Abstract
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitor is a promising new approach to the treatment of lung cancer therapy via inhibiting cell growth and inducing apoptosis. miR-15a and miR-16-1 are important tumor suppressors through modulating B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), Cyclin D1, D2, and others. However, whether HDACs inhibitor modulates the expression of miR-15a/16-1 in lung cancer is still unknown. The purpose of our study was to identify a new miRNA-mediated mechanism which plays an important role in the anti-cancer effects of HDACs inhibitor. We found HDACs inhibitors trichostatin A (TSA) and sodium butyrate upregulated the expression of miR-15a/16-1, residing in the host tumor suppressor Dleu2 gene, through increasing the histone acetylation in the region of Dleu2/miR-15a/16-1 promoter in lung cancer cells. Moreover, among class Ι HDACs subtypes, only knockdown of HDAC3 by specific siRNA increased the hyperacetylation of Dleu2/miR-15a/16-1 promoter region and finally resulted in the upregulation of miR-15a/16-1. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-15a/16-1, which were always deleted or downregulated in lung cancer cells, effectively suppressed cell growth and reduced colony formation. Finally, TSA reduced the expression of Bcl-2, an important survival protein in lung cancer cells, partly through upregulation of miR-15a/16-1. Therefore, this offers a therapeutic strategy that lung cancer patients who exhibit low level of miR-15a/16-1 or high activity of HDACs may benefit from HDACs inhibitor-based therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Smigal C, Thun MJ (2006) Cancer statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:106–130
Cho WC (2013) Targeting signaling pathways in lung cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17:107–111
Wistuba II, Gazdar AF (2006) Lung cancer preneoplasia. Annu Rev Pathol 1:331–348
Yang P, Allen MS, Aubry MC, Wampfler JA, Marks RS, Edell ES, Thibodeau S, Adjei AA, Jett J, Deschamps C (2005) Clinical features of 5,628 primary lung cancer patients: experience at Mayo Clinic from 1997 to 2003. Chest 128:452–462
Lane AA, Chabner BA (2009) Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27:5459–5468
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS, Johnson JM (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433:769–773
Negrini M, Ferracin M, Sabbioni S, Croce CM (2007) MicroRNAs in human cancer: from research to therapy. J Cell Sci 120:1833–1840
Cho WC (2010) MicroRNAs in cancer—from research to therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805:209–217
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13944–13949
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun S, Hong L, Liu J, Fan D (2008) miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 123:372–379
Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, Arnold M, Kocher V, Hasan L, Kappeler A, Brunner T, Vassella E (2009) miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 69:5553–5559
Bandi N, Vassella E (2011) miR-34a and miR-15a/16 are co-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and control cell cycle progression in a synergistic and Rb-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 10:55
Yoo CB, Jones PA (2006) Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:37–50
Miyanaga A, Gemma A, Noro R, Kataoka K, Matsuda K, Nara M, Okano T, Seike M, Yoshimura A, Kawakami A, Uesaka H, Nakae H, Kudoh S (2008) Antitumor activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer cells: development of a molecular predictive model. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1923–1930
Choi YH (2005) Induction of apoptosis by trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is associated with inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 activity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol 27:473–479
Zhang XH, Rao M, Loprieato JA, Hong JA, Zhao M, Chen GZ, Humphries AE, Nguyen DM, Trepel JB, Yu X, Schrump DS (2008) Aurora A, Aurora B and survivin are novel targets of transcriptional regulation by histone deacetylase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1388–1397
Lee EM, Shin S, Cha HJ, Yoon Y, Bae S, Jung JH, Lee SM, Lee SJ, Park IC, Jin YW, An S (2009) Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) changes microRNA expression profiles in A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Mol Med 24:45–50
Gao SM, Chen C, Wu J, Tan Y, Yu K, Xing CY, Ye A, Yin L, Jiang L (2010) Synergistic apoptosis induction in leukemic cells by miR-15a/16-1 and arsenic trioxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 403:203–208
Lerner M, Harada M, Loven J, Castro J, Davis Z, Oscier D, Henriksson M, Sangfelt O, Grander D, Corcoran MM (2009) DLEU2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs miR-15a and miR-16-1. Exp Cell Res 315:2941–2952
Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Shimizu M, Taccioli C, Zanesi N, Garzon R, Aqeilan RI, Alder H, Volinia S, Rassenti L, Liu X, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2008) MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5166–5171
Trang P, Medina PP, Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, Omotola M, Homer R, Brown D, Bader AG, Weidhaas JB, Slack FJ (2010) Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA. Oncogene 29:1580–1587
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L, Kipps T, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Croce CM (2002) Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:15524–15529
Tsai HC, Baylin SB (2011) Cancer epigenetics: linking basic biology to clinical medicine. Cell Res 21:502–517
Singh T, Prasad R, Katiyar SK (2013) Inhibition of class I histone deacetylases in non-small cell lung cancer by honokiol leads to suppression of cancer cell growth and induction of cell death in vitro and in vivo. Epigenetics 8:54–65
Croce CM (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10:704–714
Rhodes LV, Nitschke AM, Segar HC, Martin EC, Driver JL, Elliott S, Nam SY, Li M, Nephew KP, Burow ME, Collins-Burow BM (2012) The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A alters microRNA expression profiles in apoptosis-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep 27:10–16
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, Iuliano R, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Roldo C, Garzon R, Sevignani C, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM (2005) A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 353:1793–1801
Ziegler A, Luedke GH, Fabbro D, Altmann KH, Stahel RA, Zangemeister-Wittke U (1997) Induction of apoptosis in small-cell lung cancer cells by an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide targeting the Bcl-2 coding sequence. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:1027–1036
Lawson MH, Cummings NM, Rassl DM, Vowler SL, Wickens M, Howat WJ, Brenton JD, Murphy G, Rintoul RC (2010) Bcl-2 and beta1-integrin predict survival in a tissue microarray of small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 103:1710–1715
He DM, Zhang Y, Liu GX (2007) Bcl-2 small hairpin RNAs enhance radiation-induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Cell Biol Int 31:1442–1445
Huang Z, Lei X, Zhong M, Zhu B, Tang S, Liao D (2007) Bcl-2 small interfering RNA sensitizes cisplatin-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma A549/DDP cell to cisplatin and diallyl disulfide. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 39:835–843
Hu J, Colburn NH (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibition down-regulates cyclin D1 transcription by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB/p65 DNA binding. Mol Cancer Res 3:100–109
Mukhopadhyay NK, Weisberg E, Gilchrist D, Bueno R, Sugarbaker DJ, Jaklitsch MT (2006) Effectiveness of trichostatin A as a potential candidate for anticancer therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 81:1034–1042
Cho WC (2011) Promises and challenges in developing miRNA as a molecular diagnostic tool for lung cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 11:763–766
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A, Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D’Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C, Bartucci M, Muto G, Peschle C, De Maria R (2008) The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med 14:1271–1277
Diaz-Garcia CV, Agudo-Lopez A, Perez C, Lopez-Martin JA, Rodriguez-Peralto JL, de Castro J, Cortijo A, Martinez-Villanueva M, Iglesias L, Garcia-Carbonero R, Fresno Vara JA, Gamez-Pozo A, Palacios J, Cortes-Funes H, Paz-Ares L, Agullo-Ortuno MT (2013) DICER1, DROSHA and miRNAs in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: implications for outcomes and histologic classification. Carcinogenesis 34:1031–1038
Bottoni A, Piccin D, Tagliati F, Luchin A, Zatelli MC, degli Uberti EC (2005) miR-15a and miR-16-1 down-regulation in pituitary adenomas. J Cell Physiol 204:280–285
Navarro A, Diaz T, Gallardo E, Vinolas N, Marrades RM, Gel B, Campayo M, Quera A, Bandres E, Garcia-Foncillas J, Ramirez J, Monzo M (2011) Prognostic implications of miR-16 expression levels in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol 103:411–415
Kaddar T, Chien WW, Bertrand Y, Pages MP, Rouault JP, Salles G, Ffrench M, Magaud JP (2009) Prognostic value of miR-16 expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia relationships to normal and malignant lymphocyte proliferation. Leuk Res 33:1217–1223
Doi S, Soda H, Oka M, Tsurutani J, Kitazaki T, Nakamura Y, Fukuda M, Yamada Y, Kamihira S, Kohno S (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228 induces caspase-dependent apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1397–1402
Brazelle W, Kreahling JM, Gemmer J, Ma Y, Cress WD, Haura E, Altiok S (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulate checkpoint kinase 1 expression to induce cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 5:e14335
