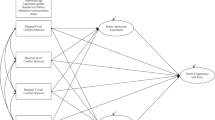
Abstract
Objectives
The current study aimed to examine the association between coparenting and adolescent emotional instability and to analyze the potential mediating effect of parent–child relationship quality between them in Chinese families.
Methods
A convenient sample of 3045 adolescents from China was selected to fill out questionnaires regarding their emotional instability and demographic variables, parental coparenting behavior, and parent–child relationship quality. Structural equation modeling was used to test the total and mediating effect models.
Results
Supportive and undermining coparenting were significantly associated with adolescent emotional instability (βSC = −0.13, βUC = 0.21, p < 0.001), and the total effect of undermining coparenting on adolescent emotional instability was stronger than that of supportive coparenting (Wald [χ2] = 4.37, p < 0.05). Mediation model analysis revealed that undermining coparenting was associated with a poor quality of parent–child relationship, which ultimately predicted a high level of emotional instability (ab/c = 0.47). By contrast, supportive coparenting was associated with a high parent–child relationship quality, which ultimately predicted a low level of emotional instability (|ab/c’| = 1.98). However, the direct effect of supportive coparenting was positively related to adolescent emotional instability (β = 0.14, p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Findings implied that undermining coparenting was a family risk factor for adolescent emotional instability, whereas supportive coparenting exhibited a double-edged (i.e., positive and negative) effect on adolescent emotional instability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Belsky, J., Putnam, S., & Crnic, K. (1996). Coparenting, parenting, and early emotional development. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, 74, 45–55.
Branje, S. J., Hale, W. W., Frijns, T., & Meeus, W. H. (2010). Longitudinal associations between perceived parent–child relationship quality and depressive symptoms in adolescence. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38(6), 751–763.
Caldera, Y. M., & Lindsey, E. W. (2006). Coparenting, mother–infant interaction, and infant–parent attachment relationships in two–parent families. Journal of Family Psychology, 20(2), 275–283.
Canli, T. (2008). Toward a neurogenetic theory of neuroticism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1129(1), 153–174.
Cox, M. J., Paley, B., & Harter, H. (2001). Interparental conflict and parent–child relationships. In J. H. Grych & F. D. Fincham (Eds), Interparental conflict and child development: Theory, research, and application (pp. 249–272). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Digman, J. M. (1997). Higher-order factors of the Big Five. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 73(6), 1246–1256.
Dormann, C. F., Elith, J., Bacher, S., Buchmann, C., Carl, G., Carré, G., & Münkemüller, T. (2013). Collinearity: A review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography, 36(1), 27–46.
Erel, O., & Burman, B. (1995). Interrelatedness of marital relations and parent–child relations: A meta–analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 118(1), 108–132.
Feinberg, M. E. (2003). The internal structure and ecological context of coparenting: A framework for research and intervention. Parenting: Science and Practice, 3(2), 95–131.
Feinberg, M., Brown, L., & Kan, M. (2012). A multi-domain self-report measure of coparenting. Parenting: Science and Practice, 12(1), 1–21.
Fernández-Berrocal, P., & Extremera, N. (2016). Ability emotional intelligence, depression, and well-being. Emotion Review, 8(4), 311–315.
Grych, J. H., & Fincham, F. D. (1990). Marital conflict and children’s adjustment: a cognitive-contextual framework. Psychological Bulletin, 108(2), 267–290.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression–based approach. New York: Guilford Press.
Heinrich, L. M., & Gullone, E. (2006). The clinical significance of loneliness: A literature review. Clinical Psychology Review, 26(6), 695–718.
Holland, A. S., & McElwain, N. L. (2013). Maternal and paternal perceptions of coparenting as a link between marital quality and the parent-toddler relationship. Journal of Family Psychology, 27(1), 117–126.
Hu, M., Wang, M., Cai, L., Zhu, X., & Yao, S. (2012). Development of subjective socioeconomic status scale for Chinese adolescents. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 20(2), 155–158.
Johnson, M. (2003). The vulnerability status of emotional instability: Over-reporting or genuine complaints? Personality and Individual Differences, 35(4), 877–887.
Johnson, M., & Galambos, N. (2014). Paths to intimate relationship quality from parent–adolescent relations and mental health. Journal of Marriage and Family, 76(1), 145–160.
