oxidation. Front Genet 12:821535. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.821535
Selman C, McLaren JS, Collins AR, Duthie GG, Speakman JR (2013) Deleterious consequences of antioxidant supplementation on lifespan in a wild-derived mammal. Biol Let 9(4):20130432. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2013.0432
Shabab T, Khanabdali R, Moghadamtousi SZ, Kadir HA, Mohan G (2017) Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci 127(7):624–633. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2016.1212854
Shah AA, Gupta A (2020) Antioxidants in health and disease with their capability to defend pathogens that attack apple species of Kashmir. Plant Antioxid Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45299-5_13-1
Shah K, Verma RJ (2012) Protection against butyl p-hydroxybenzoic acid induced oxidative stress by Ocimum sanctum extract in mice liver. Acta Pol Pharm 69(5):865–870
Sharifi-Rad M, Anil Kumar NV, Zucca P, Varoni EM, Dini L, Panzarini E et al (2020) Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front Physiol 11:694. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00694
Sharma V, Mehdi MM (2023) Oxidative stress, inflammation and hormesis: the role of dietary and lifestyle modifications on aging. Neurochem Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105490
Sharma BR, Jaiswal S, Ravindra PV (2022) Modulation of gut microbiota by bioactive compounds for prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother 152:113148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113148
Shefa U, Jeong NY, Song IO, Chung HJ, Kim D, Jung J, Huh Y (2019) Mitophagy links oxidative stress conditions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res 14(5):749. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.249218
Shi M, Wang X, Yamanaka T, Ogita F, Nakatani K, Takeuchi T (2007) Effects of anaerobic exercise and aerobic exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress. Environ Health Prev Med 12(5):202–208. https://doi.org/10.1265/ehpm.12.202
Shih CC, Shih YL, Chen JY (2021) The association between homocysteine levels and cardiovascular disease risk among middle-aged and elderly adults in Taiwan. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 21:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-021-02000-x
Shinde A, Ganu J, Naik P (2012) Effect of free radicals & antioxidants on oxidative stress: a review. J Dent Allied Sci 1(2):63. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-4696.159144
Sies H (1997) Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol Transl Integr 82(2):291–295. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.1997.sp004024
Sies H (2017) Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: oxidative eustress. Redox Biol 11:613–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.035
Sies H (2018) H2O2 as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 120:S6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.04.030
Sifuentes-Franco S, Padilla-Tejeda DE, Carrillo-Ibarra S, Miranda-Díaz AG (2018) Oxidative stress, apoptosis, and mitochondrial function in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1875870
Simioni C, Zauli G, Martelli AM, Vitale M, Sacchetti G, Gonelli A, Neri LM (2018) Oxidative stress: role of physical exercise and antioxidant nutraceuticals in adulthood and aging. Oncotarget 9(24):17181. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24729
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F (2000) Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 5:415–418. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009616228304
Simpson DS, Oliver PL (2020) ROS generation in microglia: understanding oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxidants 9(8):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080743
Singha I, Das SK (2015) Free radical scavenging properties of skin and pulp extracts of different grape cultivars in vitro and attenuation of H2O2-induced oxidative stress in liver tissue ex vivo. Indian J Clin Biochem 30(3):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0442-4
Sliter DA, Martinez J, Hao L, Chen XI, Sun N, Fischer TD et al (2018) Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature 561(7722):258–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0448-9
Small DM, Beetham KS, Howden EJ, Briskey DR, Johnson DW, Isbel NM et al (2017) Effects of exercise and lifestyle intervention on oxidative stress in chronic kidney disease. Redox Rep 22(3):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/13510002.2016.1276314
Smith MA, Rottkamp CA, Nunomura A, Raina AK, Perry G (2000) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Acta 1502(1):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4439(00)00040-5
Soares JP, Silva AM, Fonseca S, Oliveira MM, Peixoto F, Gaivão I, Mota MP (2015) How can age and lifestyle variables affect DNA damage, repair capacity and endogenous biomarkers of oxidative stress? Exp Gerontol 62:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2015.01.001
