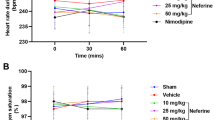
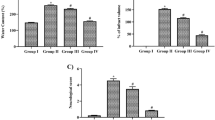
Abstract
Stroke is a life-threatening disease with major cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. The neuronal damage following cerebral ischemia is a serious risk to stroke patients. Oxidative stress and apoptotic damage play an important role in cerebral ischemic pathogenesis and may represent a target for treatment. The objective of this study was to test the hypothesis that administration of edaravone (Edv) maintains antioxidant status in brain, improves the cholinergic dysfunction and suppresses the progression of apoptosis response in rat. To test this hypothesis, male Wistar rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) of 2 h followed by reperfusion for 22 h. Edv was administered (10 mg/kg bwt) intraperitoneally 30 min before the onset of ischemia and 1 h after reperfusion. After reperfusion, rats were tested for neurobehavioral activities and were sacrificed for the infarct volume, estimation of oxidative damage markers. Edv treatment significantly reduced ischemic lesion volume, improved neurological deficits, contended oxidative loads, and suppressed apoptotic damage. In conclusion, treatment with Edv ameliorated the neurological and histological outcomes with elevated endogenous anti-oxidants status as well as reduced induction of apoptotic responses in MCA occluded rat. We theorized that Edv is among the pharmacological agents that reduce free radicals and its associated cholinergic dysfunction and apoptotic damage and have been found to limit the extent of brain damage following stroke.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hattori K, Lee H, Hurn PD, Crain BJ, Traystman RJ, DeVries AC (2000) Cognitive deficits after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 31:1939–1944
Shah MK, Shin W, Parikh VS, Ragin A, Mouannes J et al (2010) Quantitative cerebral MR perfusion imaging: preliminary results in stroke. J Magn Reson Imaging 32:796–802
Khan MM, Ishrat T, Ahmad A, Hoda MN, Khan MB et al (2010) Sesamin attenuates behavioral, biochemical and histological alterations induced by reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rats. Chem Biol Interact 183:255–263
Halliwell B (2001) Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging 18:685–716
Cherubini A, Polidori MC, Bregnocchi M, Pezzuto S et al (2000) Antioxidant profile and early outcome in stroke patients. Stroke 31:2295–2300
Saleem S, Ahmad M, Ahmad AS, Yousuf S, Ansari MA et al (2006) Effect of saffron (Crocus sativus) on neurobehavioral and neurochemical changes in cerebral ischemia in rats. J Med Food 9:246–253
Ishrat T, Hoda MN, Khan MB, Yousuf S, Ahmad M, Khan MM et al (2009) Amelioration of cognitive deficits and neurodegeneration by curcumin in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type (SDAT). Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19:636–647
Racay P, Chomova M, Tatarkova Z, Kaplan P, Hatok J, Dobrota D (2009) Ischemia-induced mitochondrial apoptosis is significantly attenuated by ischemic preconditioning. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:901–908
Choi DW (1996) Ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6:667–672
Takano K, Tatlisumak Y, Bergmann AG, Gibson DG, Fisher M (1997) Reproducibility and reliability of middle cerebral artery occlusion using a silicone-coated suture (Koizumi) in rats. J Neurol Sci 153:8–11
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Watanabe T, Tahara M, Todo S (2008) The novel antioxidant edaravone: from bench to bedside. Cardiovasc Ther 26:101–114
Yamamoto Y, Yanagisawa M, Tak NW, Watanabe K, Takahashi C et al (2009) Repeated edaravone treatment reduces oxidative cell damage in rat brain induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Redox Rep 14:251–258
Wang GH, Jiang ZL, Li YC, Li X, Shi H, Gao YQ, Vosler PS, Chen J (2011) Free-radical scavenger edaravone treatment confers neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 28:2123–2134
Yuan WJ, Yasuhara T, Shingo T, Muraoka K, Agari T et al (2008) Neuroprotective effects of edaravone-administration on 6-OHDA-treated dopaminergic neurons. BMC Neurosci 9:75
Masuo Y, Matsumoto Y, Morita S, Noguchi J (1997) A novel method for counting spontaneous motor activity in the rat. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 1:321–326
Utley HC, Bernhein F, Hochslein P (1967) Effects of sulfhydryl reagent on peroxidation in microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys 260:521–531
Islam F, Zia S, Sayeed I, Zafar KS, Ahmad AS (2002) Selenium induced alteration on lipids, lipid peroxidation, and thiol group in circadian rhythm centers of rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 90:1–12
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaghone N, Gillete JR (1974) Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic intermediate. Pharmacology 11:161–169