Kopystynska, O., Paschall, K. W., Barnett, M. A., & Curran, M. A. (2017). Patterns of interparental conflict, parenting, and children’s emotional insecurity: A person-centered approach. Journal of Family Psychology., 31(7), 922–932.
Kwon, K. A., & Elicker, J. G. (2012). The role of mothers’ and fathers’ parental control and coparenting in toddlers’ compliance. Early Education and Development, 23(5), 748–765.
Lahey, B. B. (2009). Public health significance of emotional instability. American Psychologist, 64(4), 241–256.
Láng, A., & Abell, L. (2018). Relationship between interparental functioning and adolescents’ level of Machiavellianism: A multi-perspective approach. Personality and Individual Differences, 120, 213–221.
Lerner, R. M., Easterbrooks, M. A., & Mistry, J. (2003). Handbook of psychologyy (Vol. 6): Developmental psycholog. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Li, C., Zou, H., & Yang, L. (2005). Relationship between five-factor personality, teacher–student relations, and mental health of adolescent. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 13(4), 440–443.
Lindell, M., & Whitney, D. (2001). Accounting for common method variance in cross-sectional research designs. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(1), 114–121.
Lindsey, E. W., Caldera, Y. M., & Tankersley, L. (2009). Marital conflict and the quality of young children’s peer play behavior: The mediating and moderating role of parent–child emotional reciprocity and attachment security. Journal of Family Psychology, 23(2), 130–145.
Liu, C., Wu, X., & Zou, S. (2017). Psychometric properties of the adolescence revision of co-parenting scale. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 25(5), 845–849,881.
MacKinnon, D. P. (2008). Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Margolin, G., Gordis, E. B., & John, R. S. (2001). Coparenting: A link between marital conflict and parenting in two-parent families. Journal of Family Psychology, 15(1), 3–21.
Martin, M. J., Sturge-Apple, M. L., Davies, P. T., Romero, C. V., & Buckholz, A. (2017). A process model of the implications of spillover from coparenting conflicts into the parent–child attachment relationship in adolescence. Development and Psychopathology, 29(2), 417–431.
Maxwell, S. E., & Cole, D. A. (2007). Bias in cross-sectional analyses of longitudinal mediation. Psychological Methods, 12(1), 23–44.
McCrae, R. R., Costa, P. T., Terracciano, A., Parker, W. D., Mills, C. J., De Fruyt, F., & Mervielde, I. (2002). Personality trait development from age 12 to age 18: Longitudinal, cross-sectional, and cross–cultural analyses. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 83(6), 1456–1468.
McDaniel, B. T., Teti, D. M., & Feinberg, M. E. (2017). Assessing coparenting relationships in daily life: The daily coparenting scale (D-Cop). Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(9), 2396–2411.
McHale, J. P. (1997). Overt and covert coparenting processes in the family. Family Process, 36(2), 183–201.
McHale, J. P., Dinh, K. T., & Rao, N. (2014). Understanding coparenting and family systems among East and Southeast Asian-heritage families. In H. Selin (Ed.), Parenting across cultures (pp. 163–173). Dordrecht: Springer.
McHale, J. P., Kuersten-Hogan, R., & Rao, N. (2004). Growing points for coparenting theory and research. Journal of Adult Development, 11(3), 221–234.
McHale, J. P., Rao, N., & Krasnow, A. D. (2000). Constructing family climates: Chinese mothers’ reports of their co-parenting behaviour and preschoolers’ adaptation. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 24(1), 111–118.
Minuchin, S. (1974). Families and family therapy. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Minuchin, P. (1985). Families and individual development: Provocations from the field of family therapy. Child Development, 56(2), 289–302.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16(2), 361–388.
Nakao, K., Takaishi, J., Tatsuta, K., Katayama, H., Iwase, M., Yorifuji, K., & Takeda, M. (2000). The influences of family environment on personality traits. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 54(1), 91–95.
Newland, R. P., Ciciolla, L., & Crnic, K. A. (2015). Crossover effects among parental hostility and parent–child relationships during the preschool period. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24(7), 2107–2119.
Neyer, F. J., & Lehnart, J. (2007). Relationships matter in personality development: evidence from an 8-year longitudinal study across young adulthood. Journal of Personality, 75(3), 535–568.
Offrey, L. D., & Rinaldi, C. M. (2017). Parent–child communication and adolescents’ problem-solving strategies in hypothetical bullying situations. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 22(3), 251–267.