Soladoye OP, Juárez ML, Aalhus JL, Shand P, Estévez M (2015) Protein oxidation in processed meat: mechanisms and potential implications on human health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 14(2):106–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12127
Solleiro-Villavicencio H, Rivas-Arancibia S (2018) Effect of chronic oxidative stress on neuroinflammatory response mediated by CD4+ T cells in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00114
Somade OT, Ajayi BO, Safiriyu OA, Oyabunmi OS, Akamo AJ (2019) Renal and testicular up-regulation of pro-inflammatory chemokines (RANTES and CCL2) and cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) following acute edible camphor administration is through activation of NF-kB in rats. Toxicol Rep 6:759–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.07.010
Son Y, Cheong Y-K, Kim N-H, Chung H-T, Kang DG, Pae H-O (2011) Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal Transduct 2011:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/792639
Sonnessa M, Cioffi A, Brunetti O, Silvestris N, Zito FA, Saponaro C, Mangia A (2020) NLRP3 inflammasome from bench to bedside: new perspectives for triple negative breast cancer. Front Oncol 10:1587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01587
Srinivas US, Tan BW, Vellayappan BA, Jeyasekharan AD (2019) ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol 25:101084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.101084
Srivastava RAK (2018) Life-style-induced metabolic derangement and epigenetic changes promote diabetes and oxidative stress leading to NASH and atherosclerosis severity. J Diabetes Metab Disord 17(2):381–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-018-0378-y
Stakos DA, Stamatelopoulos K, Bampatsias D, Sachse M, Zormpas E, Vlachogiannis NI et al (2020) The Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-beta hypothesis in cardiovascular aging and disease: JACC focus seminar. J Am Coll Cardiol 75(8):952–967
Stead ER, Bjedov I (2021) Balancing DNA repair to prevent ageing and cancer. Exp Cell Res 405(2):112679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112679
Steven S, Frenis K, Oelze M, Kalinovic S, Kuntic M, Bayo Jimenez MT et al (2019) Vascular inflammation and oxidative stress: major triggers for cardiovascular disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7092151
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang Q, He C, Pan H (2014) P38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett 344(2):174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.019
Sulzer D, Alcalay RN, Garretti F, Cote L, Kanter E, Agin-Liebes J et al (2017) T cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease recognize α-synuclein peptides. Nature 546(7660):656–661. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22815
Sun XL, Zhang XW, Zhai HJ, Zhang D, Ma SY (2020a) Magnoflorine inhibits human gastric cancer progression by inducing autophagy, apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by JNK activation regulated by ROS. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109118
Sun Y, Lu Y, Saredy J, Wang X, Drummer C IV, Shao Y et al (2020b) ROS systems are a new integrated network for sensing homeostasis and alarming stresses in organelle metabolic processes. Redox Biol 37:101696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101696
Sun Y, Wang H, Qu T, Luo J, An P, Ren F, Luo Y, Li Y (2023) mTORC2: a multifaceted regulator of autophagy. Cell Commun Signal 21(1):4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-022-00859-7
Suzuki YJ, Carini M, Butterfield DA (2010) Protein carbonylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 12(3):323–325. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2887
Tan BL, Norhaizan ME, Liew WPP (2018) Nutrients and oxidative stress: friend or foe? Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9719584
Teng KX, Niu LY, Yang QZ (2022) A host–guest strategy for converting the photodynamic agents from a singlet oxygen generator to a superoxide radical generator. Chem Sci 13(20):5951–5956. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01469F
Tian X, Xue Y, Xie G, Zhou Y, Xiao H, Ding F, Zhang M (2021) (−)-Epicatechin ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation via inhibiting ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in rats with COPD. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 429:115674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2021.115674
Tinkov AA, Bjørklund G, Skalny AV, Holmgren A, Skalnaya MG, Chirumbolo S, Aaseth J (2018) The role of the thioredoxin/thioredoxin reductase system in the metabolic syndrome: towards a possible prognostic marker? Cell Mol Life Sci 75:1567–1586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2745-8
Toboła-Wróbel K, Pietryga M, Dydowicz P, Napierała M, Brązert J, Florek E (2020) Association of oxidative stress on pregnancy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6398520
