Abstract
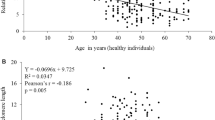
Several genetic studies were carried out among hypertensive patients to assess allelic association at the 1166 position of the 3′ untranslated region of angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene. In addition, attempts have also been made to find out whether telomere length attrition is associated with hypertension. The main aim of this study was to examine the association of A1166C polymorphism of angiotensin II type 1 receptor and telomere length with essential hypertension in Egyptian people. Angiotensin II type 1 genotyping and relative telomere length were investigated by PCR in 40 patients of essential hypertension and 15 healthy controls. The homozygous AA1166 allele frequency was 92.8% among the studied subjects. There was no intergroup variation in A allele frequency in normotensive group. The frequency of homozygous A allele was significantly higher in hypertensive than normotensive subjects (97.5 and 80%, respectively) with higher frequencies in male patients. The average telomere length ratio was significantly shorter in hypertensive than in normal subjects (1.08 ± 0.3 and 1.54 ± 0.18, respectively). No correlation was observed between telomere length ratio and body mass index. This study suggests that the homozygous A1166 allele of angiotensin II type 1 and short telomeres may be predisposing factors for essential hypertension in Egyptians and may be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. Further strategies for treating high-risk patients could result in prevention or delay of end organ damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia EA, Newhouse S, Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB (2003) Genes and hypertension. Curr Pharm 9:1679–1689
Baudin B (2005) Polymorphism in angiotensin II receptor genes and hypertension. Exp Physiol 90:277–282
Weir M (2007) Effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibition on end-organ protection: can we do better? Clin Ther 29(9):1803–1824
Inagami T, Guo DF, Kitami Y (1994) Molecular biology of angiotensin II receptors: an overview. J Hypertension 12:83–84
Takayanagi R, Ohnaka K, Skai Y, Nakao R (1992) Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding human type 1 angiotensin II receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 183:910–916
Ingelfinger JR (2009) Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 implications for blood pressure and kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 18:79–84
Wang JL, Xue L, Hao P et al (2010) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene A1166C polymorphism and essential hypertension in Chinese: a meta-analysis. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 11:1–9
Takami S, Katsuya T, Raguki H (1998) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism is associated with increased left ventricular mass but not with hypertension. Am J Hypertens 11:316–321
Kainulainen K, Perola M, Terwilliger et al (1999) Evidence for involvement of the type 1 angiotensin II receptor locus in the essential hypertension. Hypertension 33:844–849
Yang Z, Haung X, Jian H et al (2009) Short telomeres and prognosis of hypertension in a Chinese population. Hypertension 53:639–645
Blackburn EH (2001) Switching and signaling at the telomere. Cell 106:661–673
Epel ES, Blackburn EH, Lin J et al (2004) Accelerated telomere shortening in response to life stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17312–17315
Vasa-Nicotera M, Brouilette S, Mangino M et al (2005) Mapping of a major locus that determines telomere length in humans. Am J Hum Genet 76:147–151
Hunt Sc, Chen W, Gardner JP et al (2008) Leukocyte telomeres are longer in African Americans than in whites: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Family Heart study and the Bogalusa Heart study. Aging Cell 7:451–458
Matsubara Y, Murata M, Watanabe K (2006) Coronary artery disease and a functional polymorphism of hTERT. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:669–672
Edo MD, Andres V (2005) Ageing, telomeres, and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 66:213–221
Liu Y, Zhuoma C, Shan G et al (2002) A1166C polymorphism of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene and essential hypertension in Han, Tibetan and Yi populations. Hypertens Res 25:515–521
Aviva P, Caroline S (2005) Glossary of terms. In: Medical statistics at a glance, 2nd edn. Blackwell, London, pp 144–152
Ibrahim MM, Rizk H, Apple LJ et al (1995) Hypertension, prevalence, awareness. Treatment and control in Egypt. Results from the Egyptian national hypertension project. Hypertension 26:886–890
Kuriyama S, Tomonari H, Tokudome G et al (2001) Association of angiotensinogen gene polymorphism with erythropoietin-induced hypertension: a preliminary report. Hypertens Res 24:501–505
Castellano M, Muiesan ML, Beschi M et al (1996) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor AC1166 polymorphism. Hypertension 28(6):1076–1080
Paillard F, Chansel D, Brand E et al (1999) Genotype phenotype relationships for the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system n a normal population. Hypertension 34:423–429
Moul AK, Shoham DA, Ke North (2008) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor polymorphism and susceptibility to hypertension: a HuGF review. Genet Med 10:560–574
Demissie S, Levy D, Benjamin EJ et al (2006) Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, hypertension and leukocyte telomere length in men from the Framingham heart study. Aging Cell 5:325–330
Farzaneh-R LinJ, Epel E et al (2010) Telomere length trajectory and its determinants in persons with coronary artery disease: longitudinal findings from the heart and soul study. Plos One 5(1):8612
Minamino T, Miyauchi H, Yoshida T et al (2002) Endothelial cell senescence in human atherosclerosis: role of telomere in endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 105:1541–1544
Satoh M, Ishikawa Y, Takahashi Y et al (2008) Association between DNA damage and telomere shortening in circulating endothelia progenitor cells obtained from metabolic syndrome patients with chronic artery disease. Atherosclerosis 198:347–353
Acknowledgment
The authors indicate that there are no potential conflicts of interest, including any financial interest, relationships, and affiliations relevant to the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farrag, W., Eid, M., El-Shazly, S. et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphism and telomere shortening in essential hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 351, 13–18 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0706-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0706-0