Ormel, J., Jeronimus, B. F., Kotov, R., Riese, H., Bos, E. H., Hankin, B., & Oldehinkel, A. J. (2013). Emotional instability and common mental disorders: Meaning and utility of a complex relationship. Clinical Psychology Review, 33(5), 686–697.
Pedro, M. F., Ribeiro, T., & Shelton, K. H. (2012). Marital satisfaction and partners’ parenting practices: The mediating role of coparenting behavior. Journal of Family Psychology, 26(4), 509–522.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903.
Raudino, A., Fergusson, D. M., & Horwood, L. J. (2013). The quality of parent/child relationships in adolescence is associated with poor adult psychosocial adjustment. Journal of Adolescence, 36(2), 331–340.
Riina, E. M., & McHale, S. M. (2014). Bidirectional influences between dimensions of coparenting and adolescent adjustment. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 43(2), 257–269.
Roberts, B. W., & DelVecchio, W. F. (2000). The rank-order consistency of personality traits from childhood to old age: A quantitative review of longitudinal studies. Psychological Bulletin, 126(1), 3–25.
Roberts, B. W., Walton, K. E., & Viechtbauer, W. (2006). Patterns of mean-level change in personality traits across the life course: A meta–analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychological Bulletin, 132(1), 1–25.
Sobolewski, J. M., & King, V. (2005). The importance of the coparental relationship for nonresident fathers’ ties to children. Journal of Marriage and Family, 67(5), 1196–1212.
Specht, J., Bleidorn, W., Denissen, J. J., Hennecke, M., Hutteman, R., Kandler, C., & Zimmermann, J. (2014). What drives adult personality development? A comparison of theoretical perspectives and empirical evidence. European Journal of Personality, 28(3), 216–230.
Stafford, M., Kuh, D. L., Gale, C. R., Mishra, G., & Richards, M. (2016). Parent–child relationships and offspring’s positive mental wellbeing from adolescence to early older age. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 11(3), 326–337.
Suls, J., & Martin, R. (2005). The daily life of the garden-variety neurotic: Reactivity, stressor exposure, mood spillover, and maladaptive coping. Journal of Personality, 73(6), 1485–1510.
Syed, M., & Seiffge-Krenke, I. (2013). Personality development from adolescence to emerging adulthood: Linking trajectories of ego development to the family context and identity formation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 104(2), 371–384.
Teubert, D., & Pinquart, M. (2010). The association between and child adjustment: A meta–analysis. Parenting: Science and Practice, 10(4), 286–307.
Van Egeren, L., & Hawkins, D. (2004). Coming to terms with coparenting: Implications of definition and measurement. Journal of Adult Development, 11(3), 165–178.
Wu, J., Guo, X., Huang, X., & Li, S. (2011). The making of middle school student’s parent-child relationship questionnaire. Journal of Southwest University (Social Science Edition), 37(4), 39–46.
Yun, H. J., Cui, M., & Blair, B. L. (2016). The mediating roles of adolescent disclosure and parental knowledge in the association between parental warmth and delinquency among Korean adolescents. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(8), 2395–2404.
Zhou, H., Niu, L., & Zou, H. (2000). A development study on five-factor personality questionnaire for middle school students. Psychological Development and Education, 16(1), 48–54.
Zhou, N., Cao, H., & Leerkes, E. M. (2017). Interparental conflict and infants’ behavior problems: The mediating role of maternal sensitivity. Journal of Family Psychology, 31(4), 464–474.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Beijing Education Science Fund (2015) “The effect of father and mother involvement on the psychological adaptation of adolescent” (AFA15199). We would like to thank the undergraduate research assistants and teachers who helped carry out this study. We are especially indebted to the adolescents whose participation made this research possible.
Author Contributions
S.Z.: designed and executed the study, assisted with the data analyses, and wrote the paper. X.W.: collaborated with the design and writing of the study. B.H.: analyzed the data and wrote part of the results. C.L.: collaborated in the writing and editing of the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Beijing Normal University and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, S., Wu, X., Huang, B. et al. Double-Edged Effect of Coparenting on Chinese Adolescents’ Emotional Instability: An Inconsistent Mediation Model. J Child Fam Stud 29, 1413–1423 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01628-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01628-w