Tonc E, Takeuchi Y, Chou C, Xia Y, Holmgren M, Fujii C et al (2021) Unexpected suppression of tumorigenesis by c-MYC via TFAP4-dependent restriction of stemness in B lymphocytes. Blood 138(24):2526–2538. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021011711
Tong J, Hei TK (2020) Aging and age-related health effects of ionizing radiation. Radiat Med Prot 1(1):15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmp.2020.01.005
Truong VL, Jun M, Jeong WS (2018) Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. BioFactors 44(1):36–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1399
Tsermpini EE, Plemenitaš Ilješ A, Dolžan V (2022) Alcohol-induced oxidative stress and the role of antioxidants in alcohol use disorder: a systematic review. Antioxidants 11(7):1374. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11071374
Tsuchiya M, Asada A, Kasahara E, Sato EF, Shindo M, Inoue M (2002) Smoking a single cigarette rapidly reduces combined concentrations of nitrate and nitrite and concentrations of antioxidants in plasma. Circulation 105(10):1155–1157. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc1002.105935
Tu W, Wang H, Li S, Liu Q, Sha H (2019) The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis 10(3):637–651. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.0513
Turrens JF (2003) Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J Physiol 552(2):335–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2003.00335.x
ur Rahman U, Sahar A, Khan MI, Nadeem M (2014) Production of heterocyclic aromatic amines in meat: chemistry, health risks and inhibition. A review. LWT 59(1):229–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.06.005
Vaiserman AM (2011) Hormesis and epigenetics: is there a link? Ageing Res Rev 10(4):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2011.01.004
Valko M, Rhodes CJB, Moncol J, Izakovic MM, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160(1):1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(1):44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
Van de Ven RA, Santos D, Haigis MC (2017) Mitochondrial sirtuins and molecular mechanisms of aging. Trends Mol Med 23(4):320–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2017.02.005
Varma D, Sen D (2015) Role of the unfolded protein response in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 75(1):1–26
Vasileiou PVS, Evangelou K, Vlasis K, Fildisis G, Panayiotidis MI, Chronopoulos E, Passias PG, Kouloukoussa M, Gorgoulis VG, Havaki S (2019) Mitochondrial homeostasis and cellular senescence. Cells 8(7):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070686
Vasim I, Majeed CN, DeBoer MD (2022) Intermittent fasting and metabolic health. Nutrients 14(3):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030631
Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK (1996) Nrf1 and Nrf2 positively and c-Fos and Fra1 negatively regulate the human antioxidant response element-mediated expression of NAD (P) H: quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(25):14960–14965. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.25.14960
Vigneron A, Vousden KH (2010) p53, ROS and senescence in the control of aging. Aging (Albany NY) 2(8):471. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100189
Waghela BN, Vaidya FU, Agrawal Y, Santra MK, Mishra V, Pathak C (2021) Molecular insights of NADPH oxidases and its pathological consequences. Cell Biochem Funct 39(2):218–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3589
Wai T, Langer T (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics and metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 27:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.12.001
Wang CH, Wei YH (2020) Roles of mitochondrial sirtuins in mitochondrial function, redox homeostasis, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155266
Wang H, Xu J, Lazarovici P, Quirion R, Zheng W (2018a) cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB): a possible signaling molecule link in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci 11:255. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00255
Wang M, Zhang L, Zhu W, Zhang J, Kim SH, Wang Y, Ni L, Telljohann R, Monticone RE, McGraw K, Liu L, de Cabo R, Lakatta EG (2018b) Calorie restriction curbs proinflammation that accompanies arterial aging, preserving a youthful phenotype. J Am Heart Assoc 7(18):e009112. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.118.009112
Wang Y, Liu N, Lu B (2019) Mechanisms and roles of mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther 25(7):859–875. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13140
Ward NC, Hodgson JM, Puddey IB, Mori TA, Beilin LJ, Croft KD (2004) Oxidative stress in human hypertension: association with antihypertensive treatment, gender, nutrition, and lifestyle. Free Radic Biol Med 36(2):226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.10.021
