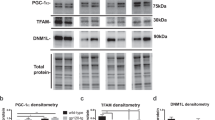
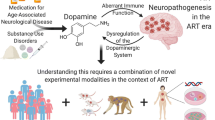
Abstract
HIV-infected individuals, even with antiretroviral therapy, often display cognitive, behavioral and motor abnormalities and have decreased dopamine (DA) levels. Minocycline prevents encephalitis and neurodegeneration in SIV models, suggesting that it might also protect against nigrostriatal dopaminergic system dysfunction. Using an SIV/macaque model of HIV-associated CNS disease, we demonstrated that striatal levels of DA were significantly lower in macaques late in infection and that levels of the metabolite DOPAC also tended to be lower. DA levels declined more than its metabolites, indicating a dysregulation of DA production or catabolism. Minocycline treatment beginning at 12 but not 21 days postinoculation prevented striatal DA loss. DA decline was not due to direct loss of dopaminergic projections to the basal ganglia as there was no difference in tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine transporter, vesicular monoamine transporter 2 or synaptophysin between minocycline-treated and untreated macaques. SIV-infected macaques had significantly higher monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity than uninfected macaques, although MAO activity was not affected by minocycline. Oxidative/nitrosative stress was examined by nitrotyrosine staining in the deep white matter and was lower in SIV-infected, minocycline-treated macaques compared with untreated macaques. These data suggest that minocycline, which has antioxidant activity, has a protective effect on DA homeostasis when administered at an appropriate time in SIV neuropathogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal L, Louboutin JP, Marusich E, Reyes BA, Van Bockstaele EJ, Strayer DS (2010) Dopaminergic neurotoxicity of HIV-1 gp120: reactive oxygen species as signaling intermediates. Brain Res 1306:116–130. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.09.113
Aksenova MV, Silvers JM, Aksenov MY, Nath A, Ray PD, Mactutus CF, Booze RM (2006) HIV-1 Tat neurotoxicity in primary cultures of rat midbrain fetal neurons: changes in dopamine transporter binding and immunoreactivity. Neurosci Lett 395(3):235–239. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.10.095
Ances BM, Ellis RJ (2007) Dementia and neurocognitive disorders due to HIV-1 infection. Semin Neurol 27(1):86–92. doi:10.1055/s-2006-956759
Antonenko YN, Rokitskaya TI, Cooper AJ, Krasnikov BF (2010) Minocycline chelates Ca2+, binds to membranes, and depolarizes mitochondria by formation of Ca2+-dependent ion channels. J Bioenerg Biomembr 42(2):151–163. doi:10.1007/s10863-010-9271-1
Ara J, Przedborski S, Naini AB, Jackson-Lewis V, Trifiletti RR, Horwitz J, Ischiropoulos H (1998) Inactivation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nitration following exposure to peroxynitrite and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(13):7659–7663. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.13.7659
Barber SA, Uhrlaub JL, DeWitt JB, Tarwater PM, Zink MC (2004) Dysregulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. Am J Pathol 164(2):355–362. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63125-2
Barnum CJ, Tansey MG (2010) Modeling neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Brain Res 184:113–132. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(10)84006-3
Berg D, Youdim MB, Riederer P (2004) Redox imbalance. Cell Tissue Res 318(1):201–213. doi:10.1007/s00441-004-0976-5
Berger JR, Arendt G (2000) HIV dementia: the role of the basal ganglia and dopaminergic systems. J Psychopharmacol 14(3):214–221. doi:10.1177/026988110001400304
Berger JR, Kumar M, Kumar A, Fernandez JB, Levin B (1994) Cerebrospinal fluid dopamine in HIV-1 infection. AIDS 8(1):67–71. doi:10.1097/00002030-199401000-00010
Campbell JH, Burdo TH, Autissier P, Bombardier JP, Westmoreland SV, Soulas C, Gonzalez RG, Ratai EM, Williams KC (2011) Minocycline inhibition of monocyte activation correlates with neuronal protection in SIV NeuroAIDS. PLoS One 6(4):e18688. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018688
Clements JE, Babas T, Mankowski JL, Suryanarayana K, Piatak M Jr, Tarwater PM, Lifson JD, Zink MC (2002) The central nervous system as a reservoir for simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV): steady-state levels of SIV DNA in brain from acute through asymptomatic infection. Infect Dis 186(7):905–913. doi:10.1086/343768
Clements JE, Li M, Gama L, Bullock B, Carruth LM, Mankowski JL, Zink MC (2005) The central nervous system is a viral reservoir in simian immunodeficiency virus–infected macaques on combined antiretroviral therapy: a model for human immunodeficiency virus patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Neurovirol 11(2):180–189. doi:10.1080/13550280590922829
