Summary
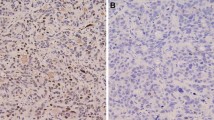
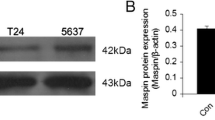
The expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) gene and its effect on chemotherapeutic sensitivity in bladder carcinoma was explored. By using immunohistochemistry, the expression of XIAP was detected in 47 bladder carcinomas and 5 normal bladder tissues. The XIAP gene was transfected into bladder cancer cell line T24 by liposome and the positive clone was screened by G418. Cellular XIAP mRNA level was detected by RT-PCR. Low-dose mitocycin C was administered to induce the apoptosis of T24 cells. The in vitro growth of bladder carcinoma cells was analyzed by MTT colorimetry, and the apoptosis rate was assayed by TUNEL methods. It was found XIAP was moderately expressed in bladder carcinomas with the the positive rate being 78.73% (37/47), but the positive rate was not correlated with carcinoma stages and grades (P<0.05). XIAP mRNA level in transfected T24 cells was significantly increased by 3.8 times as compared with that in the cells not transfected with XIAP. After treatment with low-dose mitomycin C (0.005 and 0.05 mg/mL), the growth rate in XIAP no-transfected control group was increased by (11.60±0.25)% and (16.51±0.87)% (P<0.05), and the apoptosis rate was decreased by (10.1±0.2)% and (11.9±0.2%) (P<0.05) respectively as compared with XIAP transfected group. It was concluded that XIAP was expressed in most of bladder carcimoma samples. Overexpression of XIAP in T24 could significantly reduce the MMC-induced apoptosis of bladder carcinoma, suggesting its effect on the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of T24 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deveraux Q L, Takahashi R, Salvesen G S et al. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature, 1997,388(6639):300–304
Li R Z, Pei H P, Papas T. The p42 variant of ETS1 protein rescues defective Fas-induced apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999,96(7):3876–3881
Deveraux Q L, Reed J C. IAP family proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev, 1999,13:239–252
Suzuki Y, Nakabayashi Y, Nakata K et al. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) inhibits caspase-3 and-7 in distinct modes. J Biol Chem, 2001,276:27058–27063
Riedl S J, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell, 2001,104:791–800
Asselin E, Mills G B, Tsang B K. XIAP regulates Akt activity and caspase-3-dependent cleavage during cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian epithelial cancer cells. Cancer Res, 2001,61(5):1862–1868
Liu J, Wang Q, Wang X et al. Apoptosis of bladder cancer cells induced by short-term and low-dose mitomycin-C: potential molecular mechanism and clinical implication. Int J Mol Med, 2003,11(3):389–394
Xiao C, Ash K, Tsang B. Nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression prevents rat granulosa cells from tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. Endocrinology, 2001,142:557–563
Du C, Fang M, Li Y et al. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell, 2000,102(1):33–42
Verhagen A M, Ekert P G, Pakusch M et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell, 2000,102(1):43–53
Zeng F Q, Wang L, Chen F M et al. Molecular mechanism of Smac gene enhancing the induction of chemotherapeutic drug on bladder cancer apoptosis. Chin J Urol (Chinese), 2004,25:655–658
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
WANG Liang, male, born in 1977, Doctor in Charge
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30271301).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Bi, Y., Zeng, F. et al. Expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and its effect on chemotherapeutic sensitivity of bladder carcinoma. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 285–287 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0317-5
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0317-5