Denlinger CE, Keller MD, Mayo MW, Broad RM, Jones DR (2004) Combined proteasome and histone deacetylase inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 127:1078–1086
Luszczek W, Cheriyath V, Mekhail TM, Borden EC (2010) Combinations of DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors induce DNA damage in small cell lung cancer cells: correlation of resistance with IFN-stimulated gene expression. Mol Cancer Ther 9:2309–2321
Ramalingam SS, Maitland ML, Frankel P, Argiris AE, Koczywas M, Gitlitz B, Thomas S, Espinoza-Delgado I, Vokes EE, Gandara DR, Belani CP (2010) Carboplatin and Paclitaxel in combination with either vorinostat or placebo for first-line therapy of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:56–62
Hayashi A, Horiuchi A, Kikuchi N, Hayashi T, Fuseya C, Suzuki A, Konishi I, Shiozawa T (2010) Type-specific roles of histone deacetylase (HDAC) overexpression in ovarian carcinoma: HDAC1 enhances cell proliferation and HDAC3 stimulates cell migration with downregulation of E-cadherin. Int J Cancer 127:1332–1346
Godman CA, Joshi R, Tierney BR, Greenspan E, Rasmussen TP, Wang HW, Shin DG, Rosenberg DW, Giardina C (2008) HDAC3 impacts multiple oncogenic pathways in colon cancer cells with effects on Wnt and vitamin D signaling. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1570–1580
Minamiya Y, Ono T, Saito H, Takahashi N, Ito M, Motoyama S, Ogawa J (2010) Strong expression of HDAC3 correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Tumour Biol 31:533–539
Jung KH, Noh JH, Kim JK, Eun JW, Bae HJ, Xie HJ, Chang YG, Kim MG, Park H, Lee JY, Nam SW (2012) HDAC2 overexpression confers oncogenic potential to human lung cancer cells by deregulating expression of apoptosis and cell cycle proteins. J Cell Biochem 113:2167–2177
Acknowledgments
The Project is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270131, 81200350), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY12H08003, 2010C14011, Z2080988), and Foundation of Wenzhou Municipal Science and Technology Bureau (H20080058).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chi-qi Chen and Cheng-shui Chen have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2013_1762_MOESM3_ESM.tif
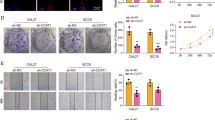
Supplemental Fig. 1: Representative of cell cycle analysis in A549 (A-D) and H1299 (E–H) cells treated with different concentrations of TSA for 24 h
11010_2013_1762_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 2: Effects of SB on anti-proliferation, colony formation and apoptosis in lung cancer cells. (A and B) Cell proliferation was detected by CCK-8 assay in A549 and H1299 cells treated with indicated concentrations of SB for 24, 48 and 72 h. (C and D) Colony formation assay in A549 (C) and H1299 (D) treated with 1.0 and 2.0 mM SB. (E and F) Apoptosis was detected by annexin V/PI assay in A549 and H1299 cells treated with 1.0 and 2.0 mM SB for 48 h. *P < 0.01 versus untreated cells
11010_2013_1762_MOESM5_ESM.tif
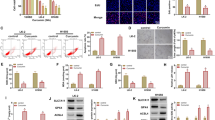
Supplemental Fig. 3: Knockdown of HDAC3 by siRNA increases the expression of Dleu2/miR-15a/16-1 in A549 and H1299 cells. A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with Scramble or si-2-HDAC3 for 48 h. (A and B) The transcript and protein levels of HDAC3 was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (A) and Western blotting (B). (C and D) The relative expression of Dleu2, miR-15a and miR-16-1 was measured by quantitative real-time PCR. *P < 0.01 versus Scramble
11010_2013_1762_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 4: 5-AZA fails to modulate the expression of miR-15a/16-1. (A) A representative of CpG dinucleotides at miR-15a/16-1 promoter region. No obvious CpG islands were found at miR-15a/16-1 promoter region when the length is longer than 200 nucleotides. (B) The relative expression of miR-15a/16-1 was detected in A549 and H1299 cells treated with 1.0 μM 5-AZA for 2, 4 and 6 days
11010_2013_1762_MOESM7_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 5: TSA inhibits cyclin E1 but not cyclin D1 and D2 expression. (A) A549 and H1299 cells were treated with 0.5 μM TSA for 48 h. The protein levels of cyclin D1, D2 and E1 were measured by Western blotting, respectively
11010_2013_1762_MOESM8_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 6: The expression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 are elevated in lung cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. A quantitative real time PCR analysis of HDAC2 (A) and HDAC3 (B) expression in 27 cases of lung cancer tissues and corresponding adjacent normal tissues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Cq., Chen, Cs., Chen, Jj. et al. Histone deacetylases inhibitor trichostatin A increases the expression of Dleu2/miR-15a/16-1 via HDAC3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 383, 137–148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1762-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1762-z