Clements JE, Mankowski JL, Gama L, Zink MC (2008) The accelerated simian immunodeficiency virus macaque model of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurological disease: from mechanism to treatment. J Neurovirol 14(4):309–317. doi:10.1080/13550280802132832
Czub S, Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Czub M, Stahl-Hennig C, Muller JG, Pedersen V, Gsell W, Heeney JL, Gerlach M, Gosztonyi G, Riederer P, ter Meulen V (2001) Enhancement of central nervous system pathology in early simian immunodeficiency virus infection by dopaminergic drugs. Acta Neuropathol 101(2):85–91. doi:10.1007/s004010000313
Diguet E, Fernagut PO, Wei X, Du Y, Rouland R, Gross C, Bezard E, Tison F (2004) Deleterious effects of minocycline in animal models of Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 19(12):3266–3276. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03372.x
Du Y, Ma Z, Lin S, Dodel RC, Gao F, Bales KR, Triarhou LC, Chernet E, Perry KW, Nelson DL, Luecke S, Phebus LA, Bymaster FP, Paul SM (2001) Minocycline prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(25):14669–14674. doi:10.1073/pnas.251341998
Ferris MJ, Mactutus CF, Booze RM (2008) Neurotoxic profiles of HIV, psychostimulant drugs of abuse, and their concerted effect on the brain: current status of dopamine system vulnerability in NeuroAIDS. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32(5):883–909. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.01.004
Follstaedt SC, Barber SA, Zink MC (2008) Mechanisms of minocycline-induced suppression of simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis: inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. J Neurovirol 14(5):376–388. doi:10.1080/13550280802199898
Gelman BB (2007) The neuropathology of HIV. Handb Clin Neurol 85:301–317. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(07)85018-4
Gelman BB, Spencer JA, Holzer CE 3rd, Soukup VM (2006) Abnormal striatal dopaminergic synapses in National NeuroAIDS Tissue Consortium subjects with HIV encephalitis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 1(4):410–420. doi:10.1007/s11481-006-9030-6
Gordon PH, Moore DH, Miller RG, Florence JM, Verheijde JL, Doorish C, Hilton JF, Spitalny GM, MacArthur RB, Mitsumoto H, Neville HE, Boylan K, Mozaffar T, Belsh JM, Ravits J, Bedlack RS, Graves MC, McCluskey LF, Barohn RJ, Tandan R, Western ALS Study Group (2007) Efficacy of minocycline in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase III randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 6(12):1045–1053. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70270-3
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59(5):1609–1623. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10990.x
Heaton RK, Clifford DB, Franklin DR Jr, Woods SP, Ake C, Vaida F, Ellis RJ, Letendre SL, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Rivera-Mindt M, Vigil OR, Taylor MJ, Collier AC, Marra CM, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Morgello S, Simpson DM, McCutchan JA, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I (2011) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders persist in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy: CHARTER Study. Neurology 75(23):2087–2096. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318200d727
Huang CL, Huang NK, Shyue SK, Chern Y (2003) Hydrogen peroxide induces loss of dopamine transporter activity: a calcium-dependent oxidative mechanism. J Neurochem 86(5):1247–1259. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01936.x
Itoh K, Mehraein P, Weis S (2000) Neuronal damage of the substantia nigra in HIV-1 infected brains. Acta Neuropathol 99(4):376–384. doi:10.1007/s004010051139
Jordan J, Fernandez-Gomez FJ, Ramos M, Ikuta I, Aguirre N, Galindo MF (2007) Minocycline and cytoprotection: shedding new light on a shadowy controversy. Curr Drug Deliv 4(3):225–231. doi:10.2174/156720107781023938
Kaul M, Lipton SA (2006) Mechanisms of neuronal injury and death in HIV-1 associated dementia. Curr HIV Res 4(3):307–318. doi:10.2174/157016206777709384
Kim HS, Suh YH (2009) Minocycline and neurodegenerative diseases. Behav Brain Res 196(2):168–179. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.09.040
Koutsilieri E, Sopper S, Scheller C, ter Meulen V, Riederer P (2002) Parkinsonism in HIV dementia. J Neural Transm 109(5–6):767–775. doi:10.1007/s007020200063
