Abstract
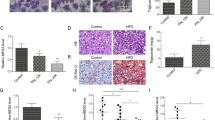
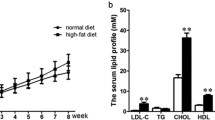
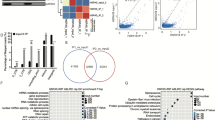
Our previous studies have confirmed that proline/serine-rich coiled-coil 1 (PSRC1) overexpression can regulate blood lipid levels and inhibit atherosclerosis (AS) development. In the current study, the gene and transcript expression profiles in the livers of ApoE−/− mice overexpressing PSRC1 were investigated. HiSeq X Ten RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis was used to examine the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and differentially expressed transcripts in the livers of PSRC1-overexpressing ApoE−/− and control mice. Then, Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were performed on these DEGs and on long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) predicted target genes. A total of 1892 significant DEGs were identified: 1431 were upregulated (e.g., Cyp2a4, Obp2a, and Sertad4), and 461 were downregulated (e.g., Moxd1, Egr1, and Elovl3). In addition, 8184 significant differentially expressed transcripts were identified, 4908 of which were upregulated and 3276 of which were downregulated. Furthermore, 1106 significant differentially expressed lncRNAs were detected, 713 of which were upregulated and 393 of which were downregulated. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) verified changes in 10 randomly selected DEGs. GO analyses showed that the DEGs and predicted lncRNA target genes were mostly enriched for actin binding and lipid metabolism. KEGG biological pathway analyses showed that the DEGs in the livers of PSRC1-overexpressing ApoE−/− mice were enriched in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. These findings reveal that PSRC1 may affect liver actin polymerization and cholesterol metabolism-related genes or pathways. These mRNAs and lncRNAs may represent new biomarkers and targets for the diagnosis and therapy of lipid metabolism disturbance and AS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moraga P, GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators (2017) Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 390:1151–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32152-9
Navarese EP, Robinson JG, Kowalewski M, Kolodziejczak M, Andreotti F, Bliden K, Tantry U, Kubica J, Raggi P, Gurbel PA (2018) Association between baseline LDL-C Level and total and cardiovascular mortality after LDL-C lowering: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 319:1566–1579. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.2525
Samani NJ, Erdmann J, Hall AS, Hengstenberg C, Mangino M, Mayer B, Dixon RJ, Meitinger T, Braund P, Wichmann HE, Barrett JH, Konig IR, Stevens SE, Szymczak S, Tregouet DA, Iles MM, Pahlke F, Pollard H, Lieb W, Cambien F, Fischer M, Ouwehand W, Blankenberg S, Balmforth AJ, Baessler A, Ball SG, Strom TM, Braenne I, Gieger C, Deloukas P, Tobin MD, Ziegler A, Thompson JR, Schunkert H (2007) Genomewide association analysis of coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 357:443–453. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa072366
Wallace C, Newhouse SJ, Braund P, Zhang F, Tobin M, Falchi M, Ahmadi K, Dobson RJ, Marcano AC, Hajat C, Burton P, Deloukas P, Brown M, Connell JM, Dominiczak A, Lathrop GM, Webster J, Farrall M, Spector T, Samani NJ, Caulfield MJ, Munroe PB (2008) Genome-wide association study identifies genes for biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: serum urate and dyslipidemia. Am J Hum Genet 82:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.11.001
Nakayama K, Bayasgalan T, Yamanaka K, Kumada M, Gotoh T, Utsumi N, Yanagisawa Y, Okayama M, Kajii E, Ishibashi S, Iwamoto S (2009) Large scale replication analysis of loci associated with lipid concentrations in a Japanese population. J Med Genet 46:370–374. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2008.064063
Arvind P, Nair J, Jambunathan S, Kakkar VV, Shanker J (2014) CELSR2-PSRC1-SORT1 gene expression and association with coronary artery disease and plasma lipid levels in an Asian Indian cohort. J Cardiol 64:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2014.02.012
Muendlein A, Geller-Rhomberg S, Saely CH, Winder T, Sonderegger G, Rein P, Beer S, Vonbank A, Drexel H (2009) Significant impact of chromosomal locus 1p13.3 on serum LDL cholesterol and on angiographically characterized coronary atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 206:494–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.02.040
Samani NJ, Braund PS, Erdmann J, Gotz A, Tomaszewski M, Linsel-Nitschke P, Hajat C, Mangino M, Hengstenberg C, Stark K, Ziegler A, Caulfield M, Burton PR, Schunkert H, Tobin MD (2008) The novel genetic variant predisposing to coronary artery disease in the region of the PSRC1 and CELSR2 genes on chromosome 1 associates with serum cholesterol. J Mol Med (Berl) 86:1233–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0387-2
Ronald J, Rajagopalan R, Ranchalis JE, Marshall JK, Hatsukami TS, Heagerty PJ, Jarvik GP (2009) Analysis of recently identified dyslipidemia alleles reveals two loci that contribute to risk for carotid artery disease. Lipids Health Dis 8:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511x-8-52
Ciuculete DM, Bandstein M, Benedict C, Waeber G, Vollenweider P, Lind L, Schioth HB, Mwinyi J (2017) A genetic risk score is significantly associated with statin therapy response in the elderly population. Clin Genet 91:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12890
Lo PK, Chen JY, Lo WC, Chen BF, Hsin JP, Tang PP, Wang FF (1999) Identification of a novel mouse p53 target gene DDA3. Oncogene 18:7765–7774. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203167
