Abstract
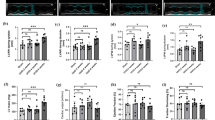
Adriamycin (ADR) increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which diminishes mitochondrial function. Angiotensin-II stimulates mitochondrial ROS generation. The aim of the study was to examine whether angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) or renin inhibitors protect against ADR-induced mitochondrial function impairment. Rats were divided into five groups as control, ADR, co-treatment ADR with captopril, co-treatment ADR with aliskiren, co-treatment ADR with both captopril and aliskiren. Left ventricular function and blood pressures were assessed at the end of treatment period. Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ATP levels were determined. ADR treatment decreased the left ventricular pressure and increased the left ventricular end-diastolic pressure. ADR decreased MMP and ATP levels in myocyte mitochondria due to increasing oxidative stress. ADR decreased MMP and ATP levels due to increased oxidative stress in the heart. Inhibitors of ACE and renin caused the elevation of the decreased of MMP and ATP levels. The pathologic changes in electrocardiogram, blood pressure and left ventricular function were decreased by inhibition of Ang-II production. We concluded that inhibitors of angiotensin II are effective against ADR cardiotoxicity via the restoration of MMP and ATP production and prevention of mitochondrial damage in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arozal W, Watanabe K, Veeraveedu PT, Thandavarayan RA, Harima M, Sukumaran V, Suzuki K, Kodama M, Aizawa Y (2010) Effect of telmisartan in limiting the cardiotoxic effect of daunorubicin in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:1776–1783. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01196.x
Boucek RJ Jr, Miracle A, Anderson M, Engelman R, Atkinson J, Dodd DA (1999) Persistent effects of doxorubicin on cardiac gene expression. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:1435–1446. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1999.0972
Boucek RJ Jr, Steele A, Miracle A, Atkinson J (2003) Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor on delayed-onset doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc Toxicol 3:319–329
Chandran K, Aggarwal D, Migrino RQ, Joseph J, McAllister D, Konorev EA, Antholine WE, Zielonka J, Srinivasan S, Avadhani NG, Kalyanaraman B (2009) Doxorubicin inactivates myocardial cytochrome c oxidase in rats: cardioprotection by Mito-Q. Biophys J 96:1388–1398. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2008.10.042
Dagenais NJ, Jamali F (2005) Protective effects of angiotensin II interruption: evidence for antiinflammatory actions. Pharmacotherapy 25:1213–1229. doi:10.1592/phco.2005.25.9.1213
de Cavanagh EM, Inserra F, Ferder M, Ferder L (2007) From mitochondria to disease: role of the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Nephrol 27:545–553. doi:10.1159/000107757
Dursun N, Taskin E, Ozturk F (2011a) Protection against adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy by carnosine in rats: role of endogenous antioxidants. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:412–424. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8875-y
Dursun N, Taskin E, Yerer Aycan MB, Sahin L (2011b) Selenium-mediated cardioprotection against adriamycin-induced mitochondrial damage. Drug Chem Toxicol 34:199–207. doi:10.3109/01480545.2010.538693
Fisher PW, Salloum F, Das A, Hyder H, Kukreja RC (2005) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition with sildenafil attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis and left ventricular dysfunction in a chronic model of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Circulation 111:1601–1610. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000160359.49478.C2
Harake D, Franco VI, Henkel JM, Miller TL, Lipshultz SE (2012) Cardiotoxicity in childhood cancer survivors: strategies for prevention and management. Future Cardiol 8:647–670. doi:10.2217/fca.12.44
Ibrahim MA, Ashour OM, Ibrahim YF, El-Bitar HI, Gomaa W, Abdel-Rahim SR (2009) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin AT(1)-receptor antagonism equally improve doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Pharm Res 60:373–381. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2009.05.007
Iqbal M, Dubey K, Anwer T, Ashish A, Pillai KK (2008) Protective effects of telmisartan against acute doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Rep 60:382–390
Montaigne D, Hurt C, Neviere R (2012) Mitochondria death/survival signaling pathways in cardiotoxicity induced by anthracyclines and anticancer-targeted therapies. Biochem Res Int 2012:951539. doi:10.1155/2012/951539
Monti M, Terzuoli E, Ziche M, Morbidelli L (2013) The sulphydryl containing ACE inhibitor Zofenoprilat protects coronary endothelium from Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. Pharmacol Res 76:171–181. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.08.003
Muller DN, Derer W, Dechend R (2008) Aliskiren-mode of action and preclinical data. J Mol Med (Berl) 86:659–662. doi:10.1007/s00109-008-0330-6
Nakamae H, Tsumura K, Terada Y, Nakane T, Nakamae M, Ohta K, Yamane T, Hino M. (2005) Notable effects of angiotensin II receptor blocker, valsartan, on acute cardiotoxic changes after standard chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone. Cancer 104:2492–2498. doi:10.1002/cncr.21478
Nakamura T, Ueda Y, Juan Y, Katsuda S, Takahashi H, Koh E (2000) Fas-mediated apoptosis in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats: in vivo study. Circulation 102:572–578