Kraus RL, Pasieczny R, Lariosa-Willingham K, Turner MS, Jiang A, Trauger JW (2005) Antioxidant properties of minocycline: neuroprotection in an oxidative stress assay and direct radical-scavenging activity. J Neurochem 94(3):819–827. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03219.x
Kumar AM, Borodowsky I, Fernandez B, Gonzalez L, Kumar M (2007) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA Levels in different regions of human brain: quantification using real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J Neurovirol 13(3):210–224. doi:10.1080/13550280701327038
Kumar AM, Fernandez J, Singer EJ, Commins D, Waldrop-Valverde D, Ownby RL, Kumar M (2009) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the central nervous system leads to decreased dopamine in different regions of postmortem human brains. J Neurovirol 15:1–18. doi:10.1080/13550280902973952
Kumar AM, Ownby RL, Waldrop-Valverde D, Fernandez B, Kumar M (2011) Human immunodeficiency virus infection in the CNS and decreased dopamine availability: relationship with neuropsychological performance. J Neurovirol 17(1):26–40. doi:10.1007/s13365-010-0003-4
Mallajosyula JK, Kaur D, Chinta SJ, Rajagopalan S, Rane A, Nicholls DG, Di Monte DA, Macarthur H, Andersen JK (2008) MAO-B elevation in mouse brain astrocytes results in Parkinson’s pathology. PLoS One 3(2):e1616. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001616
Mattson MP, Haughey NJ, Nath A (2005) Cell death in HIV dementia. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 1):893–904. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401577
McArthur JC, Brew BJ, Nath A (2005) Neurological complications of HIV infection. Lancet Neurol 4(9):543–555. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(05)70165-4
Nath A, Sacktor N (2006) Influence of highly active antiretroviral therapy on persistence of HIV in the central nervous system. Curr Opin Neurol 19(4):358–361. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000236614.51592.ca
Nath A, Anderson C, Jones M, Maragos W, Booze R, Mactutus C, Bell J, Hauser KF, Mattson M (2000) Neurotoxicity and dysfunction of dopaminergic systems associated with AIDS dementia. J Psychopharmacol 14(3):222–227. doi:10.1177/026988110001400305
Navia BA, Cho ES, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19(6):525–535. doi:10.1002/ana.410190603
Nosheny RL, Bachis A, Aden SA, De Bernardi MA, Mocchetti I (2006) Intrastriatal administration of human immunodeficiency virus-1 glycoprotein 120 reduces glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor levels and causes apoptosis in the substantia nigra. J Neurobiol 66(12):1311–1321. doi:10.1002/neu.20288
Pacher P, Beckman JS, Liaudet L (2007) Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev 87(1):315–424. doi:10.1152/physrev.00029.2006
Park SU, Ferrer JV, Javitch JA, Kuhn DM (2002) Peroxynitrite inactivates the human dopamine transporter by modification of cysteine 342: potential mechanism of neurotoxicity in dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 22(11):4399–4405
Pletnikov MV, Rubin SA, Schwartz GJ, Carbone KM, Moran TH (2000) Effects of neonatal rat Borna disease virus (BDV) infection on the postnatal development of the brain monoaminergic systems. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 119(2):179–185. doi:10.1016/S0165-3806(99)00168-6
Ratai EM, Bombardier JP, Joo CG, Annamalai L, Burdo TH, Campbell J, Fell R, Hakimelahi R, He J, Autissier P, Lentz MR, Halpern EF, Masliah E, Williams KC, Westmoreland SV, Gonzalez RG (2010) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals neuroprotection by oral minocycline in a nonhuman primate model of accelerated NeuroAIDS. PLoS One 5(5):e10523. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010523
Rumbaugh JA, Nath A (2006) Developments in HIV neuropathogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 12(9):1023–1044. doi:10.2174/138161206776055877
Sacktor N, Miyahara S, Deng L, Evans S, Schifitto G, Cohen BA, Paul R, Robertson K, Jarocki B, Scarsi K, Coombs RW, Zink MC, Nath A, Smith E, Ellis RJ, Singer E, Weihe J, McCarthy S, Hosey L, Clifford DB (2011) Minocycline treatment for HIV-associated cognitive impairment: results from a randomized trial. Neurology 77(12):1135–1142. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822f0412
Sardar AM, Czudek C, Reynolds GP (1996) Dopamine deficits in the brain: the neurochemical basis of parkinsonian symptoms in AIDS. Neuroreport 7(4):910–912. doi:10.1097/00001756-199603220-00015
Scheller C, Sopper S, Jenuwein M, Neuen-Jacob E, Tatschner T, Grunblatt E, ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2005) Early impairment in dopaminergic neurotransmission in brains of SIV-infected rhesus monkeys due to microglia activation. J Neurochem 95(2):377–387. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03373.x
