Abstract
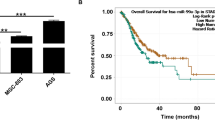
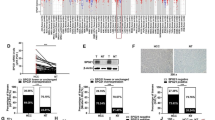
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a rapidly progressing, incurable cancer that frequently spreads to portal vein and lung. New insights are needed to identify therapeutic targets to prevent or retard HCC metastatic progression. Because microRNAs (miRNA) often act as tumor regulators, we investigated their role in preclinical models of HCC. Here we found miR-28-5p is a liver-relevant anti-proliferative miRNA whose expression, functions, and mechanisms were analyzed in human hepatoma cells, HepG2 and Huh7. Interestingly, when evaluating the specific targets of miR-28-5p, we found that ectopic miR-28-5p expression down-regulates insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) protein and that the expression of miR-28-5p correlates negatively with IGF1 protein in HCC cells. Luciferase report in HCC cells expressing miR-28-5p suggests that miR-28-5p reduces luciferase activity by targeting the 3′-UTR of IGF1 mRNA. Additionally, we show that the selective inhibition of either the PI3K/AKT pathway prior to miR-28-5p stimulation prevents the expression of previously described tumor suppressor miRNAs that are family and cluster specific. Together, our results defined miR-28-5p as a critical regulator of IGF1 mRNA translation function, down-regulated miR-28-5p in HCC was associated with tumor growth through PI3K/AKT pathway by targeting IGF1. miR-28-5p-IGF1-PI3K/AKT pathway may play an important role in the development of HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qasim W, Brunetto M, Gehring A, Xue SA, Schurich A, Khakpoor A et al (2014) Immunotherapy of HCC metastases with autologous T cell receptor redirected T cells targeting HBsAg in a liver transplant patient. J Hepatol. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.001
Ringelhan M, Protzer U, O’Connor T, Heikenwalder M (2014) The direct and indirect role of HBV in liver cancer: prospective markers for HCC-screening and potential therapeutic targets. J Pathol. doi:10.1002/path.4434
Palmer DH, Hussain SA, Smith AJ, Hargreaves S, Ma YT, Hull D et al (2013) Sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): impact of rationing in the United Kingdom. Br J Cancer 109(4):888–890. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.410
Printz C (2009) Clinical trials of note. Sorafenib as adjuvant treatment in the prevention of disease recurrence in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (STORM). Cancer 115(20):4646. doi:10.1002/cncr.24673
Mori M, Triboulet R, Mohseni M, Schlegelmilch K, Shrestha K, Camargo FD et al (2014) Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer. Cell 156(5):893–906. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.043
Ruvkun G (2006) Clarifications on miRNA and cancer. Science 311(5757):36–37. doi:10.1126/science.311.5757.36d
Li W, Liu M, Feng Y, Xu YF, Huang YF, Che JP et al (2014) Downregulated miR-646 in clear cell renal carcinoma correlated with tumour metastasis by targeting the nin one binding protein (NOB1). Br J Cancer 111(6):1188–1200. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.382
Utsunomiya T, Ishikawa D, Asanoma M, Yamada S, Iwahashi S, Kanamoto M et al (2014) Specific miRNA expression profiles of non-tumor liver tissue predict a risk for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 44(6):631–638. doi:10.1111/hepr.12164
Chen W, Cai F, Zhang B, Barekati Z, Zhong XY (2013) The level of circulating miRNA-10b and miRNA-373 in detecting lymph node metastasis of breast cancer: potential biomarkers. Tumour Biol 34(1):455–462. doi:10.1007/s13277-012-0570-5
Wagner S, Ngezahayo A, Murua Escobar H, Nolte I (2014) Role of miRNA let-7 and its major targets in prostate cancer. BioMed Res Int 2014:376326. doi:10.1155/2014/376326
Heron-Milhavet L, Karas M, Goldsmith CM, Baum BJ, LeRoith D (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor activation rescues UV-damaged cells through a p38 signaling pathway. Potential role of the IGF-I receptor in DNA repair. J Biol Chem 276(21):18185–18192. doi:10.1074/jbc.M011490200
Bodzin AS, Wei Z, Hurtt R, Gu T, Doria C (2012) Gefitinib resistance in HCC mahlavu cells: upregulation of CD133 expression, activation of IGF-1R signaling pathway, and enhancement of IGF-1R nuclear translocation. J Cell Physiol 227(7):2947–2952. doi:10.1002/jcp.23041
Locatelli D, Terao M, Fratelli M, Zanetti A, Kurosaki M, Lupi M et al (2012) Human axonal survival of motor neuron (a-SMN) protein stimulates axon growth, cell motility, C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) production. J Biol Chem 287(31):25782–25794. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.362830
Zhou Y, Capuco AV, Jiang H (2008) Involvement of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF1) stimulation of proliferation of a bovine mammary epithelial cell line. Domest Anim Endocrinol 35(2):180–189. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2008.05.003
Koti M, Gooding RJ, Nuin P, Haslehurst A, Crane C, Weberpals J et al (2013) Identification of the IGF1/PI3K/NF kappaB/ERK gene signalling networks associated with chemotherapy resistance and treatment response in high-grade serous epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 13:549. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-549