Weidinger A, Kozlov AV (2015) Biological activities of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: oxidative stress versus signal transduction. Biomolecules 5(2):472–484. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020472
Wright C (2015) Standardized methods for the regulation of cigarette-smoke constituents. Trends Anal Chem 66:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.11.011
Wright E Jr, Scism-Bacon JL, Glass LC (2006) Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: the role of fasting and postprandial glycaemia. Int J Clin Pract 60(3):308–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1368-5031.2006.00825.x
Wu T, Tang Q, Yu Z, Gao Z, Hu H, Chen W et al (2014) Inhibitory effects of sweet cherry anthocyanins on the obesity development in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65(3):351–359. https://doi.org/10.3109/09637486.2013.854749
Wu H, Medeiros LJ, Young KH (2018a) Apoptosis signaling and BCL-2 pathways provide opportunities for novel targeted therapeutic strategies in hematologic malignances. Blood Rev 32(1):8–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2017.08.004
Wu Y, Wang F, Fan L, Zhang W, Wang T, Du Y, Bai X (2018b) Baicalin alleviates atherosclerosis by relieving oxidative stress and inflammatory responses via inactivating the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 97:1673–1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.024
Wu Y, Chen M, Jiang J (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases and drug targets via apoptotic signaling. Mitochondrion 49:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2019.07.003
Wu L, Xiong X, Wu X, Ye Y, Jian Z, Zhi Z, Gu L (2020) Targeting oxidative stress and inflammation to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Mol Neurosci 13:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.00028
Xin L, Gao J, Ge X, Tian C, Ma W, Tian Z et al (2018) Increased pro-inflammatory cytokine-secreting regulatory T cells are correlated with the plasticity of T helper cell differentiation and reflect disease status in asthma. Respir Med 143:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2018.09.007
Xu X, Lai Y, Hua ZC (2019) Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20180992
Xu H, Wan XD, Zhu RR, Liu JL, Liu JC, Zhou XL (2022) Keap-NRF2 signaling contributes to the Notch1 protected heart against ischemic reperfusion injury via regulating mitochondrial ROS generation and bioenergetics. Int J Biol Sci 18(4):1651. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.63297
Yan LJ (2018) Redox imbalance stress in diabetes mellitus: role of the polyol pathway. Anim Model Exp Med 1(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/ame2.12001
Yan Y, Jiang W, Spinetti T, Tardivel A, Castillo R, Bourquin C et al (2013) Omega-3 fatty acids prevent inflammation and metabolic disorder through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunity 38(6):1154–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.05.015
Yang CC, Yang CM (2021) Chinese herbs and repurposing old drugs as therapeutic agents in the regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation in pulmonary diseases. J Inflamm Res 14:657–687. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S293135
Yang J, Nie J, Ma X, Wei Y, Peng Y, Wei X (2019) Targeting PI3K in cancer: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol Cancer 18(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0954-x
Yang H, Ren S, Yu S, Pan H, Li T, Ge S, Zhang J, Xia N (2020a) Methods favoring homology-directed repair choice in response to CRISPR/Cas9 induced-double strand breaks. Int J Mol Sci 21(18):6461. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186461
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang J et al (2020b) Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0110-5
Yeligar SM, Chen MM, Kovacs EJ, Sisson JH, Burnham EL, Brown LAS (2016) Alcohol and lung injury and immunity. Alcohol 55:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2016.08.005
Yimcharoen M, Kittikunnathum S, Suknikorn C, Nak-On W, Yeethong P, Anthony TG, Bunpo P (2019) Effects of ascorbic acid supplementation on oxidative stress markers in healthy women following a single bout of exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 16(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-019-0269-8
Yoo J, Wu M, Yin Y, Herzik MA, Lander GC, Lee SY (2018) Cryo-EM structure of a mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Science 361(6401):506–511
You L, Nepovimova E, Valko M, Wu Q, Kuca K (2023) Mycotoxins and cellular senescence: the impact of oxidative stress, hypoxia, and immunosuppression. Arch Toxicol 97(2):393–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03423-x
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H (2020) Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):209. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00312-6