Scheller C, Arendt G, Nolting T, Antke C, Sopper S, Maschke M, Obermann M, Angerer A, Husstedt IW, Meisner F, Neuen-Jacob E, Muller HW, Carey P, Ter Meulen V, Riederer P, Koutsilieri E (2010) Increased dopaminergic neurotransmission in therapy-naive asymptomatic HIV patients is not associated with adaptive changes at the dopaminergic synapses. J Neural Transm 117(6):699–705. doi:10.1007/s00702-010-0415-6
Schildknecht S, Pape R, Muller N, Robotta M, Marquardt A, Burkle A, Drescher M, Leist M (2011) Neuroprotection by minocycline caused by direct and specific scavenging of peroxynitrite. J Biol Chem 286(7):4991–5002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.169565
Silvers JM, Aksenov MY, Aksenova MV, Beckley J, Olton P, Mactutus CF, Booze RM (2006) Dopaminergic marker proteins in the substantia nigra of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected brains. J Neurovirol 12(2):140–145. doi:10.1080/13550280600724319
Steiner J, Haughey N, Li W, Venkatesan A, Anderson C, Reid R, Malpica T, Pocernich C, Butterfield DA, Nath A (2006) Oxidative stress and therapeutic approaches in HIV dementia. Antioxid Redox Signal 8(11–12):2089–2100. doi:10.1089/ars.2006.8.2089
Tepper JM, Tecuapetla F, Koos T, Ibanez-Sandoval O (2010) Heterogeneity and diversity of striatal GABAergic interneurons. Front Neuroanat 4:150. doi:10.3389/fnana.2010.00150
Theodore S, Stolberg S, Cass WA, Maragos WF (2006) Human immunodeficiency virus-1 protein tat and methamphetamine interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1074:178–190. doi:10.1196/annals.1369.018
UNAIDS (2010) Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2010. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). http://www.unaids.org/documents/20101123_GlobalReport_em.pdf. Accessed July 25, 2011
Unal B, Ibanez-Sandoval O, Shah F, Abercrombie ED, Tepper JM (2011) Distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase-expressing interneurons with respect to anatomical organization of the neostriatum. Front Syst Neurosci 5:41. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2011.00041
Wallace DR, Dodson S, Nath A, Booze RM (2006) Estrogen attenuates gp120- and tat1-72-induced oxidative stress and prevents loss of dopamine transporter function. Synapse 59(1):51–60. doi:10.1002/syn.20214
Williams KC, Hickey WF (2002) Central nervous system damage, monocytes and macrophages, and neurological disorders in AIDS. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:537–562. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro25.112701.142822
Witwer KW, Gama L, Li M, Bartizal CM, Queen SE, Varrone JJ, Brice AK, Graham DR, Tarwater PM, Mankowski JL, Zink MC, Clements JE (2009) Coordinated regulation of SIV replication and immune responses in the CNS. PLoS One 4(12):e8129. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008129
Zauli G, Secchiero P, Rodella L, Gibellini D, Mirandola P, Mazzoni M, Milani D, Dowd DR, Capitani S, Vitale M (2000) HIV-1 Tat-mediated inhibition of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in dopaminergic neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 275(6):4159–4165. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.6.4159
Zink MC, Suryanarayana K, Mankowski JL, Shen A, Piatak M Jr, Spelman JP, Carter DL, Adams RJ, Lifson JD, Clements JE (1999) High viral load in the cerebrospinal fluid and brain correlates with severity of simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. J Virol 73(12):10480–10488
Zink MC, Coleman GD, Mankowski JL, Adams RJ, Tarwater PM, Fox K, Clements JE (2001) Increased macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 in cerebrospinal fluid precedes and predicts simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. J Infect Dis 184(8):1015–1021. doi:10.1086/323478
Zink MC, Uhrlaub J, DeWitt J, Voelker T, Bullock B, Mankowski J, Tarwater P, Clements J, Barber S (2005) Neuroprotective and anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity of minocycline. JAMA 293(16):2003–2011. doi:10.1001/jama.293.16.2003
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors who are guarantors: MCZ
Studies were supported by grants from the National Institute of Mental Health: R01 MH069116, R01 MH087233, and R01 MH085554.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meulendyke, K.A., Pletnikov, M.V., Engle, E.L. et al. Early Minocycline Treatment Prevents a Decrease in Striatal Dopamine in an SIV Model of HIV-Associated Neurological Disease. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7, 454–464 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9332-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9332-1