Matta M, Bongard V, Grunenwald S, Maiza JC, Bennet A, Caron P (2011) Clinical and metabolic characteristics of acromegalic patients with high IGF1/normal GH levels during somatostatin analog treatment. Eur J Endocrinol 164(6):885–889. doi:10.1530/EJE-11-0098
Subramanian A, Sharma AK, Banerjee D, Jiang WG, Mokbel K (2007) Evidence for a tumour suppressive function of IGF1-binding proteins in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res 27(5B):3513–3518
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, Li Q, He J, Jing Y et al (2013) A regulatory circuit of miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation and tumor angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol 5(1):3–13. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjs049
Noh JH, Chang YG, Kim MG, Jung KH, Kim JK, Bae HJ et al (2013) MiR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2 in liver cancer. Cancer Lett 335(2):455–462. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.03.003
Pagliuca A, Valvo C, Fabrizi E, di Martino S, Biffoni M, Runci D et al (2013) Analysis of the combined action of miR-143 and miR-145 on oncogenic pathways in colorectal cancer cells reveals a coordinate program of gene repression. Oncogene 32(40):4806–4813. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.495
Almeida MI, Nicoloso MS, Zeng L, Ivan C, Spizzo R, Gafa R et al (2012) Strand-specific miR-28-5p and miR-28-3p have distinct effects in colorectal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 142(4):886–896 e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.047
Bolos D, Finn RS (2014) Systemic therapy in HCC: lessons from brivanib. J Hepatol 61(4):947–950. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.06.019
Huang X, Jia Z (2013) Construction of HCC-targeting artificial miRNAs using natural miRNA precursors. Exp Ther Med 6(1):209–215. doi:10.3892/etm.2013.1111
Goto M, Iwase A, Harata T, Takigawa S, Suzuki K, Manabe S et al (2009) IGF1-induced AKT phosphorylation and cell proliferation are suppressed with the increase in PTEN during luteinization in human granulosa cells. Reproduction 137(5):835–842. doi:10.1530/REP-08-0315
Montenegro LR, Leal AC, Coutinho DC, Valassi HP, Nishi MY, Arnhold IJ et al (2012) Post-receptor IGF1 insensitivity restricted to the MAPK pathway in a Silver-Russell syndrome patient with hypomethylation at the imprinting control region on chromosome 11. Eur J Endocrinol 166(3):543–550. doi:10.1530/EJE-11-0964
Yang X, Cheng Y, Li P, Tao J, Deng X, Zhang X et al (2014) A lentiviral sponge for miRNA-21 diminishes aerobic glycolysis in bladder cancer T24 cells via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2617-2
Rao E, Jiang C, Ji M, Huang X, Iqbal J, Lenz G et al (2012) The miRNA-17 approximately 92 cluster mediates chemoresistance and enhances tumor growth in mantle cell lymphoma via PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Leukemia 26(5):1064–1072. doi:10.1038/leu.2011.305
Endogenous H, Breast Cancer Collaborative G, Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam AW (2010) Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol 11(6):530–542. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70095-4
Jernstrom H, Sandberg T, Bageman E, Borg A, Olsson H (2005) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) genotype predicts breast volume after pregnancy and hormonal contraception and is associated with circulating IGF-1 levels: implications for risk of early-onset breast cancer in young women from hereditary breast cancer families. Br J Cancer 92(5):857–866. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602389
Rosenzweig SA, Atreya HS (2010) Defining the pathway to insulin-like growth factor system targeting in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 80(8):1115–1124. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.013
Galer CE, Corey CL, Wang Z, Younes MN, Gomez-Rivera F, Jasser SA et al (2011) Dual inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor I: reduction of angiogenesis and tumor growth in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 33(2):189–198. doi:10.1002/hed.21419
Schmitz S, Kaminsky-Forrett MC, Henry S, Zanetta S, Geoffrois L, Bompas E et al (2012) Phase II study of figitumumab in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: clinical activity and molecular response (GORTEC 2008-02). Ann Oncol 23(8):2153–2161. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr574
Chi KN, Gleave ME, Fazli L, Goldenberg SL, So A, Kollmannsberger C et al (2012) A phase II pharmacodynamic study of preoperative figitumumab in patients with localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(12):3407–3413. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0482
Acknowledgments
This research was Supported by Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Grant No. 31470873).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Teng, F. Down-regulated miR-28-5p in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlated with tumor proliferation and migration by targeting insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). Mol Cell Biochem 408, 283–293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2506-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2506-z