Yuk JM, Silwal P, Jo EK (2020) Inflammasome and mitophagy connection in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci 21(13):4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134714
Yun J, Finkel TM (2014) Mitohormesis. Cell Metab 19(5):757–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.011
Zeeshan HMA, Lee GH, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated ROS. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030327
Zhai M, Li B, Duan W, Jing L, Zhang B, Zhang M et al (2017) Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through SIRT 3-dependent regulation of oxidative stress and apoptosis. J Pineal Res 63(2):e12419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12419
Zhang XK (2004) Orphan receptor TR3/nur77 and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Burnham Institute, La Jolla
Zhang H, Tsao R (2016) Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Curr Opin Food Sci 8:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2016.02.002
Zhang W, Xiao S, Ahn DU (2013) Protein oxidation: basic principles and implications for meat quality. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 53(11):1191–1201. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2011.577540
Zhang B, Meng M, Xiang S, Cao Z, Xu X, Zhao Z et al (2019a) Selective activation of tumor-suppressive MAPKP signaling pathway by triptonide effectively inhibits pancreatic cancer cell tumorigenicity and tumor growth. Biochem Pharmacol 166:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.05.010
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Zhou L, Lei Y, Zhang Y, Huang C (2019b) Redox signaling and unfolded protein response coordinate cell fate decisions under ER stress. Redox Biol 25:101047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.005
Zhao Q, Liu Y, Zhong J, Bi Y, Liu Y, Ren Z et al (2019) Pristimerin induces apoptosis and autophagy via activation of ROS/ASK1/JNK pathway in human breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Discov 5(1):125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-019-0208-0
Zhao Y, Simon M, Seluanov A, Gorbunova V (2023) DNA damage and repair in age-related inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 23(2):75–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-022-00751-y
Zheng Q, Li Q, Zhao G, Zhang J, Yuan H, Gong D et al (2020) Alkannin induces cytotoxic autophagy and apoptosis by promoting ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of JNK pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 180:114167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114167
Zhou S, Tang X, Chen HZ (2018) Sirtuins and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol 9:748. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00748
Zhu C, Huang M, Kim HG, Chowdhury K, Gao J, Liu S et al (2021) SIRT6 controls hepatic lipogenesis by suppressing LXR, ChREBP, and SREBP1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1867(12):166249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166249
Zi Y, Wang X, Zi Y, Yu H, Lan Y, Fan Y, Ren C, Liao K, Chen H (2023) Cigarette smoke induces the ROS accumulation and iNOS activation through deactivation of Nrf-2/SIRT3 axis to mediate the human bronchial epithelium ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.002
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ (2014) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev 94(3):909–950. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
Zuo L, Zhou T, Chuang CC (2017) Antioxidants in physical exercise and sports performance. In: Nutritional antioxidant therapies: treatments and perspectives. Springer, Cham, pp 247–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67625-8_10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors authenticate that they have prepared the intellectual content of this paper and have complied with the following three requirements: (a) material contributions to the conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; (b) drafting or revising the article for intellectual content; and (c) final approval of the article as published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mani Raj Chaudhary, Sakshi Chaudhary, Yogita Sharma, Thokchom Arjun Singh, Alok Kumar Mishra, Shweta Sharma, Mohammad Murtaza Mehdi are not associated with or involved in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria, consultancies, membership, educational grants, employment, speaking engagements, stock ownership, or other equity interest, expert testimony, or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as a personal or professional relationship).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, M.R., Chaudhary, S., Sharma, Y. et al. Aging, oxidative stress and degenerative diseases: mechanisms, complications and emerging therapeutic strategies. Biogerontology 24, 609–662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-023-10050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-023-10050-1