Octavia Y, Tocchetti CG, Gabrielson KL, Janssens S, Crijns HJ, Moens AL (2012) Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol 52:1213–1225. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.03.006
Okumura K, Jin D, Takai S, Miyazaki M (2002) Beneficial effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in hamsters. Jpn J Pharmacol 88:183–188
Ozdogan K, Taskin E, Dursun N (2011) Protective effect of carnosine on adriamycin-induced oxidative heart damage in rats. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 11:3–10. doi:10.5152/akd.2011.003
Pfeffer JM, Pfeffer MA, Braunwald E (1985) Influence of chronic captopril therapy on the infarcted left ventricle of the rat. Circ Res 57:84–95
Rashikh A, Abul Kalam N, Akhtar M, Mahmood D, Pillai KK, Ahmad SJ (2011) Protective effects of aliskiren in doxorubicin-induced acute cardiomyopathy in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 30:102–109. doi:10.1177/0960327110369819
Rashikh A, Ahmad SJ, Pillai KK, Kohli K, Najmi AK (2012) Aliskiren attenuates myocardial apoptosis and oxidative stress in chronic murine model of cardiomyopathy. Biomed Pharmacother 66:138–143. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2011.11.020
Rashikh A, Pillai KK, Ahmad SJ, Akhtar M, Najmi AK (2013a) Aliskiren alleviates doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and podocyte injury. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 14:14–22. doi:10.1177/1470320312459980
Rashikh A, Pillai KK, Najmi AK (2013b) Protective effect of a direct renin inhibitor in acute murine model of cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. doi:10.1111/fcp.12054
Roig Minguell E (2004) Clinical use of markers of neurohormonal activation in heart failure. Rev Esp Cardiol 57:347–356
Sacco G, Mario B, Lopez G, Evangelista S, Manzini S, Maggi CA (2009) ACE inhibition and protection from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in the rat. Vasc Pharmacol 50:166–170. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2009.01.001
Shi Y, Moon M, Dawood S, McManus B, Liu PP (2011) Mechanisms and management of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Herz 36:296–305. doi:10.1007/s00059-011-3470-3
Simmons TW, Jamall IS (1989) Relative importance of intracellular glutathione peroxidase and catalase in vivo for prevention of peroxidation to the heart. Cardiovasc Res 23:774–779
Singal PK, Iliskovic N, Li T, Kumar D (1997) Adriamycin cardiomyopathy: pathophysiology and prevention. FASEB J 11:931–936
St-Jacques R, Toulmond S, Auger A, Binkert C, Cromlish W, Fischli W, Harris J, Hess P, Jie Lan, Liu S, Riendeau D, Steiner B, Percival MD (2011) Characterization of a stable, hypertensive rat model suitable for the consecutive evaluation of human renin inhibitors. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 12:133–145. doi:10.1177/1470320310392618
Taskin EDN (2014) Recovery of adriamycın induced mitochondrıal dysfunctıon in liver by selenium. Cytotechnology. doi:10.1007/S10616-014-9736-X
Taskin E, Dursun N (2012) The protection of selenium on adriamycin-induced mitochondrial damage in rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 147:165–171. doi:10.1007/s12011-011-9273-9
Taskin E, Ozdogan K, Kunduz Kindap E, Dursun N (2014) The restoration of kidney mitochondria function by inhibition of angiotensin-II production in rats with acute adriamycin-induced nephrotoxicity. Ren Fail 36:606–612. doi:10.3109/0886022X.2014.882737
Tokarska-Schlattner M, Wallimann T, Schlattner U (2006) Alterations in myocardial energy metabolism induced by the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin. CR Biol 329:657–668. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2005.08.007
Toko H, Oka T, Zou Y, Sakamoto M, Mizukami M, Sano M, Yamamoto R, Sugaya T, Komuro I (2002) Angiotensin II type 1a receptor mediates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Hypertens Res 25:597–603
Venkatesan N, Ramesh CV, Jayakumar R, Chandrakasan G (1993) Angiotensin I converting enzyme activity in adriamycin induced nephrosis in rats. Toxicology 85:137–148
Wallace KB (2003) Doxorubicin-induced cardiac mitochondrionopathy. Pharmacol Toxicol 93:105–115
Wallace KB (2007) Adriamycin-induced interference with cardiac mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. Cardiovasc Toxicol 7:101–107. doi:10.1007/s12012-007-0008-2
Westermann D, Riad A, Lettau O, Roks A, Savvatis K, Becher PM, Escher F, Jan Danser AH, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C (2008) Renin inhibition improves cardiac function and remodeling after myocardial infarction independent of blood pressure. Hypertension 52:1068–1075. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116350
Xu M, Sheng L, Zhu X, Zeng S, Chi D, Zhang GJ (2010) Protective effect of tetrandrine on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Tumori 96:460–464
Zhu SG, Kukreja RC, Das A, Chen Q, Lesnefsky EJ, Xi L (2011) Dietary nitrate supplementation protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by improving mitochondrial function. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:2181–2189. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.01.024
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank to Prof. Dr. Cem SUER and Prof. Dr. Yunus DURSUN for helping statistical analysis of data. This work was supported by the Medical Research Council of Erciyes University (Grant number TSD-09-733).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taskin, E., Kindap, E.K., Ozdogan, K. et al. Acute adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity is exacerbated by angiotension II. Cytotechnology 68, 33–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9748-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-014-9748-6