Levine S (1960) Anoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in rats. Am J Pathol 36:1–17
Mohandas J, Marshall JJ, Duggin GG, Horvath JS, Tiller D (1984) Differential distribution of glutathione and glutathione related enzymes in rabbit kidneys: possible implication in analgesic neuropathy. Cancer Res 44:5086–5091
Carlberg I, Mannerviek B (1975) Glutathione reductase levels in rat brain. J Biol Chem 250:5475–5480
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Zaheer N, Tiwari KK, Krishnan PS (1965) Exposure and solubilization of hepatic mitochondrial shunt dehydrogenases. Arch Biochem Biophys 109:646–648
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Itoh T, Satou T, Nishida S, Tsubaki M, Imano M, Hashimoto S, Ito H (2010) Edaravone protects against apoptotic neuronal cell death and improves cerebral function after traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurochem Res 35:348–355
Schwarting RK, Bonatz AE, Carey RJ, Huston JP (1991) Relationships between indices of behavioral asymmetries and neurochemical changes following mesencephalic 6-hydroxydopamine injections. Brain Res 554:46–55
Zhao J, Zhao Y, Zheng W, Lu Y, Feng G, Yu S (2008) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1229:224–232
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM et al (1986) Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 17:1304–1308
Liszczak TM, Hedley-Whyte ET, Adams JF et al (1984) Limitation of tetrazolium salts in delineating infarcted brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 65:150–157
Faraci FM (2006) Reactive oxygen species: influence on cerebral vascular tone. J Appl Physiol 100:739–743
Chang CY, Ke DS, Chen JY (2009) Essential fatty acids and human brain. Acta Neurol Taiwan 18:231–241
Sarkar S, Das N (2006) Mannosylated liposomal flavonoid in combating age-related ischemia-reperfusion induced oxidative damage in rat brain. Mech Ageing Dev 127:391–397
Imam SZ, Ali SF (2000) Selenium, an antioxidant, attenuates methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic toxicity and peroxynitrite generation. Brain Res 855:186–191
Watanabe T, Yuki S, Egawa M, Nishi H (1994) Protective effects of MCI-186 on cerebral ischemia: possible involvement of free radical scavenging and antioxidant actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1597–1604
Cheung RT (2003) The utility of melatonin in reducing cerebral damage resulting from ischemia and reperfusion. J Pineal Res 34:153–160
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2003) Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J Neurochem 85:1026–1036
Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Yagita Y, Sugiura S, Omura-Matsuoka E et al (2006) Bcl2 enhances survival of newborn neurons in the normal and ischemic hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 84:1187–1196
Amemiya S, Kamiya T, Nito C, Inaba T, Kato K et al (2005) Anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects of edaravone following transient focal ischemia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 516:125–130
Okazaki T, Magaki T, Takeda M, Kajiwara Y, Hanaya R et al (2008) Intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells increases survivin and Bcl-2 protein expression and improves sensorimotor function following ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 430:109–114
Zeevalk GD, Bernard LP, Sinha C, Ehrhart J, Nicklas WJ (1998) Excitotoxicity and oxidative stress during inhibition of energy metabolism. Dev Neurosci 20:444–453
Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:11–21
Davare MA, Hell JW (2003) Increased phosphorylation of the neuronal L-type Ca(2+) channel Ca(v)1.2 during aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:16018–16023
Kiewert C, Mdzinarishvili A, Hartmann J, Bickel U, Klein J (2010) Metabolic and transmitter changes in core and penumbra after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 1312:101–107
Jiao L, Zhang J, Li Z, Liu H, Chen Y, Xu S (2011) Edaravone alleviates delayed neuronal death and long-dated cognitive dysfunction of hippocampus after transient focal ischemia in Wistar rat brains. Neuroscience 182:177–183
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga and Naturalpathy, Unani, Siddha and Homeopath (AYUSH), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, New Delhi for financial assistance. The authors wish to thanks Mr. Dharamvir Singh for his assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, A., Moshahid Khan, M., Javed, H. et al. Edaravone ameliorates oxidative stress associated cholinergic dysfunction and limits apoptotic response following focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Mol Cell Biochem 367, 215–225 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1335-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1335-6