Xi D, Zhao J, Liu J, Xiong H, He W, Hu J, Lai W, Guo Z (2016) The impact of serum amyloid P-component on gene expression in RAW264.7 mouse macrophages. Biomed Res Int 2016:9380290. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9380290
Guo K, Hu L, Xi D, Zhao J, Liu J, Luo T, Ma Y, Lai W, Guo Z (2018) PSRC1 overexpression attenuates atherosclerosis progression in apoE(-/-) mice by modulating cholesterol transportation and inflammation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 116:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.01.013
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28:511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621
Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li Y, Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE, Naar AM (2010) MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science 328:1566–1569. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1189123
Hafner M, Rezen T, Rozman D (2011) Regulation of hepatic cytochromes p450 by lipids and cholesterol. Curr Drug Metab 12:173–185
Huang H, Xie Z, Yokoyama W, Yu L, Wang TT (2016) Identification of liver CYP51 as a gene responsive to circulating cholesterol in a hamster model. J Nutr Sci 5:e16. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.3
DeBose-Boyd RA, Ye J (2018) SREBPs in lipid metabolism, insulin signaling, and beyond. Trends Biochem Sci 43:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.01.005
Monte MJ, Marin JJ, Antelo A, Vazquez-Tato J (2009) Bile acids: chemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology. World J Gastroenterol 15:804–816. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.804
Blanchard V, Khantalin I, Ramin-Mangata S, Chemello K, Nativel B, Lambert G (2019) PCSK9: from biology to clinical applications. Pathology 51:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathol.2018.10.012
Marechal L, Laviolette M, Rodrigue-Way A, Sow B, Brochu M, Caron V, Tremblay A (2018) The CD36-PPARgamma pathway in metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051529
Febbraio M, Podrez EA, Smith JD, Hajjar DP, Hazen SL, Hoff HF, Sharma K, Silverstein RL (2000) Targeted disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J Clin Invest 105:1049–1056. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci9259
Pearen MA, Muscat GE (2010) Minireview: nuclear hormone receptor 4A signaling: implications for metabolic disease. Mol Endocrinol 24:1891–1903. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2010-0015
Chao LC, Wroblewski K, Zhang Z, Pei L, Vergnes L, Ilkayeva OR, Ding SY, Reue K, Watt MJ, Newgard CB, Pilch PF, Hevener AL, Tontonoz P (2009) Insulin resistance and altered systemic glucose metabolism in mice lacking Nur77. Diabetes 58:2788–2796. https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-0763
Weinhofer I, Kunze M, Rampler H, Bookout AL, Forss-Petter S, Berger J (2005) Liver X receptor alpha interferes with SREBP1c-mediated Abcd2 expression. Novel cross-talk in gene regulation. J Biol Chem 280:41243–41251. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509450200
Malaval C, Laffargue M, Barbaras R, Rolland C, Peres C, Champagne E, Perret B, Terce F, Collet X, Martinez LO (2009) RhoA/ROCK I signalling downstream of the P2Y13 ADP-receptor controls HDL endocytosis in human hepatocytes. Cell Signal 21:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.09.016
Sedgwick A, Olivia Balmert M, D’Souza-Schorey C (2018) The formation of giant plasma membrane vesicles enable new insights into the regulation of cholesterol efflux. Exp Cell Res 365:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.03.001
Singh RK, Haka AS, Bhardwaj P, Zha X, Maxfield FR (2019) Dynamic actin reorganization and Vav/Cdc42-dependent actin polymerization promote macrophage aggregated LDL (low-density lipoprotein) uptake and catabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 39:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.118.312087
Zhou X, Yin Z, Guo X, Hajjar DP, Han J (2010) Inhibition of ERK1/2 and activation of liver X receptor synergistically induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux. J Biol Chem 285:6316–6326. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.073601
Liu T, Li C, Sun H, Luo T, Tan Y, Tian D, Guo Z (2014) Curcumin inhibits monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression and enhances cholesterol efflux by suppressing the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in macrophage. Inflamm Res 63:841–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-014-0758-9
Liu J, Guo K, Hu L, Luo T, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Lai W, Guo Z (2019) ZAP70 deficiency promotes reverse cholesterol transport through MAPK/ERK pathway in Jurkat cell. Mol Immunol 107:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.01.001
Kopp F, Mendell JT (2018) Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 172:393–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.011
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhongshan Major Science and Technology Development Project (Zhong Ke Fa No. 2016B1002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MW and KG planned and designed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. MW performed the experiments and data collection. PL is responsible for re-analyzing data and revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, M., Li, P. & Guo, K. The impact of PSRC1 overexpression on gene and transcript expression profiling in the livers of ApoE−/− mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol Cell Biochem 465, 125–139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03673-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03673-x